|
Pain With Sex
Dyspareunia ( ) is painful sexual intercourse due to medical or psychological causes. The term ''dyspareunia'' covers both female dyspareunia and male dyspareunia, but many discussions that use the term without further specification concern the female type, which is more common than the male type. In females, the pain can primarily be on the external surface of the genitalia, or deeper in the pelvis upon deep pressure against the cervix. Medically, dyspareunia is a pelvic floor dysfunction and is frequently underdiagnosed. It can affect a small portion of the vulva or vagina or be felt all over the surface. Understanding the duration, location, and nature of the pain is important in identifying the causes of the pain. Numerous physical, psychological, and social or relationship causes can contribute to pain during sexual encounters. Commonly, multiple underlying causes contribute to the pain. The pain can be acquired or congenital. Symptoms of dyspareunia may also occur after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, forming the combined area of Obstetrics and gynaecology, obstetrics and gynecology (OB-GYN). The term comes from Greek and means "the science of woman, women". Its counterpart is andrology, which deals with medical issues specific to the male reproductive system. Etymology The word "gynaecology" comes from the oblique stem (γυναικ-) of the Ancient Greek, Greek word γυνή (''gyne)'' semantics, semantically attached to "woman", and ''-logia'', with the semantic attachment "study". The word gynaecology in Kurdish languages, Kurdish means "jinekolojî", separated word as "jin-ekolojî", so the Kurdish "jin" called like "gyn" and means in Kurdish "woman". History Antiquity The Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Their presence in both vertebrates and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient evolutionary history. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterized by the growth of cells that proliferate on the inside of the uterus ( endometrium) atypically located among the cells of the uterine wall ( myometrium), as a result, thickening of the uterus occurs. As well as being misplaced in patients with this condition, endometrial tissue is completely functional. The tissue thickens, sheds and bleeds during every menstrual cycle. The condition is typically found in women between the ages of 35 and 50, but also affects younger women. Patients with adenomyosis often present with painful menses (dysmenorrhea), profuse menses ( menorrhagia), or both. Other possible symptoms are pain during sexual intercourse, chronic pelvic pain and irritation of the urinary bladder. In adenomyosis, ''basal'' endometrium penetrates into hyperplastic myometrial fibers. Unlike the functional layer, the basal layer does not undergo typical cyclic changes with the menstrual cycle. Adenomyosis may involve the uteru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
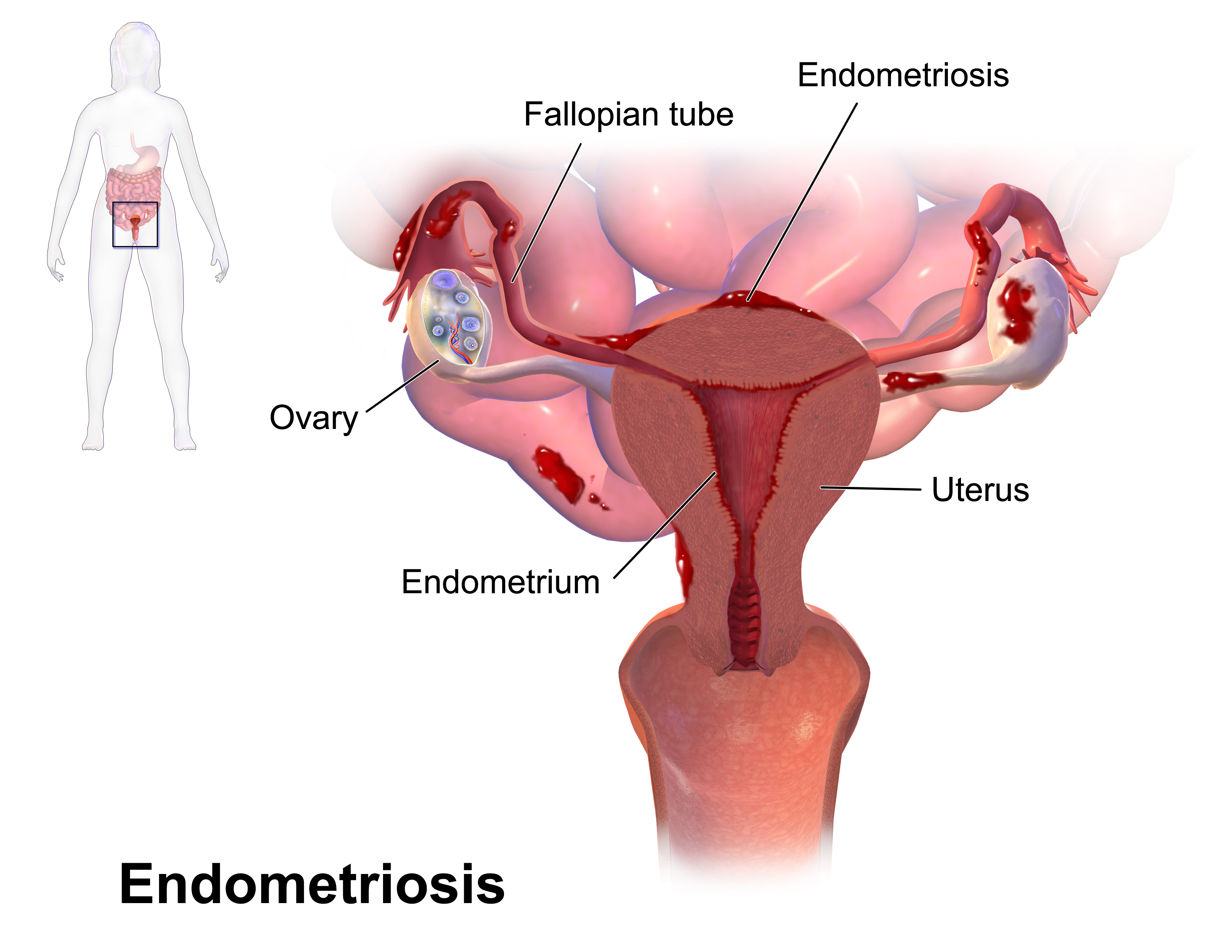
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends towards or through the opening of the vagina. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sex, trouble urinating, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Often it gets worse over time. Low back pain and vaginal bleeding may also occur. Risk factors include pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, constipation, and chronic coughing. Diagnosis is based on examination. It is a form of pelvic organ prolapse, together with bladder prolapse, large bowel prolapse, and small bowel prolapse. Preventive efforts include managing chronic breathing problems, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Mild cases may be treated with a pessary together with hormone replacement therapy. More severe cases may require surgery such as a vaginal hysterectomy. About 14% of women are affected. It occurs most commonly after menopause. Causes The most common cause of uterine prolapse is trauma during childbirth, in particular multiple or difficul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroverted Uterus
A retroverted uterus (tilted uterus, tipped uterus) is a uterus that is oriented posteriorly, towards the back of the body. This is in contrast to the typical uterus, which is oriented forward (slightly " anteverted") toward the bladder, with the anterior part slightly concave. Depending on the source, one in three to five uteruses is retroverted, or oriented backwards towards the spine. Related terms The following table distinguishes among some of the terms used for the position of the uterus: A retroverted uterus should be distinguished from the following: Additional terms include: * ''retrocessed uterus:'' both the superior and inferior ends of the uterus are pushed posteriorly * ''severely anteflexed uterus:'' a pronounced forward bend in an anteflexed uterus * ''vertical uterus:'' the fundus (top of the uterus) is straight up Causes In most cases, a retroverted uterus is a normal variation present from birth. There are other factors, however, that can cause the uter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Orifice
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (from Ancient Greek ὑπo- ''hypo-'' 'under' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Dictionary of Cell and Molecular Biology (11 March 2008) Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells.Hypoplasia Stedman's Medical Dictionary. lww.com Hypoplasia is similar to aplasia, but less severe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Septum
A vaginal septum is a vaginal anomaly that is partition within the vagina; such a septum could be either longitudinal or transverse. In some affected women, the septum is partial or does not extend the length or width of the vagina. Pain during intercourse can be a symptom. A longitudinal vaginal septum develops during embryogenesis when there is an incomplete fusion of the lower parts of the two Müllerian ducts. As a result, there may appear to be two openings to the vagina. There may be associated duplications of the more cranial parts of the Müllerian derivatives, a double cervix, and either a uterine septum or uterus didelphys (double uterus). A transverse septum forms during embryogenesis when the Müllerian ducts do not fuse to the urogenital sinus. A complete transverse septum can occur across the vagina at different levels. Menstrual flow can be blocked, and is a cause of primary amenorrhea. The accumulation of menstrual debris behind the septum is termed cryptome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymen
The hymen is a thin piece of mucosal tissue that surrounds or partially covers the external vaginal opening. It forms part of the vulva, or external genitalia, and is similar in structure to the vagina. In children, a common appearance of the hymen is crescent-shaped, although many shapes are possible. During puberty, estrogen causes the hymen to change in appearance and become very elastic. Normal variations of the post-pubertal hymen range from thin and stretchy to thick and somewhat rigid. Very rarely, it may be completely absent. The hymen can rip or tear during first penetrative intercourse, which usually results in pain and, sometimes, mild temporary bleeding or spotting. Sources differ on how common tearing or bleeding after first intercourse are. The state of the hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity, though " virginity testing" remains a common practice in some cultures, sometimes accompanied by surgical restoration of hymen to give the appearance of virgini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |