|
Posterior Clinoid Process
The posterior clinoid processes are the tubercles of the sphenoid bone situated at the superior angles of the dorsum sellae (one on each angle) which represents the posterior boundary of the sella turcica. They vary considerably in size and form. The posterior clinoid processes deepen the sella turcica, and give attachment to (the attached border of) the tentorium cerebelli, and the dura forming the floor of the hypophyseal fossa (sella turcica). The petroclinoid ligament The petroclinoid ligament is a fold of dura matter. It extends between the posterior clinoid process and anterior clinoid process and the petrosal part of the temporal bone The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ... of the skull. There are two separate bands of the ligament; named the anterior and pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly, bat or wasp with its wings extended. The name presumably originates from this shape, since () means in Ancient Greek. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
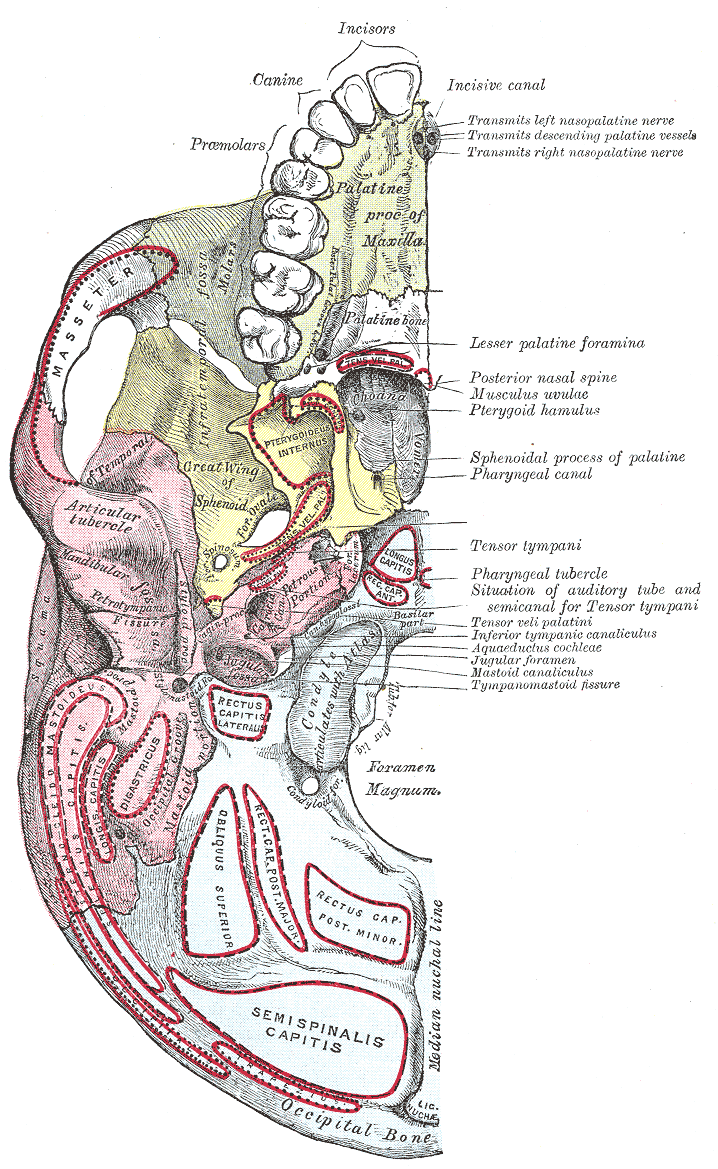
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses * Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus * Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen * Foramen lacerum * Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen * Internal auditory meatus * Mastoid foramen * Sphenoidal emissary foramen * Foramen spinosum Sutures * Frontoethmoidal suture * Sphenofrontal suture * Sphenopetrosal suture * Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture * Sphenosquamosal suture Other * Sphenoidal lingula * Subarcuate fossa * Dorsum sellae * Jugular process * Petro-occipital fissure * Condylar canal * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly, bat or wasp with its wings extended. The name presumably originates from this shape, since () means in Ancient Greek. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum Sellae
The dorsum sellae is part of the sphenoid bone in the skull. Together with the basilar part of the occipital bone it forms the clivus. In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the middle clinoid processes, while the posterior boundary is formed by a square-shaped plate of bone, the dorsum sellae, ending at its superior angles in two tubercles, the posterior clinoid processes The posterior clinoid processes are the tubercles of the sphenoid bone situated at the superior angles of the dorsum sellae (one on each angle) which represents the posterior boundary of the sella turcica. They vary considerably in size and form. ..., the size and form of which vary considerably in different individuals. Additional images File:Gray569.png, Tentorium cerebelli from above. File:Slide2iiii.JPG, Dorsum sellae References External links * * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sella Turcica
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely believed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentorium Cerebelli
The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is one of four dural folds that separate the cranial cavity into four (incomplete) compartments. The cerebellar tentorium separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum forming a supratentorial and an infratentorial region; the cerebrum is supratentorial and the cerebellum infratentorial. The free border of the tentorium gives passage to the midbrain (the upper-most part of the brainstem). Structure Free border The free border of the tentorium is U-shaped; it forms an aperture - the tentorial notch (tentorial incisure) - which gives passage to the midbrain. The free border of each side extends anteriorly beyond the medial end of the superior petrosal sinus (i.e. the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone) to overlap the attached margin, thenceforth forming a ridge of dura matter upon the roof of the cavernous sinus, terminating anteriorly by attaching at the anterior clinoid process. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophyseal Fossa
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely believed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Clinoid Process
The anterior clinoid process is a posterior projection of the sphenoid bone at the junction of the medial end of either lesser wing of sphenoid bone with the body of sphenoid bone. The bilateral processes flank the sella turcica anteriorly. The ACP is an important structure for cranial and endovascular surgical operations for several structures, including the pituitary gland and the internal carotid artery. Anatomy The anterior clinoid process is a pyramid-shaped bony projection of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and forms part of the lateral wall of the optic canal. Between each ACP lies the sella turcica, which holds the pituitary gland. Additionally, the ACP is part of the anterior roof of the cavernous sinus. The posterior and inferior portions of the ACP border the internal carotid artery. Attachments The free border of the tentorium cerebelli extends anteriorly on either side beyond the attached border of the same side (which ends anteriorly at the posterior clin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bones fuse. Each temple is covered by a temporal muscle. The temporal bones house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts—the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoparesis
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease. Internal ophthalmoplegia means involvement limited to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. External ophthalmoplegia refers to involvement of only the extraocular muscles. Complete ophthalmoplegia indicates involvement of both. Presentation Causes Ophthalmoparesis can result from disorders of various parts of the eye and nervous system: * Infection around the eye. Ophthalmoplegia is an important finding in orbital cellulitis. * The orbit of the eye, including mechanical restrictions of eye movement, as in Graves' disease. * The muscle, as in progressive external ophthalmoplegia or Kearns–Sayre syndrome. * The neuromuscular junction, as in myasthenia gravis. * The relevant cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor, trochlear, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Clinoid Process
The posterior clinoid processes are the tubercles of the sphenoid bone situated at the superior angles of the dorsum sellae (one on each angle) which represents the posterior boundary of the sella turcica. They vary considerably in size and form. The posterior clinoid processes deepen the sella turcica, and give attachment to (the attached border of) the tentorium cerebelli, and the dura forming the floor of the hypophyseal fossa (sella turcica). The petroclinoid ligament The petroclinoid ligament is a fold of dura matter. It extends between the posterior clinoid process and anterior clinoid process and the petrosal part of the temporal bone The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ... of the skull. There are two separate bands of the ligament; named the anterior and pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |