|
Pyrenoids
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 56, 99-131. and in a single group of land plants, the hornworts.Villarreal, J. C., & Renner, S. S. (2012) Hornwort pyrenoids, carbon-concentrating structures, evolved and were lost at least five times during the last 100 million years. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'',109(46), 1873-1887. Pyrenoids are associated with the operation of a carbon-concentrating mechanism (CCM). Their main function is to act as centres of carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation, by generating and maintaining a CO2 rich environment around the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO). Pyrenoids therefore seem to have a role analogous to that of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria. Algae are restricted to aqueous env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrena
A pyrena or pyrene (commonly called a "pit" or "stone") is the fruitstone within a drupe or drupelet produced by the ossification of the endocarp or lining of the fruit. It consists of a hard endocarp tissue surrounding one or more seeds (also called the "kernel"). The hardened endocarp which constitutes the pyrene provides a protective physical barrier around the seed, shielding it from pathogens and herbivory. While many drupes are monopyrenous, containing only one pyrene, pome-type fruit with a hard, stony (rather than leathery) endocarp are typically polypyrenous drupes, containing multiple pyrenes. Development The hardening of the endocarp of a developing drupe occurs via secondary cell wall formation and lignification. The biopolymer lignin, also found in wood, provides a structure within secondary cell walls which supports the polymerisation of cellulose and hemicellulose; together these polymers provide the endocarp with tensile strength and stiffness. Furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
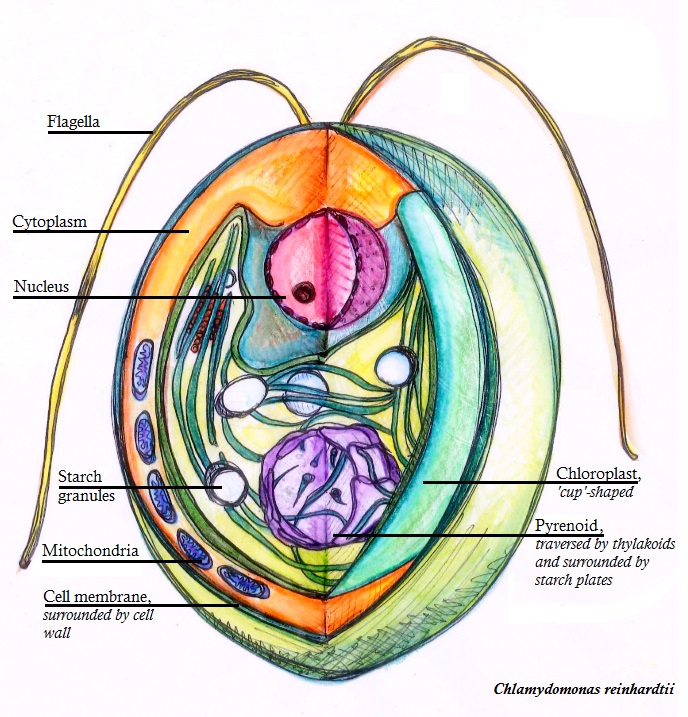
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. ''Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' name h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucophytes
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants (Viridiplantae or Chloroplastida), they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes. The glaucophytes are of interest to biologists studying the development of chloroplasts because some studies suggest they may be similar to the original algal type that led to green plants and red algae in that glaucophytes may be basal Archaeplastida. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes only have asexual reproduction. Characteristics The plastids of glaucophytes are known as 'muroplasts', 'cyanoplasts' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae '' sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced /ɑːrkɪ'plastɪdə/) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group glaucophytes. It also includes the non-photosynthetic lineage Rhodelphidia, a predatorial (eukaryotrophic) flagellate that is sister to the Rhodophyta, and probably the microscopic picozoans. The Archaeplastida have chloroplasts that are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting that they were acquired directly through a single endosymbiosis event by feeding on a cyanobacterium. All other groups which have chloroplasts, besides the amoeboid genus '' Paulinella'', have chloroplasts surrounded by three or four membranes, suggesting they were acquired secondarily from red or green algae. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes have never been involved in secondary endosymbiosis events. The cells of the Archaeplastida typically lack centri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic. The Proterozoic covers the time from the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life (such as trilobites or corals) on the Earth. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two forms of ultimately Greek origin: meaning 'former, earlier', and , 'of life'. The well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes; several glaciations, which produced the hypothesized Snowball Earth during the Cryogenian Period in the late Neoproterozoic Era; and the Ediacaran Period (635 to 538.8 Ma) which is cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charophyceae
Charophyceae is a class of charophyte green algae. AlgaeBase places it in division Charophyta. Extant (living) species are placed in a single order Charales, commonly known as "stoneworts" and "brittleworts". Fossil members of the class may be placed in separate orders, e.g. Sycidiales and Trochiliscales. Charophyceae is basal in the Phragmoplastophyta clade which contains the embryophytes (land plants).Hoek, C. van den, Mann, D. G. & Jahns, H. M. 1995''Algae: An Introduction to Phycology'' Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. McCourt, R. M., Chapman, R. L., Buchheim, M. & Mishler, B. D“Green Plants” Accessed 13 December 2007 In 2018, the first nuclear genome sequence from a species belonging to the Charophyceae was published: that of '' Chara braunii''. Description The thallus is erect with regular nodes and internodes. At each node there is a whorl of branches. The whole plant is calcified and ''Equisetum ''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroma (fluid)
Stroma, in botany, refers to the colorless fluid surrounding the grana within the chloroplast. Within the stroma are grana (stacks of thylakoid), and the sub-organelles or daughter cells, where photosynthesis is commenced before the chemical changes are completed in the stroma. Kramer & Scott ''flower'' iv. 80 1979 Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first stage, ''light-dependent reactions'' capture the energy of light and use it to make the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH. During the second stage, the '' light-independent reactions'' use these products to fix carbon by capturing and reducing carbon dioxide. The series of biochemical redox reactions which take place in the stroma are collectively called the Calvin cycle or '' light-independent reactions''. There are three phases: carbon fixation, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration. The stroma is also the location of chloroplast DNA and chloroplast ribosomes, and thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonic Anhydrases
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate and hydrogen ions). The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion. They are therefore classified as metalloenzymes. The enzyme maintains acid-base balance and helps transport carbon dioxide. Carbonic anhydrase helps maintain acid–base homeostasis, regulate pH, and fluid balance. Depending on its location, the role of the enzyme changes slightly. For example, carbonic anhydrase produces acid in the stomach lining. In the kidney, the control of bicarbonate ions influences the water content of the cell. The control of bicarbonate ions also influences the water content in the eyes. Inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase are used to treat glaucoma, the excessive build-up of water in the eyes. Blocking this enzyme shifts the fluid balance in the eyes to reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylakoid
Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal/stromal thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment. In thylakoid membranes, chlorophyll pigments are found in packets called quantasomes. Each quantasome contains 230 to 250 chlorophyll molecules. Etymology The word ''Thylakoid'' comes from the Greek word ''thylakos'' or ''θύλακος'', meaning "sac" or "pouch". Thus, ''thylakoid'' means "sac-like" or "pouch-like". Structure Thylakoids are membrane-bound structures embedded in the chloroplast stroma. A stack of thylakoids is called a granum and resembles a stack of coins. Membrane The thylakoid membrane is the site of the light- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |