|
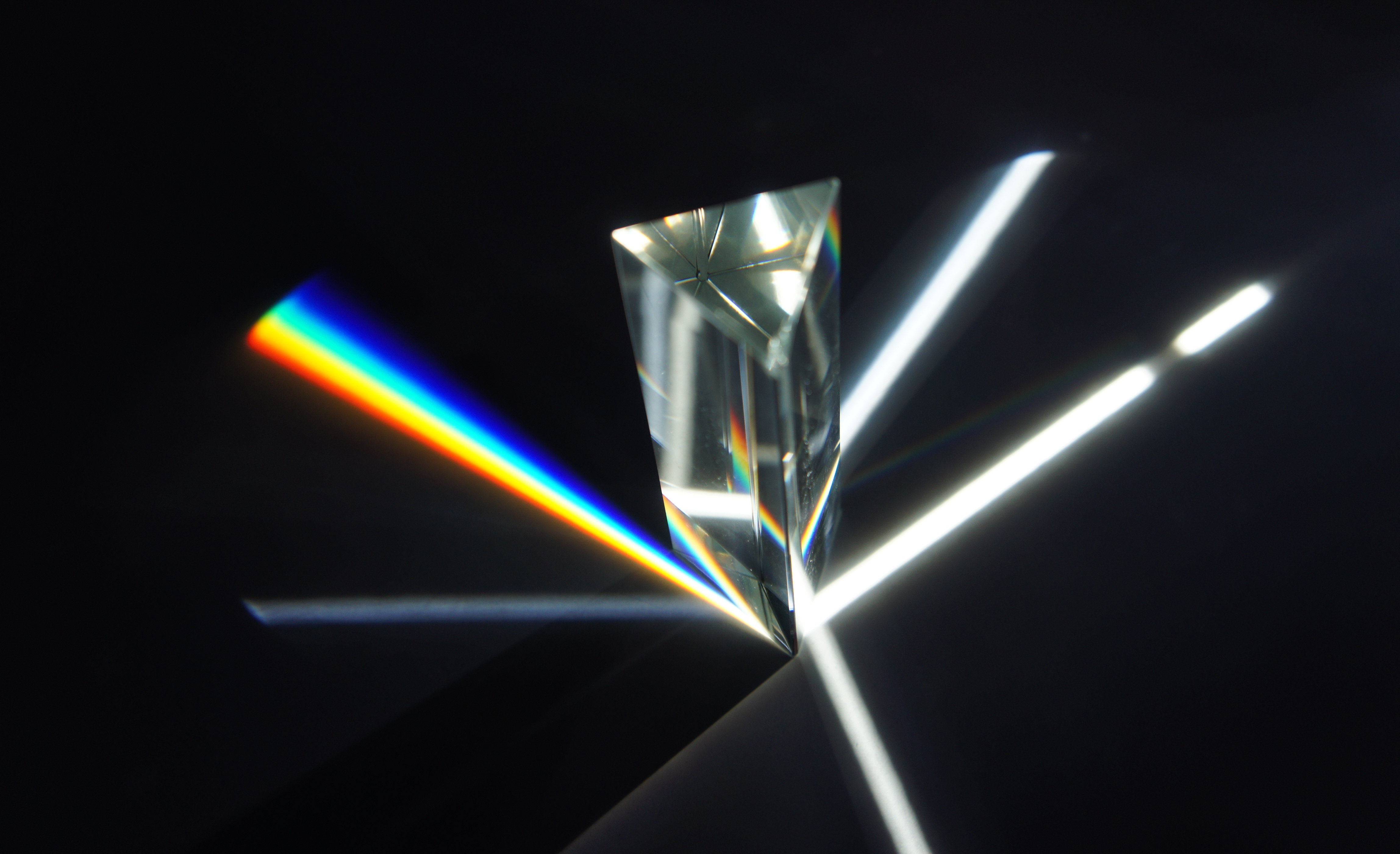
Prismatic
An optical prism is a transparent optics, optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refraction, refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are ''not'' prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are prism (geometry), geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic glass, acrylic and fluorite#Optics, fluorite. A dispersive prism can be used to break white#White light, white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflection (physics), reflect light, or to split light into components with differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prism (geometry)
In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an polygon Base (geometry), base, a second base which is a Translation (geometry), translated copy (rigidly moved without rotation) of the first, and other Face (geometry), faces, necessarily all parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All Cross section (geometry), cross-sections parallel to the bases are translations of the bases. Prisms are named after their bases, e.g. a prism with a pentagonal base is called a pentagonal prism. Prisms are a subclass of prismatoids. Like many basic geometric terms, the word ''prism'' () was first used in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements''. Euclid defined the term in Book XI as "a solid figure contained by two opposite, equal and parallel planes, while the rest are parallelograms". However, this definition has been criticized for not being specific enough in regard to the nature of the bases (a cause of some confusion amongst generations of later geometry writers). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Prism
In geometry, a triangular prism or trigonal prism is a Prism (geometry), prism with 2 triangular bases. If the edges pair with each triangle's vertex and if they are perpendicular to the base, it is a ''right triangular prism''. A right triangular prism may be both Semiregular polyhedron, semiregular and Uniform polyhedron, uniform. The triangular prism can be used in constructing another polyhedron. Examples are some of the Johnson solids, the truncated right triangular prism, and Schönhardt polyhedron. Properties A triangular prism has 6 vertices, 9 edges, and 5 faces. Every prism has 2 congruent faces known as its ''bases'', and the bases of a triangular prism are triangles. The triangle has 3 vertices, each of which pairs with another triangle's vertex, making up another 3 edges. These edges form 3 parallelograms as other faces. If the prism's edges are perpendicular to the base, the lateral faces are rectangles, and the prism is called a ''right triangular prism''. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Internal Reflection
In physics, total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (boundary) from one medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely reflected back into the first ("internal") medium. It occurs when the second medium has a higher wave speed (i.e., lower refractive index) than the first, and the waves are incident at a sufficiently oblique angle on the interface. For example, the water-to-air surface in a typical fish tank, when viewed obliquely from below, reflects the underwater scene like a mirror with no loss of brightness (Fig.1). TIR occurs not only with electromagnetic waves such as light and microwaves, but also with other types of waves, including sound and water waves. If the waves are capable of forming a narrow beam (Fig.2), the reflection tends to be described in terms of " rays" rather than waves; in a medium whose properties are independent of direction, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal-mounted military models. Unlike a (monocular) telescope, binoculars give users a stereopsis, three-dimensional image: each eyepiece presents a slightly different image to each of the viewer's eyes and the parallax allows the visual cortex to generate an depth perception, impression of depth. Optical design evolution Galilean Almost from the invention of the telescope in the 17th century the advantages of mounting two of them side by side for binocular vision seems to have been explored. Most early binoculars used Galilean telescope, Galilean optics; that is, they used a convex lens, convex objective (optics), objective and a concave lens, concave eyepi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littrow Prism
In optics, a Littrow prism, or Littrow mirror, originally part of a Littrow spectrograph (after Otto von Littrow), is a retro-reflecting, dispersing prism arranged in such a way that an incident light beam which enters at the Brewster angle undergoes minimal deviation and hence maximum dispersion. Description Littrow Prism (optics), (optical) prisms typically have the shape of a Prism (geometry), (geometric) prism with a 30°/60°/90° Right triangle, right triangular Base (geometry), base, equivalent to half an equilateral triangle. Typically, they are coated with a reflective film coating on the surface opposite the 60° angle. This design was devised by Otto von Littrow (1843–1864). Applications Typically Littrow prisms are used in lasers at the end of an optical cavity to offer fine adjustment of the laser's output frequency by altering the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. Before the ready availability of diffraction gratings Littrow prisms were used wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amici Prism
An Amici prism, named for the astronomer Giovanni Battista Amici, is a type of compound dispersion (optics), dispersive prism (optics), prism used in spectrometers. The Amici prism consists of two triangular prisms in contact, with the first typically being made from a medium-dispersion Crown glass (optics), crown glass, and the second from a higher-dispersion flint glass. Light entering the first prism is refraction, refracted at the first air–glass interface, refracted again at the interface between the two prisms, and then exits the second prism at near-Normal (geometry), normal incidence. The prism angles and materials are chosen such that one wavelength (colour) of light, the ''centre wavelength'', exits the prism parallel to (but offset from) the entrance beam. The prism assembly is thus a ''direct-vision prism'' and is commonly used as such in hand-held spectroscopes. Other wavelengths are deflected at angles depending on the glass Dispersion (optics), dispersion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Prism
A compound prism is a set of multiple triangular prism, triangular prism elements placed in contact, and often cemented together to form a solid assembly. The use of multiple elements gives several advantages to an optical designer:Nathan Hagen and Tomasz S. Tkaczyk,Compound prism design principles, I" ''Appl. Opt.'' 50: 4998-5011 (2011). * One can achieve Dispersion (optics), spectral dispersion without causing the deviation of the beam at the design wavelength. Thus, light at the design wavelength which enters at an angle \theta_0 with respect to the optical axis, exits the prism at the same angle with respect to the same axis. This kind of effect is often called "direct vision dispersion" or "nondeviating dispersion". * One can achieve deviation of the incident beam while also greatly reducing the dispersion introduced into the beam: an achromatic Prism (optics)#Deflecting prisms, deflecting prism. This effect is used in beam steering.Zhilin Hu and Andrew M. Rollins, "Fourier dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grism
A grism (also called a grating prism) is a combination of a prism and grating arranged so that light at a chosen central wavelength passes straight through. The advantage of this arrangement is that one and the same camera can be used both for imaging (without the grism) and spectroscopy (with the grism) without having to be moved. Grisms are inserted into a camera beam that is already collimated. They then create a dispersed spectrum centered on the object's location in the camera's field of view. The resolution of a grism is proportional to the tangent of the wedge angle of the prism in much the same way as the resolutions of gratings are proportional to the angle between the input and the normal to the grating. The dispersed wavefront sensing system (as part the NIRCam instrument) on the James Webb Space Telescope uses grisms. The system allows coarse optical path length matching between the different mirror segments. See also * Diffraction grating * Echelle grating An e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersive Prism
In optics, a dispersive prism is an optical prism that is used to disperse light, that is, to separate light into its spectral components (the colors of the rainbow). Different wavelengths (colors) of light will be deflected by the prism at different angles. This is a result of the prism material's index of refraction varying with wavelength (dispersion). Generally, longer wavelengths (red) undergo a smaller deviation than shorter wavelengths (blue). The dispersion of white light into colors by a prism led Sir Isaac Newton to conclude that white light consisted of a mixture of different colors. Triangular prisms are the most common type of dispersive prism. Other types of dispersive prism exist that have more than two optical interfaces; some of them combine refraction with total internal reflection. Principle Light changes speed as it moves from one medium to another (for example, from air into the glass of the prism). This speed change causes the light to be refracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellin–Broca Prism
A Pellin–Broca prism is a type of constant-deviation dispersive prism similar to an Abbe prism. The prism is named for its inventors, the French instrument maker Ph. Pellin and professor of physiological optics André Broca. The prism consists of a four-sided block of glass shaped as a right prism with 90°, 75°, 135°, and 60° angles on the end faces. Light enters the prism through face AB, undergoes total internal reflection from face BC, and exits through face AD. The refraction of the light as it enters and exits the prism is such that one particular wavelength of the light is deviated by exactly 90°. As the prism is rotated around an axis O, the line of intersection of bisector of ∠BAD and the reflecting face BC, the selected wavelength which is deviated by 90° is changed without changing the geometry or relative positions of the input and output beams. The prism is commonly used to separate a single required wavelength from a light beam containing multiple wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |