|
Pubic Tubercle
The pubic tubercle is a prominent tubercle on the superior ramus of the pubis bone of the pelvis. Structure The pubic tubercle is a prominent forward-projecting tubercle on the upper border of the medial portion of the superior ramus of the pubis bone. The inguinal ligament attaches to it. Part of the abdominal external oblique muscle inserts onto it. The inferior epigastric artery passes between the pubic tubercle and the anterior superior iliac spine. The pubic spine is a rough ridge that extends from the pubic tubercle to the upper border of the pubic symphysis. Clinical significance The pubic tubercle may be palpated. It serves as a landmark for local anaesthetic A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sense, sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sen ... of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis (: symphyses) is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is attached to the suspensory ligament of the clitoris. In most adults, it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing ( ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
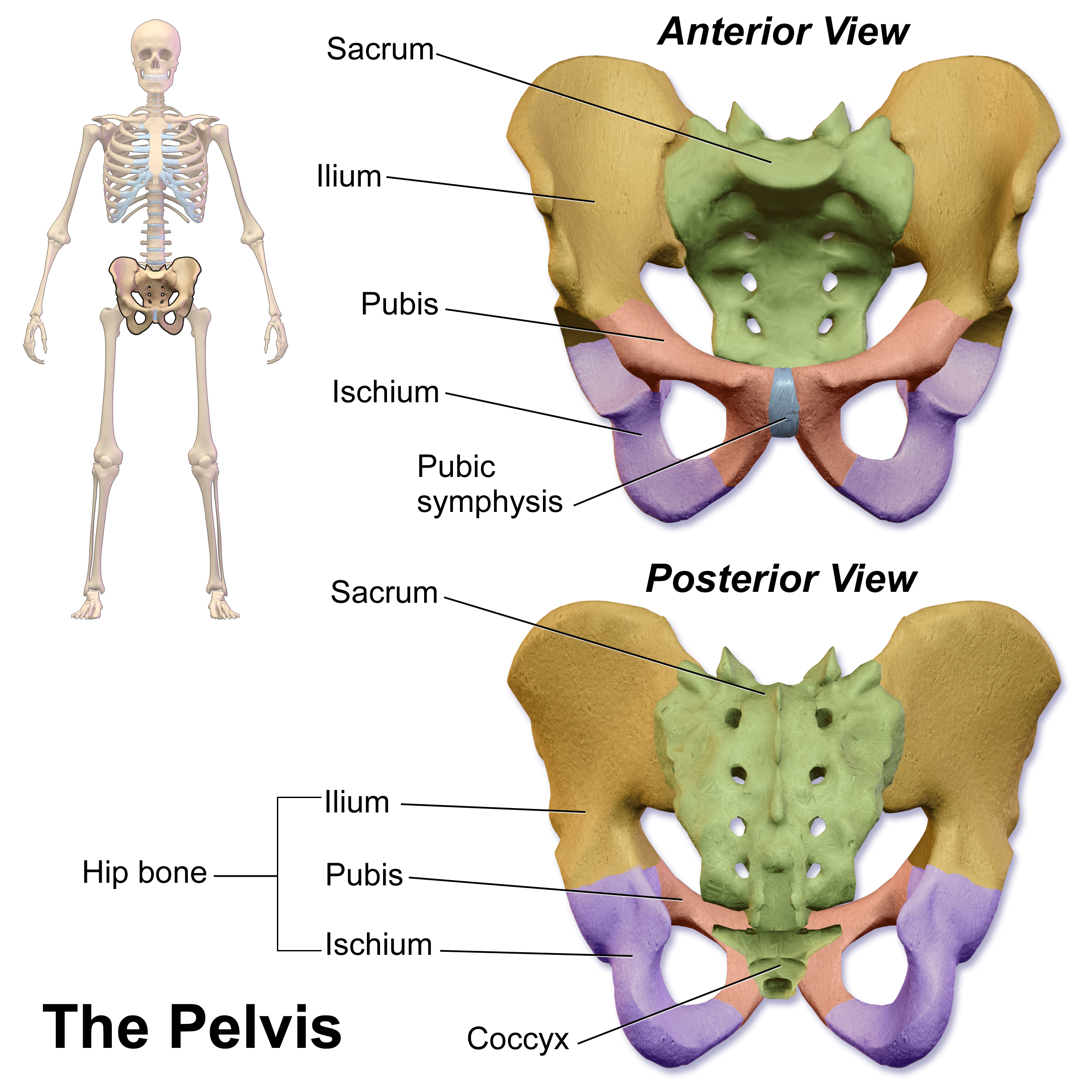
Pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Superior Pubic Ramus
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of Adipose tissue, fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing ( ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inguinal Ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop. Structure The inguinal ligament runs from the anterior superior iliac crest of the ilium to the pubic tubercle of the pubic bone. It is formed by the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis and is continuous with the fascia lata of the thigh. There is some dispute over the attachments. Structures that pass deep to the inguinal ligament include: * Psoas major, iliacus, pectineus * Femoral nerve, artery, and vein * Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh *Lymphatics Function The ligament serves to contain soft tissues as they course anteriorly from the trunk to the lower extremity. This structure demarcates the superior border of the femoral triangle. It demarcates the inferior border of the inguinal triangle. The midpoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abdominal External Oblique Muscle
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat Abdomen#Muscles, abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen. Structure The external oblique is situated on the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen. It is broad, thin, and irregularly quadrilateral, its muscular portion occupying the side, its aponeurosis the anterior wall of the abdomen. In most humans, the oblique is not visible, due to subcutaneous adipose, fat deposits and the small size of the muscle. It arises from eight fleshy digitations, each from the external surfaces and inferior borders of the fifth to twelfth ribs (lower eight ribs). These digitations are arranged in an oblique line which runs inferiorly and anteriorly, with the upper digitations being attached close to the cartilages of the corresponding ribs, the lowest to the apex of the cartilage of the last rib, the intermediate ones to the ribs at some distance fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inferior Epigastric Artery
In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold (which represents the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.) The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath. Structure Origin The inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery, immediately superior to the inguinal ligament. Course and relations It curves forward in the subperitoneal tissue, and then ascends obliquely along the medial margin of the abdominal inguinal ring; continuing its course upward, it pierces the transversalis fascia, and, passing in front of the linea semicircularis, ascends betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
The anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle. The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle. Structure The anterior superior iliac spine refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. This is a key surface landmark, and easily palpated. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, the sartorius muscle, and the tensor fasciae latae muscle. A variety of structures lie close to the anterior superior iliac spine, including the subcostal nerve, the femoral artery (which passes between it and the pubic symphysis), and the iliohypogastric nerve. Clinical significance The anterior superior iliac spine provides a clue i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location (for example, a veterinarian can feel the stomach of a pregnant animal to ensure good health and successful delivery). Palpation is an important part of the physical examination; the somatosensory system, sense of touch is just as important in this examination as the visual perception, sense of sight is. Physicians develop great skill in palpating problems below the surface of the body, becoming able to detect things that untrained persons would not. Mastery of anatomy and much practice (learning method), practice are required to achieve a high level of skill. The concept of being able to detect or notice subtle tactile medical sign, signs and to recognize their significance or implications is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |