|
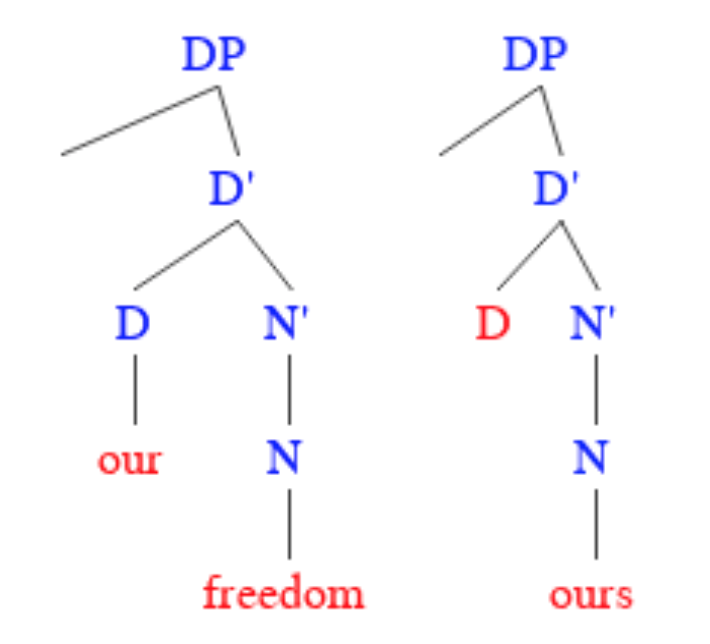
Pronominal Argument Hypothesis
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Subtypes include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The name of the adjective that belongs with a "pronoun" is called a "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or phra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the Cognition, cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the main parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as determiners. Here are some examples: * That's a funny idea. ( attributive) * That idea is funny. ( predicative) * * The good, the bad, and the funny. ( substantive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of grc, ἐπίθετον ὄνομα, epítheton ónoma, additional noun (whence also English '' epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were inflected for gender, number, and case like nouns (a process called declension), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent. Understanding verb phrase analysis depends on knowing which theory applies in context. In phrase structure gramma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dummy Pronoun
A dummy pronoun is a deictic pronoun that fulfills a syntactical requirement without providing a contextually explicit meaning of its referent. As such, it is an example of exophora. Dummy pronouns are used in many Germanic languages, including German and English. Pronoun-dropping languages such as Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, and Turkish do not require dummy pronouns. A dummy pronoun is used when a particular verb argument (or preposition) is nonexistent (it could also be unknown, irrelevant, already understood, or otherwise "not to be spoken of directly") but when a reference to the argument (a pronoun) is nevertheless syntactically required. For example, in the phrase "It is obvious that the violence will continue", ''it'' is a dummy pronoun, not referring to any agent. Unlike a regular pronoun of English, it cannot be replaced by any noun phrase. The term ''dummy pronoun'' refers to the function of a word in a particular sentence, not a property of individual w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative Word
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', '' who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of them start with '' wh-'' (compare Five Ws). They may be used in both direct questions (''Where is he going?'') and in indirect questions (''I wonder where he is going''). In English and various other languages the same forms are also used as relative pronouns in certain relative clauses (''The country where he was born'') and certain adverb clauses (''I go where he goes''). It can also be used as a modal, since question words are more likely to appear in modal sentences, like (''Why was he walking?'') A particular type of interrogative word is the interrogative particle, which serves to convert a statement into a yes–no question, without having any other meaning. Examples include ''est-ce que'' in French, ли ''li'' in Russian, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who (pronoun)
The pronoun ''who'', in English, is an interrogative pronoun and a relative pronoun, used primarily to refer to persons. Unmarked, ''who'' is the pronoun’s subjective form; its inflected forms are the objective ''whom'' and the possessive ''whose''. The set has derived indefinite forms ''whoever'', ''whomever'', and ''whoseever,'' as well as a further, earlier such set ''whosoever,'' ''whomsoever'', and ''whosesoever'' (see also "-ever"). Etymology The interrogative and relative pronouns ''who'' derive from the Old English singular interrogative , and whose paradigm is set out below: It was not until the end of the 17th century that ''who'' became the only pronoun that could ask about the identity of persons and ''what'' fully lost this ability. "The first occurrences of wh-relatives date from the twelfth century (with the possible exception (see Kivimaa 1966: 35)). The wh- form does not become frequent, however, until the fourteenth century." Notably, relative ''whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
It (pronoun)
In Modern English, ''it'' is a singular, neuter, third-person pronoun. Morphology In Modern English, ''it'' has only three shapes representing five word forms: * ''it'': the nominative (subjective) and accusative (objective) forms. (The accusative case is also called the " oblique".) * ''its:'' the dependent and independent genitive (possessive) forms * ''itself'': the reflexive form Historically, though, the morphology is more complex. History Old English Old English had a single third-person pronoun – from the Proto-Germanic demonstrative base *''khi''-, from PIE *''ko''- "this" – which had a plural and three genders in the singular. The modern pronoun ''it'' developed out of the neuter, singular. The older pronoun had the following forms: This neuter pronoun, like the masculine and feminine ones, was used for both people and objects (inanimate or abstract). Common nouns in Anglo-saxon had grammatical genders, which were not necessarily the same as the gender o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meaning (linguistics)
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's '' An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough termed also , Logick. In 1831, the term is suggested for the third branch of division of knowledge akin to Locke; the "signs of our knowledge". In 1857, the term ''semasiology'' (borrowed from German ''Semasiologie'') is attested in Josiah W. Gibbs' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentence (linguistics)
In linguistics and grammar, a sentence is a linguistic expression, such as the English example "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." In traditional grammar, it is typically defined as a string of words that expresses a complete thought, or as a unit consisting of a subject and predicate. In non-functional linguistics it is typically defined as a maximal unit of syntactic structure such as a constituent. In functional linguistics, it is defined as a unit of written texts delimited by graphological features such as upper-case letters and markers such as periods, question marks, and exclamation marks. This notion contrasts with a curve, which is delimited by phonologic features such as pitch and loudness and markers such as pauses; and with a clause, which is a sequence of words that represents some process going on throughout time. A sentence can include words grouped meaningfully to express a statement, question, exclamation, request, command, or suggestion. Typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with any objects and other modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unvoiced if it is retrievable from context, especially in null-subject language but also in other languages, including English instances of the imperative mood. A complete simple sentence includes a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain multiple clauses including at least one '' independent clause'' (meaning, a clause that can stand alone as a simple sentence) coordinated either with at least one dependent clause (also called an embedded clause) or with one or more independent clauses. Two major distinctions A primary division for the discussion of clauses is the distinction between independent clauses and dependent clauses. An independent clau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase
In syntax and grammar, a phrase is a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a constituent. Common and technical use There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as " all rights reserved", " economical with the truth", " kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single word, which plays a particular role withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonological, grammatical or orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations. The concept of "word" is distinguished from that of a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of language that has a meaning, even if it cannot stand on its own. Words are made out of at leas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)