|
Prompt Critical
In nuclear engineering, prompt criticality is the criticality (the state in which a nuclear chain reaction is self-sustaining) that is achieved with prompt neutrons alone (without the efforts of delayed neutrons). As a result, prompt supercriticality causes a much more rapid growth in the rate of energy release than other forms of criticality. Nuclear weapons are based on prompt criticality, while nuclear reactors rely on delayed neutrons or external neutrons to achieve criticality. Criticality An assembly is critical if each fission event causes, on average, exactly one additional such event in a continual chain. Such a chain is a self-sustaining fission chain reaction. When a uranium-235 (U-235) atom undergoes nuclear fission, it typically releases between one and seven neutrons (with an average of 2.4). In this situation, an assembly is critical if every released neutron has a 1/2.4 = 0.42 = 42 % probability of causing another fission event as opposed to either being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Engineering
Nuclear engineering is the engineering discipline concerned with designing and applying systems that utilize the energy released by nuclear processes. The most prominent application of nuclear engineering is the generation of electricity. Worldwide, some 440 nuclear reactors in 32 countries generate 10 percent of the world's energy through nuclear fission. In the future, it is expected that nuclear fusion will add another nuclear means of generating energy. Both reactions make use of the nuclear binding energy released when atomic nucleons are either separated (fission) or brought together (fusion). The energy available is given by the binding energy curve, and the amount generated is much greater than that generated through chemical reactions. Fission of 1 gram of uranium yields as much energy as burning 3 tons of coal or 600 gallons of fuel oil, without adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. History Nuclear engineering was born in 1938, with the discovery of nuclear fission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle, they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction. In principle, a reaction can involve more than two particles collision, colliding, but because the probability of three or more nuclei to meet at the same time at the same place is much less than for two nuclei, such an event is exceptionally rare (see triple alpha process for an example very close to a three-body nuclear reaction). The term "nuclear reaction" may refer either to a change in a nuclide induced by collision with another particle or to a spontaneous change of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chernobyl Disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only two nuclear energy accidents rated at the maximum severity on the International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident. The response involved more than Chernobyl liquidators, 500,000 personnel and cost an estimated 18billion Soviet ruble, rubles (about $84.5billion USD in 2025). It remains the worst nuclear disaster and the List of disasters by cost, most expensive disaster in history, with an estimated cost of US$700 billion. The disaster occurred while running a test to simulate cooling the reactor during an accident in blackout conditions. The operators carried out the test despite an accidental drop in reactor power, and due to a design issue, attempting to shut down the reactor in those conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fission Products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the ''fission products''. (See also Fission products (by element)). About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%). The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and additional gamma radiation that begins immediately after, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission event its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Defense In Depth (nuclear Engineering)
U.S. non-military nuclear material is regulated by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, which uses the concept of defense in depth when protecting the health and safety of the public from the hazards associated with nuclear materials. The NRC defines defense in depth as creating multiple independent and redundant layers of protection and response to failures, accidents, or fires in power plants. For example, defense in depth means that if one fire suppression system fails, there will be another to back it up. The idea is that no single layer, no matter how robust, is exclusively relied upon; access controls, physical barriers, redundant and diverse key safety functions, and emergency response measures are used. Defense in depth is designed to compensate for potential human and mechanical failures, which are assumed to be unavoidable. Any complex, close-coupled system, no matter how well-engineered, cannot be said to be failure-proof. That is especially true if people operate cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons production and Research reactor, research. Fissile material, Fissile nuclei (primarily uranium-235 or plutonium-239) absorb single neutron, neutrons and split, releasing energy and multiple neutrons, which can induce further fission. Reactors stabilize this, regulating Neutron absorber, neutron absorbers and neutron moderator, moderators in the core. Fuel efficiency is exceptionally high; Enriched uranium#Low-enriched uranium (LEU), low-enriched uranium is 120,000 times more energy dense than coal. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid Nuclear reactor#By coolant, coolant. In commercial reactors, this drives Turbine, turbines and electrical generator shafts. Some reactors are used for district heating, and isotopes, isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Control Rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without themselves decaying. These elements have different neutron capture cross sections for neutrons of various energies. Boiling water reactors (BWR), pressurized water reactors (PWR), and heavy-water reactors (HWR) operate with thermal neutrons, while breeder reactors operate with fast neutrons. Each reactor design can use different control rod materials based on the energy spectrum of its neutrons. Control rods have been used in nuclear aircraft engines like Project Pluto as a method of control. Operating principle Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to control the rate of the nuclear chain reaction and, thereby, the thermal power output of the reactor, the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
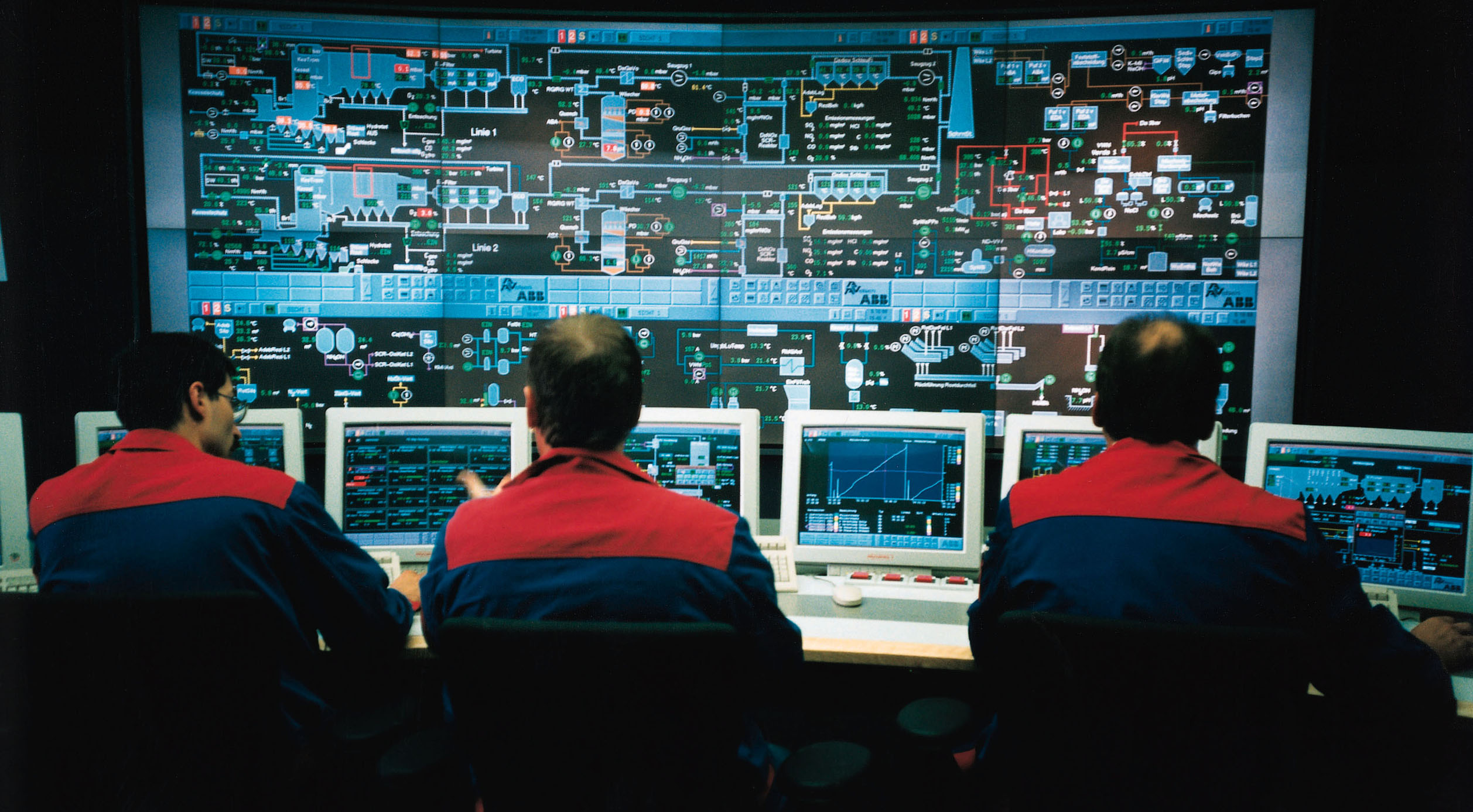
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control Feedback control systems Logic control Logic control systems for indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process ( generator) or used to power a mechanical effect ( motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering. Electromechanical devices are ones which have both electrical and mechanical processes. Strictly speaking, a manually operated switch is an electromechanical component due to the mechanical movement causing an electrical output. Though this is true, the term is usually understood to refer to devices which involve an electrical signal to create mechanical movement, or vice versa mechanical movement to create an ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Delayed Criticality
Delay or DeLay may refer to: People * B. H. DeLay (1891–1923), American aviator and movie stunt pilot * Dorothy DeLay (1917–2002), American violin instructor * Florence Delay (born 1941), French academician and actor * Jan Delay, stage name of German musician Jan Phillip Eißfeldt (born 1976) * Jason Delay (born 1995), American baseball player * Jean Delay (1907–1987), French psychiatrist, neurologist, and writer * Paul deLay (1952–2007), American blues musician * Tom DeLay (born 1947), American politician * Tom Delay (businessman) (born 1959), British businessman * Vladislav Delay (born 1976), Finnish musician Other uses * Delay (audio effect), a technology for producing delayed playback of an audio signal * Delay (programming), a programming language construct for delaying evaluation of an expression * ''Delay 1968'' or ''Delay'', a 1981 compilation album by German experimental rock band Can * ''The Delay'', a 2012 Uruguayan film See also * Delays, an English in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |