|
Post-anesthesia Care Unit
A post-anesthesia care unit, often abbreviated PACU and sometimes referred to as post-anesthesia recovery or PAR, or simply Recovery, is a vital part of hospitals, ambulatory care centers, and other medical facilities. Patients who received general anesthesia, regional anesthesia, or local anesthesia are transferred from the operating room suites to the recovery area. The patients are monitored typically by anesthesiologists, certified registered nurse anesthetists, and other medical staff. Providers follow a standardized handoff to the medical PACU staff that includes, which medications were given in the operating room suites, how hemodynamics were during the procedures, and what is expected for their recovery. After initial assessment and stabilization, patients are monitored for any potential complications, until the patient is transferred back to their hospital rooms. Initial handoff The initial handoff, or otherwise referred as handover, is an interdisciplinary transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' (geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment (see psychiatric hospital) and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received. A teac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common conditions of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and they have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. Emphysema is defined as enlarged airspaces ( alveoli) whose walls have broken down resulting in permanent damage to the lung tissue. Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Both of these conditions can exist without airflow limitation when they are not classed as COPD. Emphysema is just one of the structural abnormalities that can limit airflow and can exist without ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome (a complication of some forms of cancer), and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days. The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness. It is in pregnancy category C in the United States, meaning that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ondansetron
Ondansetron, sold under the brand name Zofran among others, is a medication used to prevent nausea and vomiting caused by cancer chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery. It is also effective for treating gastroenteritis. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a muscle or into a vein. Common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headache, sleepiness, and itchiness. Serious side effects include QT prolongation and severe allergic reaction. It appears to be safe during pregnancy but has not been well studied in this group. It is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. It does not have any effect on dopamine receptors or muscarinic receptors. Ondansetron was patented in 1984 and approved for medical use in 1990. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 83rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8million prescriptions. Medical uses A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postoperative Nausea And Vomiting
Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) is the phenomenon of nausea, vomiting, or retching experienced by a patient in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) or within 24 hours following a surgical procedure. PONV affects about 10% of the population undergoing general anaesthesia each year. PONV can be unpleasant and lead to a delay in mobilization and food, fluid, and medication intake following surgery. Cause Emetogenic drugs commonly used in anaesthesia include nitrous oxide, physostigmine, and opioids. The intravenous anaesthetic propofol is currently the least emetogenic general anaesthetic. These medications are thought to stimulate the chemoreceptor trigger zone. This area is on the floor of the fourth ventricle and is effectively outside of the blood-brain barrier, which makes it incredibly sensitive to toxin and pharmacological stimulation. Several neurotransmitters are known, such as histamine, dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine, and the more recently discovered neurokini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
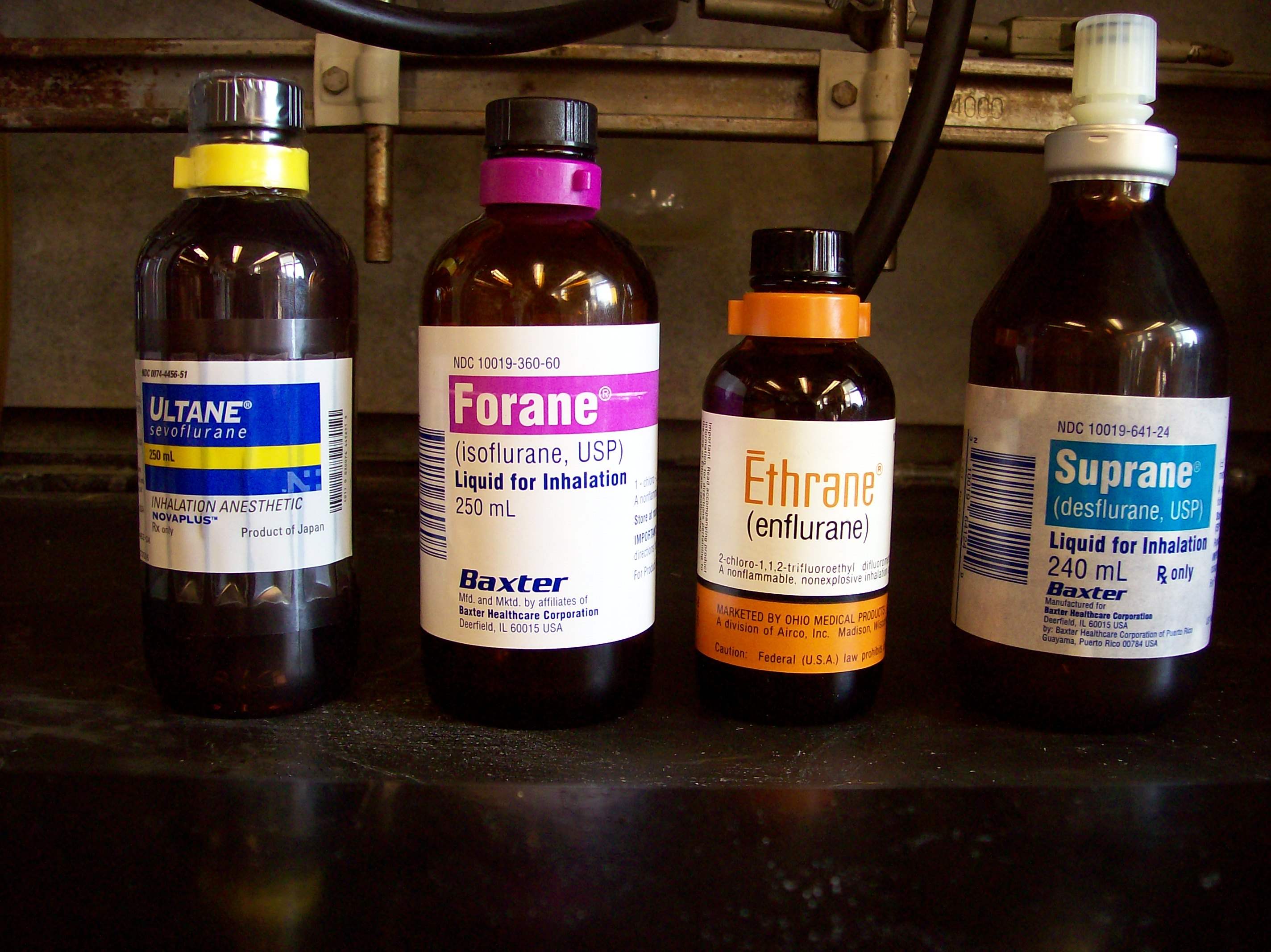
Inhalational Anesthetic
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vaporiser and an anesthetic delivery system. Agents of significant contemporary clinical interest include volatile anesthetic agents such as isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane, as well as certain anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and xenon. List of inhalational anaesthetic agents Currently-used agents * Desflurane * Isoflurane * Nitrous oxide * Sevoflurane * Xenon Previously-used agents Although some of these are still used in clinical practice and in research, the following anaesthetic agents are primarily of historical interest in developed countries: * Acetylene * Chloroethane (ethyl chloride) * Chloroform * Cryofluorane * Cyclopropane * Diethyl ether * Divinyl ether * Enflurane * Ethylene * Fluroxene * Halothane (still wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventriculostomy
Ventriculostomy is a neurosurgical procedure that involves creating a hole (stoma) within a cerebral ventricle for drainage. It is most commonly performed on those with hydrocephalus. It is done by surgically penetrating the skull, dura mater, and brain such that the ventricular system ventricle of the brain is accessed. When catheter drainage is temporary, it is commonly referred to as an external ventricular drain (EVD). When catheter drainage is permanent, it is usually referred to as a shunt. There are many catheter-based ventricular shunts that are named for where they terminate, for example, a ventriculi-peritoneal shunt terminates in the peritoneal cavity, a ventriculoarterial shunt terminates within the atrium of the heart, etc. The most common entry point on the skull is called Kocher's point, which is measured 11 cm posterior to the nasion and 3 cm lateral to midline. EVD ventriculostomy is done primarily to monitor the intracranial pressure as well as to drai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
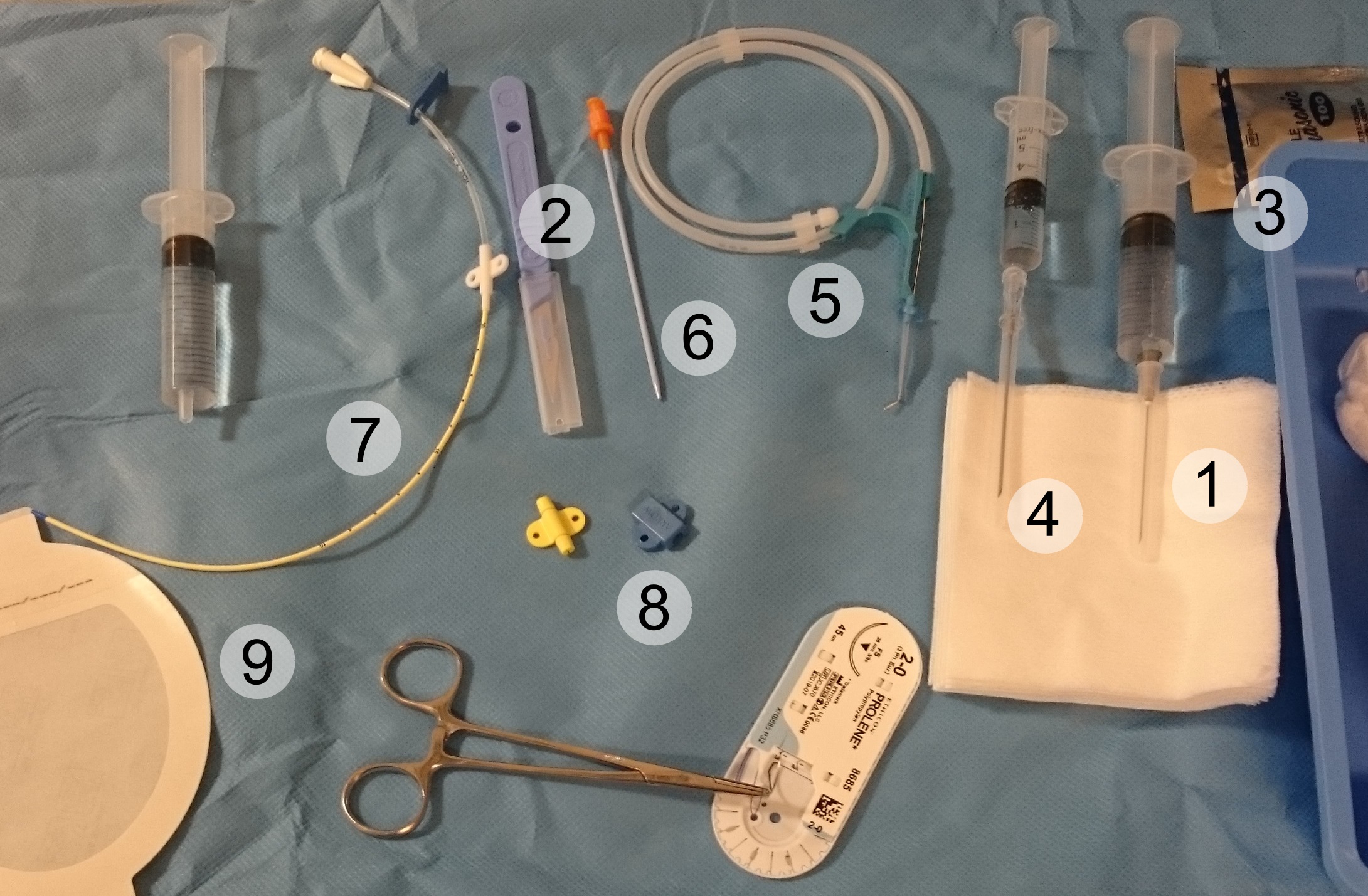
Central Venous Catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest ( subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). Central lines are used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), administer fluid or blood products for large volume resuscitation, and measure central venous pressure. The catheters used are commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |