|
Proceduralist
Proceduralist is the broad term for a physician, usually a specialist or subspecialist who performs different diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Depending on the type of procedure, this is commonly referring to a: * Surgeon (for surgical procedures) * Interventional radiology, Interventional radiologist (for radiologically guided procedures) * Gastroenterologist (for Endoscopy, endoscopic investigations / therapies) * Respiratory physician (for bronchoscopy) * Cardiologist (for Coronary angiogram, coronary angiography) It may also be used to refer to any other provider of a procedure, even when it may not be their primary role (e.g. an intensivist inserting a Central venous catheter, central venous line, or a psychiatrist performing electroconvulsive therapy.) Proceduralists, regardless of their specific specialty, are commonly responsible for obtaining informed consent from the patient for the intervention they will receive, performing the procedure, and often care following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospital Medicine
Hospital medicine is a medical specialty that exists in some countries as a branch of family medicine or internal medicine, dealing with the care of acutely ill hospitalized patients. Physicians whose primary professional focus is caring for hospitalized patients only while they are in the hospital are called hospitalists. Originating in the United States, this type of medical practice has extended into Australia and Canada. The vast majority of physicians who refer to themselves as hospitalists focus their practice upon hospitalized patients. Hospitalists are not necessarily required to have separate board certification in hospital medicine. The term ''hospitalist'' was first coined by Robert Wachter and Lee Goldman in a 1996 ''New England Journal of Medicine'' article. The scope of hospital medicine includes acute patient care, teaching, research, and executive leadership related to the delivery of hospital-based care. Hospital medicine, like emergency medicine, is a specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis and therapy, treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as Specialty (medicine), specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practitioner, general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the Discipline (academia), academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, underlying diseases, and their treatment, which is the science of medicine, and a decent Competence (human resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatry, psychiatric treatment that causes a generalized seizure by passing electrical current through the brain. ECT is often used as an intervention for mental disorders when other treatments are inadequate. Conditions responsive to ECT include major depressive disorder, mania, and catatonia.FDAFDA Executive Summary Prepared for the January 27–28, 2011 meeting of the Neurological Devices Panel Meeting to Discuss the Classification of Electroconvulsive Therapy Devices (ECT). Quote, p. 38: "Three major practice guidelines have been published on ECT. These guidelines include: APA Task Force on ECT (2001); Third report of the Royal College of Psychiatrists' Special Committee on ECT (2004); National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE 2003; NICE 2009). There is significant agreement between the three sets of recommendations." The general physical risks of ECT are similar to those of brief general anesthesia. Immediately fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Surgical Safety Checklist
The World Health Organization (WHO) published the WHO Surgical Safety Checklist in 2008 in order to increase the safety of patients undergoing surgery. The checklist serves to remind the surgical team of important items to be performed Preoperative care, before and Surgery#postoperative care, after the surgical procedure in order to reduce adverse events such as Perioperative mortality, surgical site infections or retained instruments. It is one affordable and sustainable tool for reducing deaths from surgery in low and middle income countries. Several studies have shown the checklist to reduce the rate of deaths and surgical complications by as much as one-third in centres where it is used. While the checklist has been widely adopted due to its efficacy in many studies as well as for its simplicity, some hospitals still struggle with implementation due to local customs and to a lack of buy-in from surgical staff. Background In 2004, the World Health Assembly (WHA) founded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient Safety
Patient safety is a specialized field about enhancing healthcare quality through the systematic prevention, reduction, reporting, and analysis of medical errors and preventable harm that contribute to severe outcomes for the patient. While healthcare risks have always existed, patient safety only gained formal recognition in the 1990s after multiple nations reported alarming rates of medical error-related injuries. The urgency of the issue was underscored when the World Health Organization (WHO) identified that 1 in 10 patients globally experience harm due to healthcare errors, declaring patient safety an "Endemic (epidemiology), endemic concern" in modern medicine. Today, patient safety stands as a distinct Health care, healthcare discipline, supported by a growing—though still evolving—scientific framework. A robust Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary body of theoretical and empirical research underpins this field, with emerging technologies like MHealth, mobile health ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries, the terms are synonymous, while in other countries, they refer to different positions and ''anesthetist'' is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists. The core element of the specialty is the prevention and mitigation of pain and distress using various anesthetic agents, as well as the monitoring and maintenance of a patient's vital functions throughout the perioperative period. Since the 19th century, anesthesiology has developed from an experimental area with non-specialist practitioners using novel, untested drugs and techniques into what is now a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise require physical restraint in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * ''General anesthesia'' suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of Sensation (psychology), sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * ''Sedation'' suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiolysis, anxiety and creation of long-term memory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam. Medical uses Sedation is typically used in minor surgical procedures such as endoscopy, vasectomy, or dentistry and for reconstructive surgery, some cosmetic surgeries, removal of wisdom teeth, or for high-anxiety patients. Sedation methods in dentistry include inhalation sedation (using nitrous oxide), oral sedation, and intravenous (IV) sedation. Inhalation sedation is also sometimes referred to as "relative analgesia". Sedation is also used extensively in the intensive care unit so that patients who are being mechanical ventilation, ventilated tolerate having an endotracheal tube in their vertebrate trachea, trachea. It can also be used during a long term brain EEG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry. Psychiatrists are physicians who evaluate patients to determine whether their symptoms are the result of a physical illness, a combination of physical and mental ailments or strictly mental issues. Sometimes a psychiatrist works within a multi-disciplinary team, which may comprise clinical psychologists, social workers, occupational therapists, and nursing staff. Psychiatrists have broad training in a biopsychosocial approach to the assessment and management of mental illness. As part of the clinical assessment process, psychiatrists may employ a mental status examination; a physical examination; brain imaging such as a computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or positron emission tomography scan; and blood testing. Psychiatrists use pharmacologic, psychotherapeutic, or interventional approaches to treat mental disorders. Subspecialties The field of psychiatry has many subspecialties that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecialist
A subspecialty or subspeciality (see spelling differences) is a narrow field of professional knowledge/skills within a specialty of trade, and is most commonly used to describe the increasingly more diverse medical specialties. A subspecialist is a specialist of a subspecialty. In medicine, subspecialization is particularly common in internal medicine, cardiology, neurology and pathology, psychiatry and has grown as medical practice has: # become more complex, and # it has become clear that a physician's case volume is negatively associated with their complication rate; that is, complications tend to decrease as the volume of cases per physician goes up. See also * Medical specialty A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer (oncology), ... Notes and references Medical specialties< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
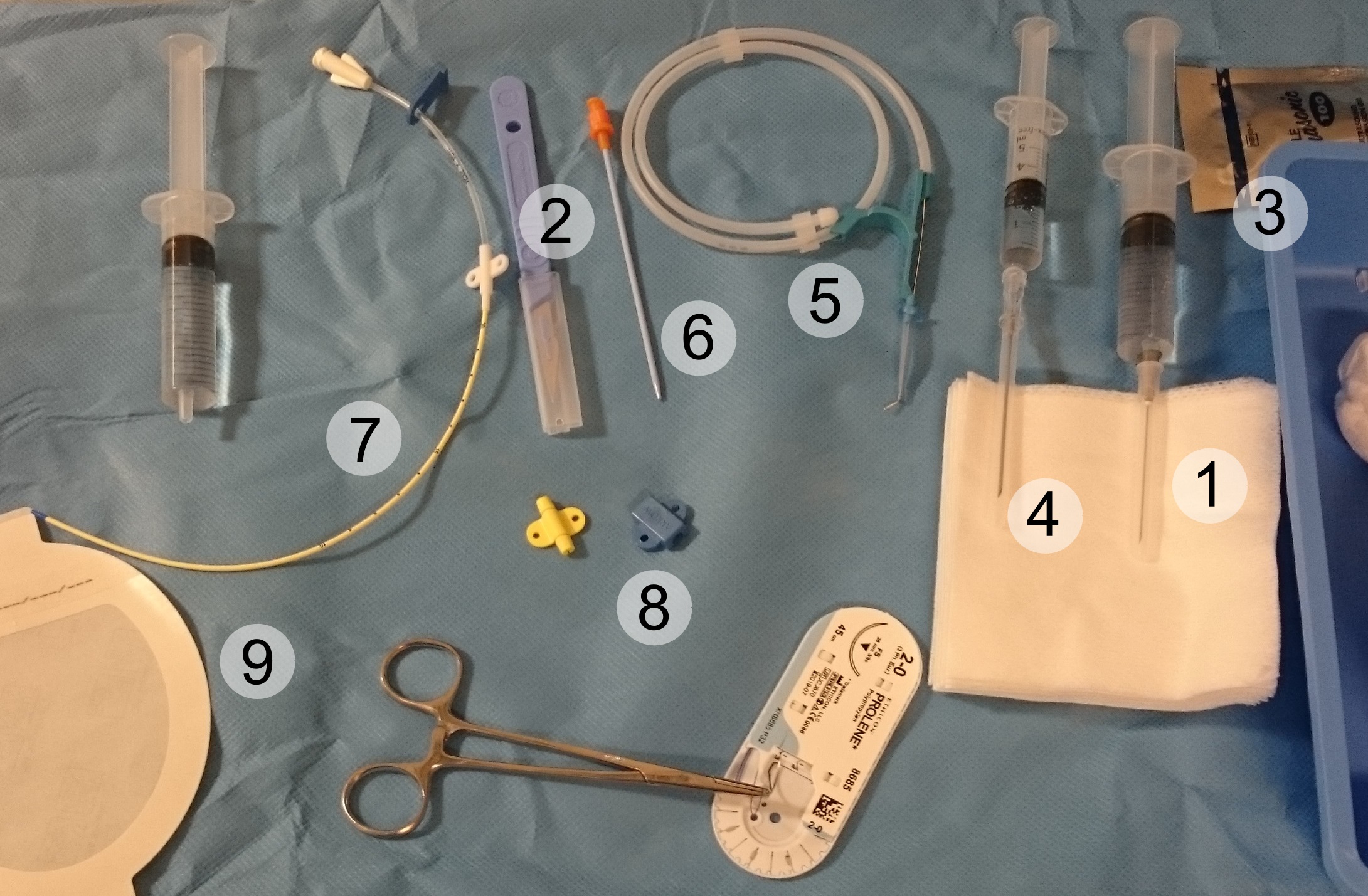
Central Venous Catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest (subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). Central lines are used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), administer fluid or blood products for large volume resuscitation, and measure central venous pressure. The catheters used are commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensivist
An intensivist, also known as a critical care doctor, is a medical practitioner who specializes in the care of critically ill patients, most often in the intensive care unit (ICU). Intensivists can be internists or internal medicine sub-specialists (most often pulmonologists), anaesthesiologists, emergency medicine physicians, paediatricians (including neonatologists), or surgeons who have completed a fellowship in critical care medicine. The intensivist must be competent not only in a broad spectrum of conditions among critically ill patients but also with the technical procedures and equipment used in the intensive care setting such as airway management, rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia, maintenance and weaning of sedation, central venous and arterial catheterisation, point of care ultrasound, renal replacement therapy and management of mechanical ventilators. Training in different countries Australia and New Zealand Training in the medical speciality of intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |