|
Preceramic Polymers
The term preceramic polymer refers to one of various polymeric compounds, which through pyrolysis under appropriate conditions (generally in the absence of oxygen) are converted to ceramic compounds, having high thermal and chemical stability. Ceramics resulting from the pyrolysis of preceramic polymers are known as polymer derived ceramics, or PDCs. Polymer derived ceramics are most often silicon based and include silicon carbide, silicon oxycarbide, silicon nitride and silicon oxynitride. Such PDCs are most commonly amorphous, lacking long-range crystalline order. Kizhakke Veettil et alA versatile stereolithographic approach assisted by thiol-ene click chemistry, ''Additive Manufacturing 2019, volume 27 pages 80-90'' The field of preceramic polymers and polymer derived ceramics in general emerged from the requirements in aerospace industries for heat shield materials such as fiber reinforced ceramic / ceramic composite materials. The use of preceramic polymers allows for diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. Polymers are studied in the fields of polymer science (which includes polymer chemistry and polymer physics), biophys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Oxycarbide
Oxycarbide glass, also referred to as silicon oxycarbide, is a type of glass that contains oxygen and carbon in addition to silicon dioxide. It is created by substituting some oxygen atoms with carbon atoms. This glass may contain particles of amorphous carbon, and silicon carbide. SiOC materials of varying stoichiometery are attractive owing to their generally high density, hardness and high service temperatures. Through diverse forming techniques high performance parts in complex shapes can be achieved. Unlike pure SiC, the versatile stoichiometry of SiOC offers further avenues to tune physical properties through appropriate selection of processing parameters. Amorphous silicon oxycarbide can form as the pyrolysis product of preceramic polymers including polycarbosilane. Such materials are of increasing interest towards the additive manufacturing of ceramic parts using stereolithography Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
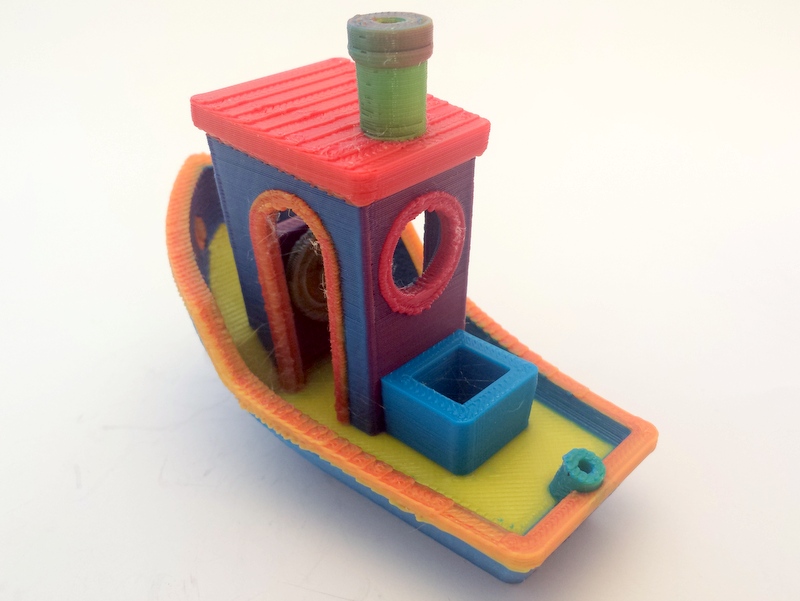
Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiphoton Lithography
Multiphoton lithography (also known as direct laser lithography or direct laser writing) is similar to standard photolithography techniques; structuring is accomplished by illuminating negative-tone or positive-tone photoresists via light of a well-defined wavelength. The main difference is the avoidance of photomasks. Instead, two-photon absorption is utilized to induce a change in the solubility of the resist for appropriate developers. Hence, multiphoton lithography is a technique for creating small features in a photosensitive material, without the use of excimer lasers or photomasks. This method relies on a multi-photon absorption process in a material that is transparent at the wavelength of the laser used for creating the pattern. By scanning and properly modulating the laser, a chemical change (usually polymerization) occurs at the focal spot of the laser and can be controlled to create an arbitrary three-dimensional pattern. This method has been used for rapid prototyping o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
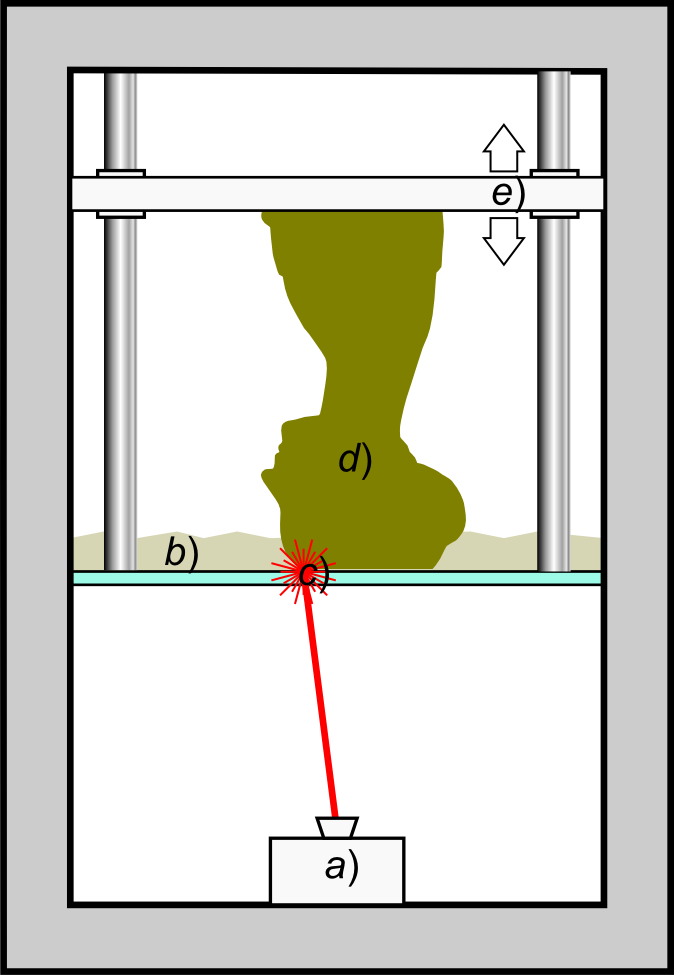
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers. U.S. Patentbr>4,575,330(“Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography”) Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fused Filament Fabrication
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in use. Fused filament printing has in the 2010s-2020s been the most popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Natural occurrence Naturally occurring moissanite is found in only minute quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Greek language, Greek-derived morpheme, elements ''pyro-'' (from Ancient Greek : - "fire, heat, fever") and ''lysis'' ( : - "separation, loosening"). Applications Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic compound, organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in the charring of wood or pyrolysis of biomass. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves Char (chemistry), char, a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly carbon as the residue, is called carbonization. Pyrolysis is considered one of the steps in the processes of gasification or combustion. Laypeople often confuse pyrolysis gas with syngas. Pyrolysis gas has a high percentage of heavy tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, grease, silicone rubber, rubber, silicone resin, resin, and Caulking, caulk. Silicone is often confused with one of its constituent elements, silicon, but they are distinct substances. Silicon is a chemical element, a hard dark-grey semiconductor, semiconducting metalloid, which in its crystalline form is used to make integrated circuits ("electronic chips") and solar cells. Silicones are compounds that contain silicon, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and perhaps other kinds of atoms as well, and have many very different physical and chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Films
A thin film is a layer of materials ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. A familiar example is the household mirror, which typically has a thin metal coating on the back of a sheet of glass to form a reflective interface. The process of silvering was once commonly used to produce mirrors, while more recently the metal layer is deposited using techniques such as sputtering. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, integrated passive devices, light-emitting diodes, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage ( thin-film ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |