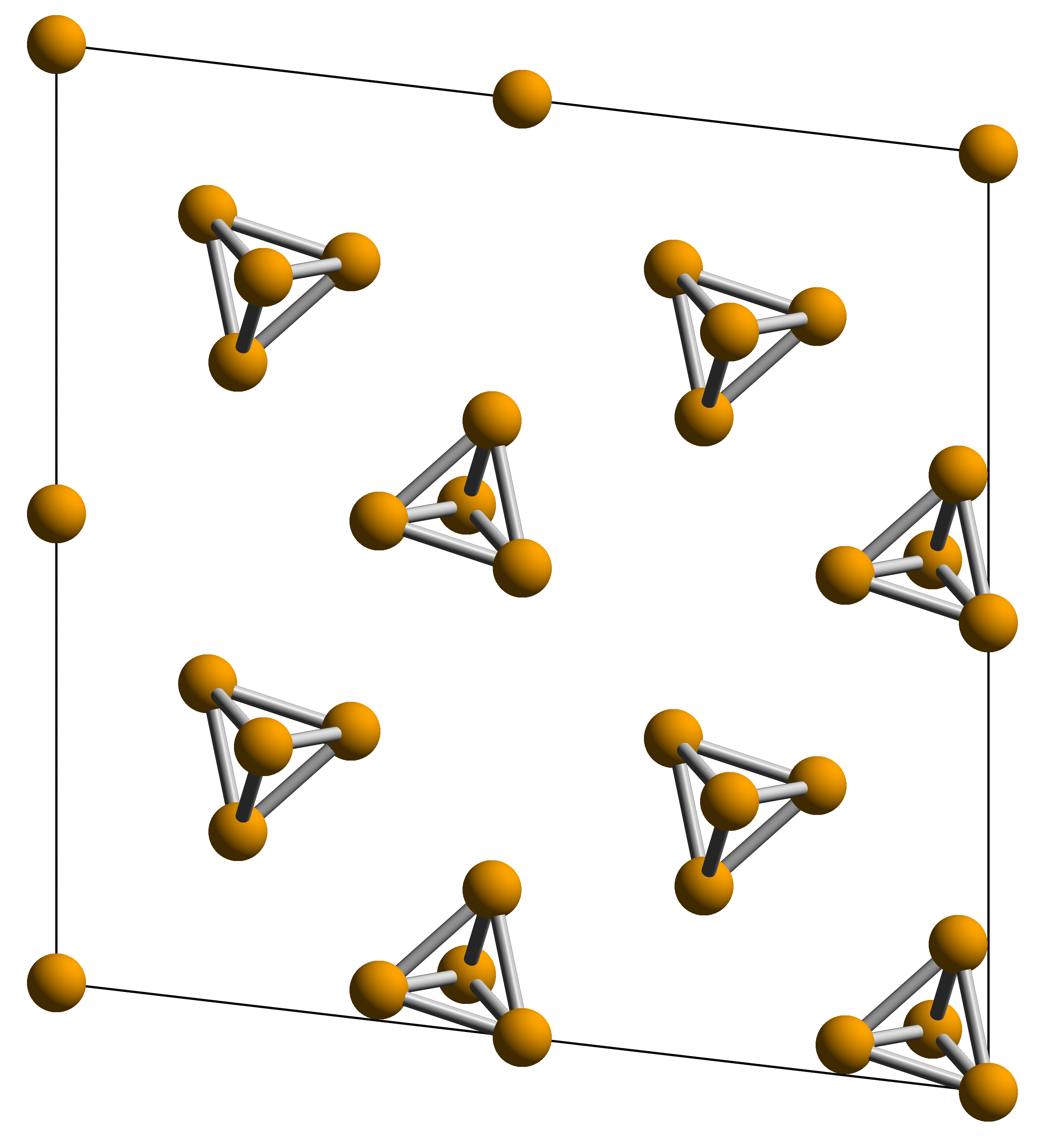|
Pyrophoricity
A substance is pyrophoric (from , , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolithium compounds and triethylborane. Pyrophoric materials are often water-reactive as well and will ignite when they contact water or humid air. They can be handled safely in atmospheres of argon or (with a few exceptions) nitrogen. Fire classification fire extinguishers are designated for use in fires involving metals but not pyrophoric materials in general. A related concept is hypergolicity, in which two compounds spontaneously ignite when mixed. Uses The creation of sparks from metals is based on the pyrophoricity of small metal particles, and pyrophoric alloys are made for this purpose. Practical applications include the sparking mechanisms in lighters and various toys, using ferrocerium; starting fires without matches, using a firesteel; the flintlock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoricity, pyrophoric and reacts with water even at . It is the least electronegativity, electronegative stable element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactor technology, nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometres. The German chemist Robert Bunsen and physicist Gustav Kirchhoff discovered caesium in 1860 by the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organolithium Compound
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric. History and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spark (fire)
A spark is an incandescent particle. Sparks may be produced by pyrotechnics, by metalworking or as a by-product of fires, especially when burning wood. Pyrotechnics In pyrotechnics, charcoal, iron filings, aluminum, titanium and metal alloys such as magnalium may be used to create sparks. The quantity and style of sparks produced depends on the composition and pyrophoricity of the metal and can be used to identify the type of metal by spark testing. In the case of iron, the presence of carbon is required, as in carbon steel — about 0.7% is best for large sparks. The carbon burns explosively in the hot iron and this produces pretty, branching sparks. The color of sparks used in pyrotechnics is determined by the material that the sparks are made from, with the possibility of adding different chemical compounds to certain materials to further influence the color of the sparks. The basic color of sparks is limited to red/orange, gold (yellow) and silver (white). This is expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flintlock Mechanism
The flintlock mechanism is a type of lock (firearm), lock used on muskets, rifles, and pistols from the early 17th to the mid-19th century. It is commonly referred to as a "flintlock" (without the word ''mechanism''). The term is also used for the weapons themselves as a whole, and not just the lock mechanism. The flintlock mechanism, also known as the true flintlock, was developed in France in the early 17th century. It quickly replaced earlier technologies, such as the matchlock, wheellock and earlier flintlocks. It continued to be in common use for over two centuries, until it was finally replaced by the percussion lock. History Flintlock firing mechanisms made their appearance in the 16th century in the form of the snaplock, the snaphance, the miquelet, and the doglock. The so-called ''true flintlock'' was developed in France in the early 17th century. Though its exact origins are not known, credit for the development of the true flintlock is usually given to Marin le Bourgeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Firesteel
A fire striker is a piece of carbon steel from which sparks are struck by the sharp edge of flint, chert or similar rock. It is a specific tool used in fire making. History Before the invention of matches, percussion fire making was often used to start fires. Before the advent of steel, a variety of iron pyrite or marcasite was used with flint and other stones to produce a high-temperature spark that could be used to create fire. There are indications that the Iceman, also known as Ötzi, may have used iron pyrite to make fire. From the Iron Age forward, until the invention of the friction match in 1826 by John Walker, the use of flint and steel was a common method of fire lighting. Percussion fire-starting was prevalent in Europe during ancient times, the Middle Ages and the Viking Age. When flint and steel were used, the fire steel was often kept in a metal tinderbox together with flint and tinder. In Tibet and Mongolia, they were instead carried in a leather pouch cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sodium Hydride
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula Na H. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to molecular hydrides such as borane, silane, germane, ammonia, and methane. It is an ionic material that is insoluble in all solvents (other than molten sodium metal), consistent with the fact that H− ions do not exist in solution. Basic properties and structure NaH is colorless, although samples generally appear grey. NaH is around 40% denser than Na (0.968 g/cm3). NaH, like LiH, KH, RbH, and CsH, adopts the NaCl crystal structure. In this motif, each Na+ ion is surrounded by six H− centers in an octahedral geometry. The ionic radii of H− (146 pm in NaH) and F− (133 pm) are comparable, as judged by the Na−H and Na−F distances. "Inverse sodium hydride" (hydrogen sodide) A very unusual situation occurs in a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
White Phosphorus
White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus, or simply tetraphosphorus (P4) is an allotrope of phosphorus. It is a translucent waxy solid that quickly yellows in light (due to its photochemical conversion into red phosphorus), and impure white phosphorus is for this reason called yellow phosphorus. White phosphorus is the first allotrope of phosphorus, and in fact the first elementary substance to be discovered that was not known since ancient times. It glows greenish in the dark (when exposed to oxygen) and is highly flammable and pyrophoric (self-igniting) upon contact with air. It is toxic, causing severe liver damage on ingestion and phossy jaw from chronic ingestion or inhalation. The odour of combustion of this form has a characteristic garlic odor, and samples are commonly coated with white " diphosphorus pentoxide", which consists of tetrahedra with oxygen inserted between the phosphorus atoms and at their vertices. White phosphorus is only slightly soluble in water and can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Triethylborane
Triethylborane (TEB), also called triethylboron, is an organoborane (a compound with a B–C bond). It is a colorless pyrophoric liquid. Its chemical formula is or , abbreviated . It is soluble in organic solvents tetrahydrofuran and hexane. Preparation and structure Triethylborane is prepared by the reaction of trimethyl borate with triethylaluminium: :Et3Al + (MeO)3B → Et3B + (MeO)3Al The molecule is monomeric, unlike H3B and Et3Al, which tend to dimerize. It has a planar BC3 core. Applications Turbojet engines Triethylborane was used to ignite the JP-7 fuel in the Pratt & Whitney J58 turbojet/ ramjet engines powering the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird and its predecessor, the A-12 OXCART. Triethylborane is suitable because it ignites readily upon exposure to oxygen. It was chosen as an ignition method for reliability reasons, and in the case of the Blackbird, because JP-7 fuel has very low volatility and is difficult to ignite. Conventional ignition plugs posed a high r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mineral Oil
Mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils. The name 'mineral oil' by itself is imprecise, having been used for many specific oils, since 1771. Other names, similarly imprecise, include 'white oil', 'paraffin oil', 'Liquid paraffin (medicinal), liquid paraffin' (a highly refined medical grade), (Latin), and 'liquid petroleum'. Most often, mineral oil is a liquid obtained from Oil refinery, refining crude oil to make gasoline and other petroleum products. Mineral oils used for lubrication are known specifically as base oils. More generally, mineral oil is a Transparency and translucency, transparent, colorless oil, composed mainly of alkanes and cycloalkanes, related to petroleum jelly. It has a density of around . Nomenclature Some of the imprecision in the definition of the names used for mineral oil (such as 'white oil') ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |