|
Proto-Dravidian
Proto-Dravidian is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Dravidian languages native to the Indian subcontinent. It is thought to have differentiated into Proto-North Dravidian, Proto-Central Dravidian, and Proto-South Dravidian, although the date of diversification is still debated. History As a proto-language, Proto-Dravidian is not itself attested in historical records. Its modern conception is based solely on reconstruction. It is suggested that the language was spoken in the 4th millennium BCE, and started evolving into various branches around 3rd-millennium BCE. The origin and territory of the Proto-Dravidian speakers is uncertain, but some suggestions have been made based on the reconstructed Proto-Dravidian vocabulary. The reconstruction has been done on the basis of cognate words present in the different branches ( Northern, Central and Southern) of the Dravidian language family. According to , the botanical vocabulary of Proto-Dravidian is cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
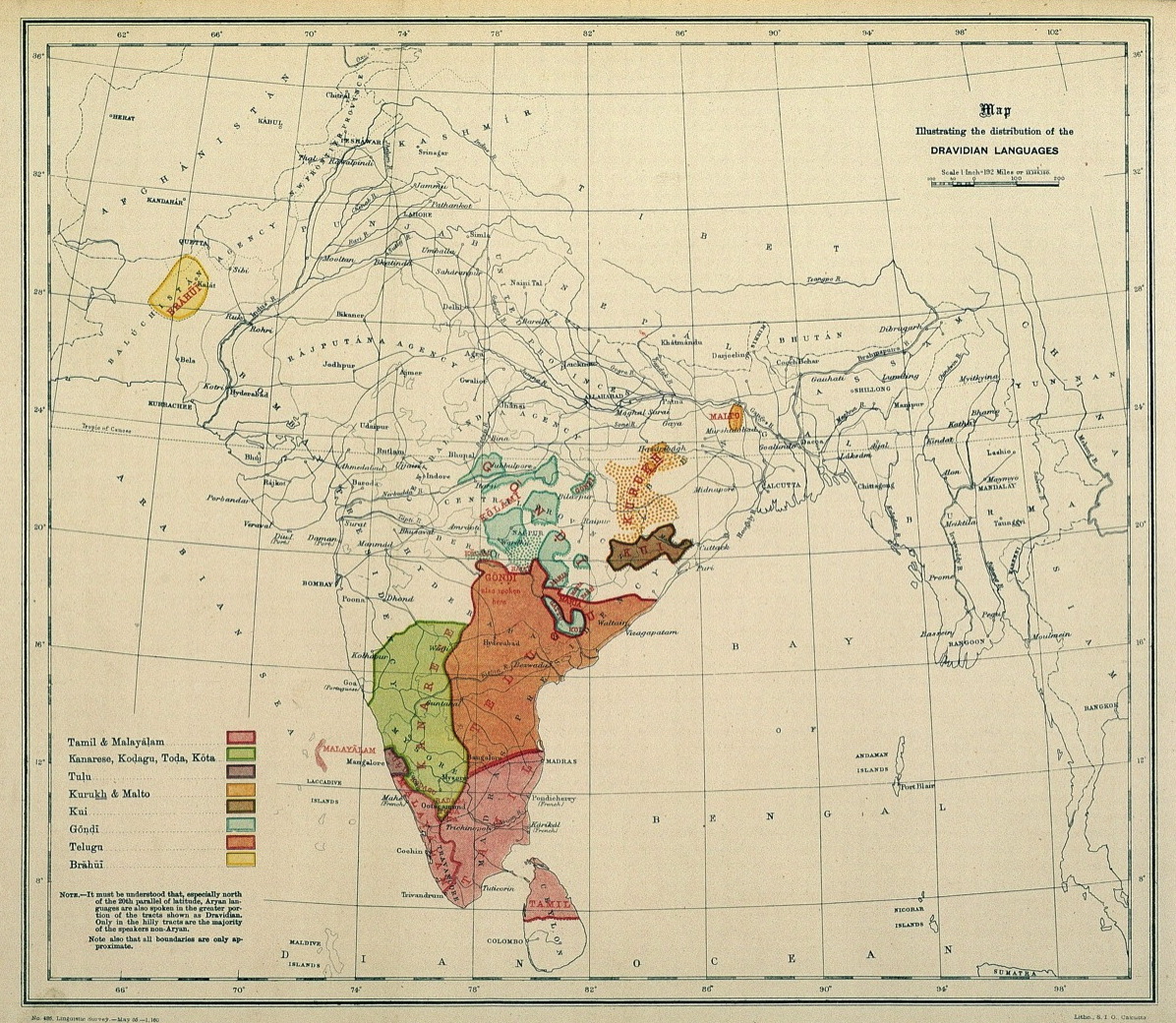
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto and Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Iranian Balochistan, Afghanistan and around the Marw oasis in Turkmenistan. During the British colonial period, Dravidian speakers were sent as indentured labourers to Southeast Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto South-Dravidian Language
Proto-South Dravidian is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the southern Dravidian languages native to southern India. Its descendants include Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam, Tulu, Badaga, Kodava, Irula, Kota and Toda. South Dravidian is sometimes referred to as South Dravidian I (SD1) by linguists. History Going by attested changes in written documents, the Proto-South Dravidian I (PSD1) language has been hypothesised to have been present in the second half of the first millennium BC. Some linguists infer it to have split from Proto-South Dravidian II (Also known as South Central Dravidian or Telugu-Kui) at the beginning of the first millennium BC. These datings however, have been noted to be vague approximations. Til the 4th-5th century BC, Proto-South Dravidian remained one language, with possible dialectal variations. Phonology Vowels Proto-South Dravidian inherited the system of five short and long vowels from Proto-Dravidian: ''*a'', ''*ā'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dravidian People
The Dravidian peoples, Dravidian-speakers or Dravidians, are a collection of ethnolinguistic groups native to South Asia who speak Dravidian languages. There are around 250 million native speakers of Dravidian languages. Telugus form the largest Dravidian ethnic group, whilst Tamilians, Kannadigas and Malayalis form the vast-majority of the rest of Dravidian speakers. Dravidian speakers form the majority of the population of South India and are natively found in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, the Maldives, Nepal, Bhutan and Sri Lanka. The four languages of these ethnic groups along with Urdu constitute the official languages of South India. Dravidian peoples are also present in Singapore, Mauritius, Malaysia, France, South Africa, Myanmar, East Africa, the Caribbean, and the United Arab Emirates through recent migration. Proto-Dravidian may have been spoken in the Indus civilization, suggesting a "tentative date of Proto-Dravidian around the early part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meluhha
or ( ) is the Sumerian name of a prominent trading partner of Sumer during the Middle Bronze Age. Its identification remains an open question, but most scholars associate it with the Indus Valley Civilisation. Etymology Asko Parpola identifies Proto-Dravidians with the Harappan Culture and the Meluhhan people mentioned in Sumerian records. In his book ''Deciphering the Indus Script.'' Parpola states that the Brahui people of Pakistan are remnants of the Harappan culture. According to him, the word "Meluhha" derives from the Dravidian words ''mel'' ("elevated") and ''akam'' ("place"). Parpola also relates Meluhha with Balochistan, which he calls the " Proto-Dravidian homeland". He also relates Meluhha with the transient word Mleccha, a Vedic word used to mean "barbarian" and used by the incoming Aryan speaking population for the native Harappan population. Another piece of possible evidence that points to the people of Meluhha as being Proto-Dravidian is the fact that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Southworth
Franklin C. Southworth (born 1929) is an American linguist and Professor Emeritus of South Asian linguistics at the University of Pennsylvania The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f .... Publications *"South Asia: Dravidian linguistic history" in ''The Encyclopedia of Global Human Migration'' (2013) *''Rice in Dravidian'' (2011) *''Proto-Dravidian Agriculture'' *''Linguistic archaeology of South Asia'' (2005) *''Prehistoric implications of the Dravidian element in the NIA lexicon, with special reference to Marathi'' (2005) *''Reconstructing social context from language: Indo-Aryan and Dravidian prehistory'' (1995) *''South Asian emblematic gestures'' (1992) *''The reconstruction of prehistoric South Asian language contact'' (1990) *''Linguistic archaeology and the Indus Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-language
In the tree model of historical linguistics, a proto-language is a postulated ancestral language from which a number of attested languages are believed to have descended by evolution, forming a language family. Proto-languages are usually unattested, or partially attested at best. They are reconstructed by way of the comparative method. In the family tree metaphor, a proto-language can be called a mother language. Occasionally, the German term ' (; from 'primordial', 'original' + 'language') is used instead. It is also sometimes called the ''common'' or ''primitive'' form of a language (e.g. Common Germanic, Primitive Norse). In the strict sense, a proto-language is the most recent common ancestor of a language family, immediately before the family started to diverge into the attested ''daughter languages''. It is therefore equivalent with the ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'' of a language family. Moreover, a group of lects that are not considered separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asko Parpola
Asko Heikki Siegfried Parpola (born 12 July 1941, in Forssa) is a Finnish Indologist, current professor emeritus of Indology at the University of Helsinki. He specializes in the Indus Valley Civilization, specifically the study of the Indus script. Biography Parpola is a brother of the Akkadian language epigrapher Simo Parpola. He is married to Marjatta Parpola, who has authored a study on the traditions of Kerala's Nambudiri Brahmins. Scholarship Parpola's research and teaching interests fall within the following topics: * Indus Civilization / Indus script and religion / Corpus of Indus Seals and Inscriptions * Veda / Vedic ritual / Samaveda / Jaiminiya Samaveda texts and rituals / Purva-Mimamsa * South Asian religions / Hinduism / Saiva and Sakta tradition / Goddess Durga * South India / Kerala / Tamil Nadu / Karnataka * Sanskrit / Malayalam / Kannada / Tamil / Prehistory of Indian languages * Prehistoric archaeology of South Asia and (in broad sense) Central Asia / Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Reconstruction
Linguistic reconstruction is the practice of establishing the features of an unattested ancestor language of one or more given languages. There are two kinds of reconstruction: * Internal reconstruction uses irregularities in a single language to make inferences about an earlier stage of that language – that is, it is based on evidence from that language alone. * Comparative reconstruction, usually referred to just as reconstruction, establishes features of the ancestor of two or more related languages, belonging to the same language family, by means of the comparative method. A language reconstructed in this way is often referred to as a proto-language (the common ancestor of all the languages in a given family). Texts discussing linguistic reconstruction commonly preface reconstructed forms with an asterisk (*) to distinguish them from attested forms. An attested word from which a root in the proto-language is reconstructed is a . More generally, a reflex is the known deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian Language
Sumerian ) was the language of ancient Sumer. It is one of the List of languages by first written account, oldest attested languages, dating back to at least 2900 BC. It is a local language isolate that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia, in the area that is modern-day Iraq, Iraq. Akkadian language, Akkadian, a Semitic languages, Semitic language, gradually replaced Sumerian as the primary spoken language in the area (the exact date is debated), but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Akkadian-speaking Mesopotamian states, such as Assyria and Babylonia, until the 1st century AD. Thereafter, it seems to have fallen into obscurity until the 19th century, when Assyriologists began Decipherment, deciphering the cuneiform inscriptions and excavated tablets that had been left by its speakers. In spite of its extinction, Sumerian exerted a significant influence on the languages of the area. The Cuneiform, cuneiform script, original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loan Words
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term that is well established in the linguistic field despite its acknowledged descriptive flaws: nothing is taken away from the donor language and there is no expectation of returning anything (i.e., the loanword). Loanwords may be contrasted with calques, in which a word is borrowed into the recipient language by being directly translated from the donor language rather than being adopted in (an approximation of) its original form. They must also be distinguished from cognates, which are words in two or more related languages that are similar because they share an etymological origin in the ancestral language, rather than because one borrowed the word from the other. Examples and related terms A loanword is distinguished from a calque (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |