|
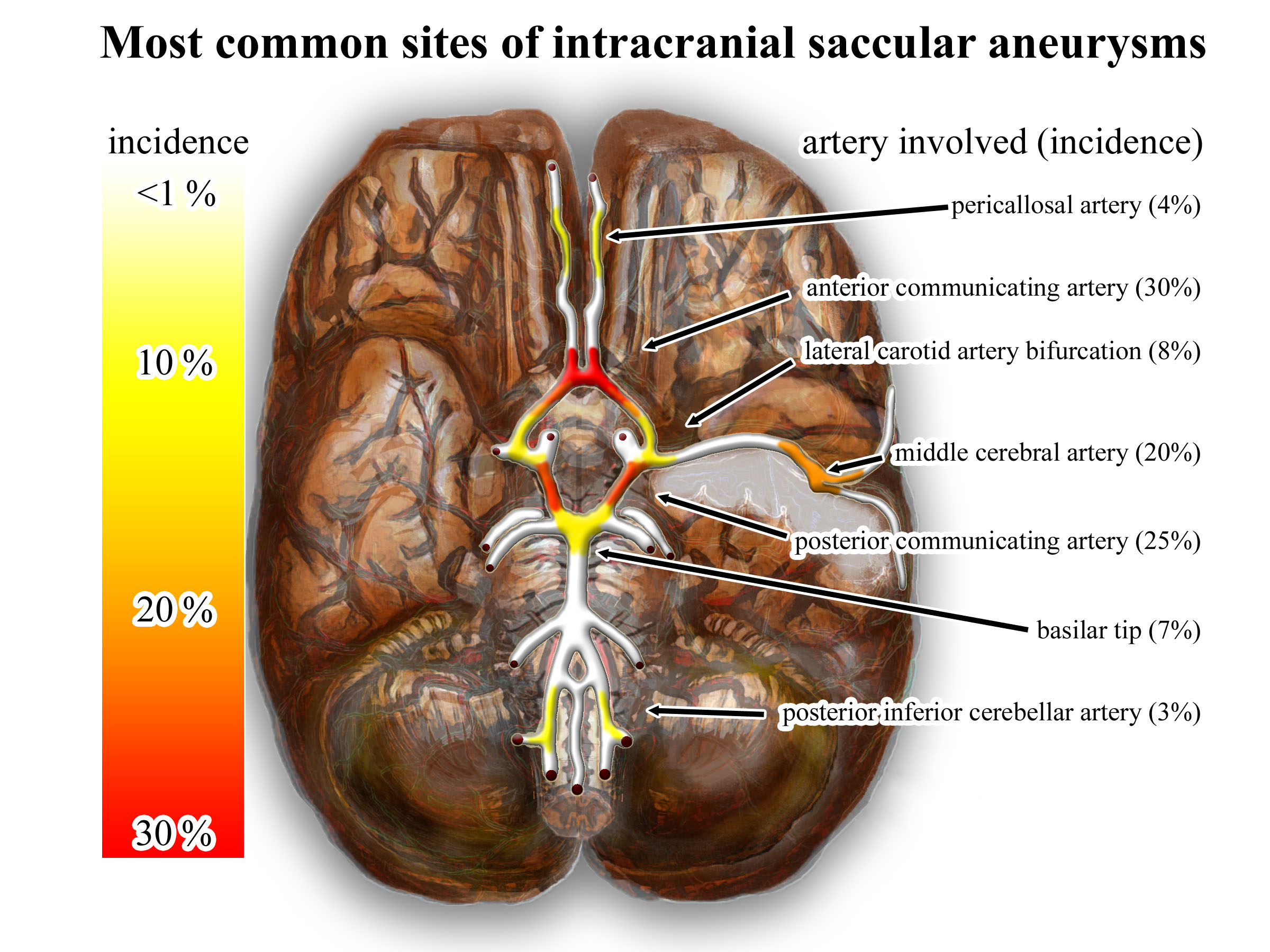
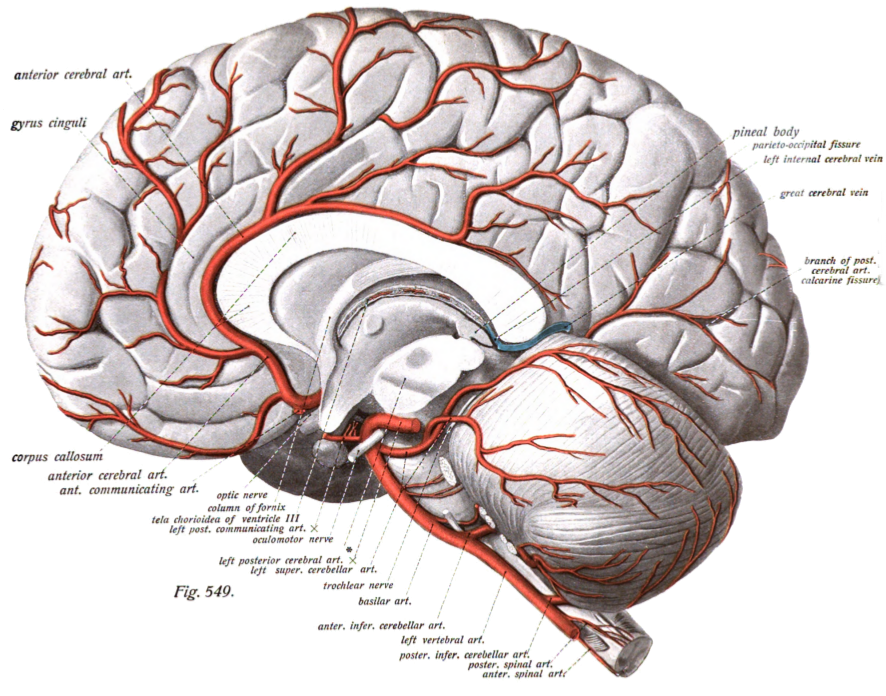
Posterior Communicating Artery
In human anatomy, the left and right posterior communicating arteries are arteries at the base of the brain that form part of the circle of Willis. Each posterior communicating artery connects the three cerebral arteries of the same side. Anteriorly, it connects to the internal carotid artery (ICA) prior to the terminal bifurcation of the ICA into the anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery. Posteriorly, it communicates with the posterior cerebral artery. The brain is supplied with blood by the internal carotid arteries and also by the posterior cerebral arteries; the posterior communicating arteries connects the two systems. This provides redundancies or collaterals in the cerebral circulation so that, if one system is blocked or narrowed, the other can take over. Development The development of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) in the fetal brain occurs relatively late and arises from the fusion of several embryonic vessels near the caudal end of the posterior co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621–1675), an English physician. Structure The circle of Willis is a part of the cerebral circulation and is composed of the following arteries: * Anterior cerebral artery (left and right) * Anterior communicating artery * Internal carotid artery (left and right) * Posterior cerebral artery (left and right) * Posterior communicating artery (left and right) The middle cerebral arteries, supplying the brain, are not considered part of the circle of Willis. Origin of arteries The left and right internal carotid arteries arise from the left and right common carotid arteries. The posterior communicating artery is given off as a branch of the internal carotid artery just before it divides into i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Cerebral Artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices. The left and right MCAs rise from trifurcations of the internal carotid arteries and thus are connected to the anterior cerebral arteries and the posterior communicating arteries, which connect to the posterior cerebral arteries. The MCAs are not considered a part of the Circle of Willis. Structure The middle cerebral artery divides into four segments, named by the region they supply as opposed to order of branching as the latter can be somewhat variable: *M1: The ''sphenoidal'' segment (stem), receiving its name due to its course along the adjacent sphenoid bone. It is also referred to as the ''horizontal'' seg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculomotor Nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two third nerve nuclei located laterally on either side of the cerebral aqueduct then pass through the red nucleus. From the red n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Communicating Artery
In human anatomy, the anterior communicating artery is a blood vessel of the brain that connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries. Anatomy The anterior communicating artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries across the commencement of the longitudinal fissure. Sometimes this vessel is wanting, the two arteries joining to form a single trunk, which afterward divides; or it may be wholly, or partially, divided into two. Its length averages about 4 mm, but varies greatly. It gives off some of the anteromedial ganglionic vessels, but these are principally derived from the anterior cerebral artery. It is part of the cerebral arterial circle, also known as the circle of Willis. Physiology Anatomical variations of the anterior communicating artery are relatively common. The artery is sometimes duplicated, multiplicated, fenestrated ("net-like") or very short, giving the impression that two anterior cerebral arteries are fused at the point where the anter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus (starting point) for clot formation ( thrombosis) and embolization. As an aneurysm increases in size, the risk of rupture, which leads to uncontrolled bleeding, increases. Although they may occur in any blood vessel, particularly lethal examples include aneurysms of the Circle of Willis in the brain, aortic aneurysms affecting the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Aneurysms can arise in the heart itself following a heart attack, including both ventricular and atrial septal aneurysms. There are congenital atrial septal aneurysms, a rare heart defect. Etymology The word is from Greek: ἀνεύρυσμα, aneurysma, "dilation", from ἀνευρύνειν, aneurynein, "to dilate". Classification Aneurysms are classified b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a brain aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder in which weakness in the wall of a cerebral artery or vein causes a localized dilation or ballooning of the blood vessel. Aneurysms in the posterior circulation (basilar artery, vertebral arteries and posterior communicating artery) have a higher risk of rupture. Basilar artery aneurysms represent only 3–5% of all intracranial aneurysms but are the most common aneurysms in the posterior circulation. Classification Cerebral aneurysms are classified both by size and shape. Small aneurysms have a diameter of less than 15 mm. Larger aneurysms include those classified as large (15 to 25 mm), giant (25 to 50 mm), and super-giant (over 50 mm). Berry (saccular) aneurysms Saccular aneurysms, also known as berry aneurysms, appear as a round outpouching and are the most common form of cerebral aneurysm. Causes include connective tissue disorders, polycystic kidney disease, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collateral Circulation
Collateral circulation is the alternate circulation around a blocked artery or vein via another path, such as nearby minor vessels. It may occur via preexisting vascular redundancy (analogous to engineered redundancy), as in the circle of Willis in the brain, or it may occur via new branches formed between adjacent blood vessels (neovascularization), as in the eye after a retinal embolism or in the brain when moyamoya occurs. Its formation may be provoked by pathological conditions such as high vascular resistance or ischaemia. An example of the usefulness of collateral circulation is a systemic thromboembolism in cats. This is when a thrombotic embolus lodges above the external iliac artery (common iliac artery), blocking the external and internal iliac arteries and effectively shutting off all blood supply to the hind leg. Even though the main vessels to the leg are blocked, enough blood can get to the tissues in the leg via the collateral circulation to keep them alive. Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cerebral Artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries. Structure The posterior cerebral artery is subdivided into 4 sections P1: pre-communicating segment * Originated at the termination of the basilar artery * May give rise to the artery of Percheron if present P2: post-communicating segment * From the PCOM around the midbrain * Terminates as it enters the quadrigeminal ganglion * Gives rise to the choroidal branches (medial and lateral posterior choroidal arteries) P3: quadrigeminal segment * Courses posteromedially through the quadrigeminal cistern * Terminates as it enters the sulk of the occipi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. *A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (medial le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Arteries
The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of arteries and their branches, which perfuse the cerebrum of the brain. The three main arteries are the: * '' Anterior cerebral artery'' (ACA) * ''Middle cerebral artery The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to ma ...'' (MCA) * '' Posterior cerebral artery'' (PCA) Both the ACA and MCA originate from the cerebral portion of internal carotid artery, while PCA branches from the intersection of the posterior communicating artery and the anterior portion of the basilar artery. The three pairs of arteries are linked via the anterior communicating artery and the posterior communicating arteries. All three arteries send out arteries that perforate brain in the medial central portions prior to branching and bifurcating further. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |