|
Phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation. Phenethylamine is sold as a dietary supplement for purported mood and weight loss-related therapeutic benefits; however, in orally ingested phenethylamine, a significant amount is metabolized in the small intestine by monoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTAAR1
Trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAAR1'' gene. TAAR1 is an intracellular amine-activated and G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is primarily expressed in several peripheral organs and cells (e.g., the stomach, small intestine, duodenum, and white blood cells), astrocytes, and in the intracellular milieu within the presynaptic plasma membrane (i.e., axon terminal) of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). TAAR1 was discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of investigators, Borowski ''et al.'' and Bunzow ''et al.'' TAAR1 is one of six functional human trace amine-associated receptors, which are so named for their ability to bind endogenous amines that occur in tissues at trace concentrations. TAAR1 plays a significant role in regulating neurotransmission in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin neurons in the CNS; it also affects immune system and neuroimmune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Amine-associated Receptor 1
Trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAAR1'' gene. TAAR1 is an intracellular amine-activated and G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is primarily expressed in several peripheral organs and cells (e.g., the stomach, small intestine, duodenum, and white blood cells), astrocytes, and in the intracellular milieu within the presynaptic plasma membrane (i.e., axon terminal) of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). TAAR1 was discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of investigators, Borowski ''et al.'' and Bunzow ''et al.'' TAAR1 is one of six functional human trace amine-associated receptors, which are so named for their ability to bind endogenous amines that occur in tissues at trace concentrations. TAAR1 plays a significant role in regulating neurotransmission in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin neurons in the CNS; it also affects immune system and neuroimmune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or illicitly) as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or '' comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" (with "amphetamines" including amphetamine and methamphetamine) the value was 0.7%, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Amine
Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems. Trace amines play significant roles in regulating the quantity of monoamine neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft of monoamine neurons with . They have well-characterized presynaptic ''amphetamine-like'' effects on these monoamine neurons via TAAR1 activation; specifically, by activating TAAR1 in neurons they promote the release and prevent reu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
Phenylethanolamine ''N''-methyltransferase (PNMT) is an enzyme found primarily in the adrenal medulla that converts norepinephrine (noradrenaline) to epinephrine (adrenaline). It is also expressed in small groups of neurons in the human brain and in selected populations of cardiomyocytes. Structure PNMT is a protein whose encoding gene is found on chromosome 17 in humans. It consists of 4 exons and is a 30 kDa protein. It shares many properties found among the other methyltransferases. It is closest in sequence to glycine-''N''-methyl transferase ( GNMT). It also shares many structural properties like the shape of the folding lip with catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), though it shares less sequence identity. Several features of the structure like this folding lip suggest that PNMT is a recent adaptation to the catecholamine synthesizing enzyme family, evolving later than COMT, but before other methyltransferases like GNMT. ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) is a requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
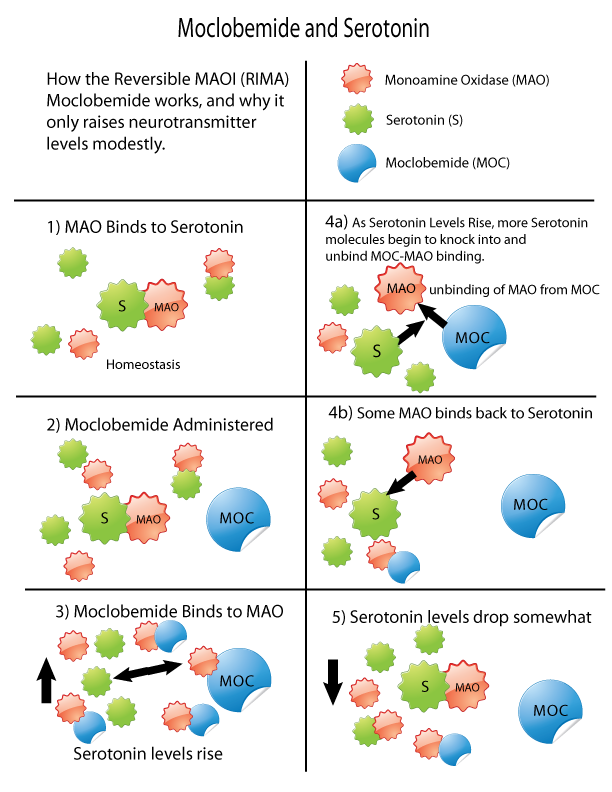
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase B
Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAOB, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOB'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the flavin monoamine oxidase family. It is an enzyme located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. It catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and plays an important role in the catabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues (such as dopamine). This protein preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenethylamine. Similarly to monoamine oxidase A (MAOA), it also degrades dopamine hough some new research contradicts this, suggesting that MAOB does ''not'' directly degrade dopamine, but is responsible for GABA synthesis Structure Monoamine oxidase B has a hydrophobic bipartite elongated cavity that (for the "open" conformation) occupies a combined volume close to 700 Å3. hMAO-A has a single cavity that exhibits a rounder shape and is larger in volume than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
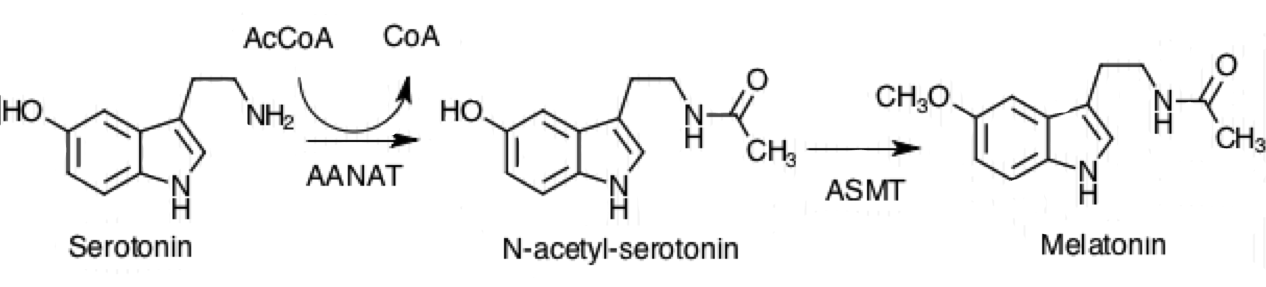
Aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase
Aralkylamine ''N''-acetyltransferase (AANAT) (), also known as arylalkylamine ''N''-acetyltransferase or serotonin ''N''-acetyltransferase (SNAT), is an enzyme that is involved in the day/night rhythmic production of melatonin, by modification of serotonin. It is in humans encoded by the ~2.5 kb '' AANAT gene'' containing four exons, located on chromosome 17q25. The gene is translated into a 23 kDa large enzyme. It is well conserved through evolution and the human form of the protein is 80 percent identical to sheep and rat AANAT. It is an acetyl-CoA-dependent enzyme of the GCN5-related family of ''N''-acetyltransferases (GNATs). It may contribute to multifactorial genetic diseases such as altered behavior in sleep/wake cycle and research is on-going with the aim of developing drugs that regulate AANAT function. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is acetyl-CoA:2-arylethylamine N-acetyltransferase. Other names in common use include: * AANAT * Arylalkyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavin-containing Monooxygenase 3
Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), also known as dimethylaniline monooxygenase -oxide-forming3 and trimethylamine monooxygenase, is a flavoprotein enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''FMO3'' gene. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction, among others: :trimethylamine + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons trimethylamine ''N''-oxide + NADP+ + H2O FMO3 is the main flavin-containing monooxygenase isoenzyme that is expressed in the liver of adult humans. The human FMO3 enzyme catalyzes several types of reactions, including: the of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines; the of nucleophilic sulfur-containing compounds; and the of the anti-cancer agent dimethylxanthenone acetic acid ( DMXAA). FMO3 is the primary enzyme in humans which catalyzes the ''N''-oxidation of trimethylamine into trimethylamine ''N''-oxide; FMO1 also does this, but to a much lesser extent than FMO3. Genetic deficiencies of the FMO3 enzyme cause primary trimethylaminuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , |
L-Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin. It is encoded by the codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement for its analgesic and antidepressant effects. It is a direct precursor to the neuromodulator phenethylamine, a commonly used dietary supplement. As an essential amino acid, phenylalan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |