|
Positive Reinforcer
In Behaviorism, behavioral psychology, reinforcement refers to consequences that increase the likelihood of an organism's future behavior, typically in the presence of a particular ''Antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimulus''. For example, a rat can be trained to push a lever to receive food whenever a light is turned on; in this example, the light is the antecedent stimulus, the lever pushing is the ''operant behavior'', and the food is the ''reinforcer''. Likewise, a student that receives attention and praise when answering a teacher's question will be more likely to answer future questions in class; the teacher's question is the antecedent, the student's response is the behavior, and the praise and attention are the reinforcements. Punishment (psychology), Punishment is the inverse to reinforcement, referring to any behavior that decreases the likelihood that a response will occur. In operant conditioning terms, punishment does not need to involve any type of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skinner Box Scheme 01
Skinner may refer to: People and fictional characters *Skinner (surname), a list of people and fictional characters with that surname *Skinner (profession), a person who makes a living by working with animal skins or driving mules *Skinner, a ring name of professional wrestler Steve Keirn in early 1990s *B. F. Skinner, American Psychologist American geography *Skinner, Missouri, an unincorporated community *Skinner Butte, a prominent hill beside the Willamette River in Oregon *Skinner Reservoir, a reservoir in Riverside County, California Other uses *Skinner (film), ''Skinner'' (film), a 1993 horror film *''The Skinner'', a 2002 science fiction novel by Neal Asher *Skinner, Inc., also known as Skinner, an auction house for fine art and antiques *''The Colour Identification Guide to Moths of the British Isles'', referred to as Skinner, by Bernard Skinner See also *Skinners (other) * * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Dependence
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has developed within the individual from psychoactive substance consumption that results in the experience of withdrawal and that necessitates the re-consumption of the drug. A ''drug addiction'', a distinct concept from substance dependence, is defined as compulsive, out-of-control drug use, despite negative consequences. An ''addictive drug'' is a drug which is both rewarding and reinforcing. ΔFosB, a gene transcription factor, is now known to be a critical component and common factor in the development of virtually all forms of behavioral and drug addictions, but not dependence. The International Classification of Diseases classifies substance dependence as a mental and behavioural disorder. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
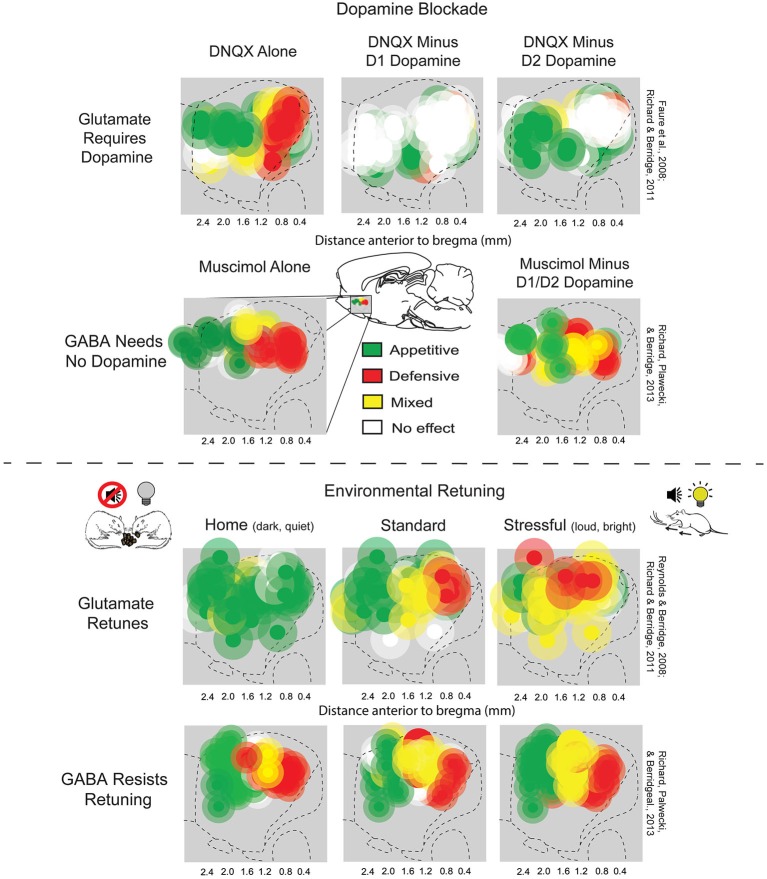
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangovers
A hangover is the experience of various unpleasant physiological and psychological effects usually following the consumption of alcohol, such as wine, beer, and liquor. Hangovers can last for several hours or for more than 24 hours. Typical symptoms of a hangover may include headache, drowsiness, weakness, concentration problems, dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue, muscle ache, gastrointestinal distress (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), absence of hunger, light sensitivity, depression, sweating, hyper-excitability, high blood pressure, irritability, and anxiety. While the causes of a hangover are still poorly understood, several factors are known to be involved including acetaldehyde accumulation, changes in the immune system and glucose metabolism, dehydration, metabolic acidosis, disturbed prostaglandin synthesis, increased cardiac output, vasodilation, sleep deprivation, and malnutrition. Beverage-specific effects of additives or by-products such as congeners in alcoholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Surfing
Channel surfing (also known as channel hopping or zapping) is the practice of quickly scanning through different television channels or radio frequencies to find something interesting to watch or listen to. Modern viewers, who may have cable or satellite services beaming down dozens if not hundreds or thousands of channels, are frequently channel surfing. It is common for people to scan channels when commercial broadcasters switch from a show over to running commercials. The term is most commonly associated with television, where the practice became common with the wide availability of the remote control. The first published use of the term is November 1986, in an article by ''The Wall Street Journal''. Viewers' propensity to channel surf was apparently a factor leading toward the current ATSC standard for terrestrial television, digital television in North America. An ATSC signal can be locked onto and start being decoded within about one second, while it can take several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aversives
In psychology, aversives are unpleasant stimuli that induce changes in behavior via negative reinforcement or positive punishment. By applying an aversive immediately before or after a behavior, the likelihood of the target behavior occurring in the future may be reduced. Aversives can vary from being slightly unpleasant or irritating to physically, psychologically and/or emotionally damaging. Types of stimuli There are two types of aversive stimuli: Unconditioned Unconditioned aversive stimuli naturally result in pain or discomfort and are often associated with biologically harmful or damaging substances or events. Examples include extreme heat or cold, bitter flavors, electric shocks, loud noises and pain. Aversives can be applied naturally (such as touching a hot stove) or in a contrived manner (such as during torture or behavior modification). Conditioned A conditioned aversive stimulus is an initially neutral stimulus that becomes aversive after repeated pairing with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behaviorist
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understand the behavior of humans and other animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex elicited by the pairing of certain antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individual's history, including especially reinforcement and punishment contingencies, together with the individual's current motivational state and controlling stimuli. Although behaviorists generally accept the important role of heredity in determining behavior, deriving from Skinner's two levels of selection: phylogeny and ontogeny. they focus primarily on environmental events. The cognitive revolution of the late 20th century largely replaced behaviorism as an explanatory theory with cognitive psychology, which unlike behaviorism views internal mental states as explanations for observable behavior. Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s as a reaction to depth psychology and other traditional forms of psychology, which often had difficul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Probability Instruction
The high probability instruction (HPI) treatment is a behaviorist treatment based on the idea of positive reinforcement Positive is a property of positivity and may refer to: Mathematics and science * Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation * Positive number, a number that is greater than 0 * Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a posit .... It consists of the idea of reinforcing an instruction with a low probability of compliance by using the reinforcement of an instruction with a high probability. Sources * Luce Doze (2005), under the direction of Ph.D Esteve Freixa i Bacquet (University of Picardie, France) and Mrs. Rivière (University of Lille-III, France). Treatment by HPI of an autistic child - (An example of complementarity between fundamental research and clinical practice from an autistic child case). Results shown at th2005 seminarof thAssociation Picardie de Pratiques Cognitives et Comportementales(Picard Association of Cognitive and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punishment (psychology)
Punishment is any change in a human or animal's surroundings which, occurring after a given behavior or response, reduces the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. Reinforcement, referring to any behavior that increases the likelihood that a response will occurs, plays a large role in punishment. Motivating operations (MO) can be categorized in abolishing operations, decrease the effectiveness of the stimuli and establishing, increase the effectiveness of the stimuli. For example, a painful stimulus which would act as a punisher for most people may actually reinforce some behaviors of masochistic individuals. There are two types of punishment: positive and negative. Positive punishment involves the introduction of a stimulus to decrease behavior while negative punishment involves the removal of a stimulus to decrease behavior. While similar to reinforcement, punishment's goal is to decrease behaviors while reinforcement's goal is to increase behaviors. Differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning (also respondent conditioning and Pavlovian conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent Stimulus (physiology), stimulus (e.g. food, a puff of air on the eye, a potential rival) is paired with a neutral stimulus (e.g. the sound of a Triangle (musical instrument), musical triangle). The term ''classical conditioning'' refers to the process of an automatic, conditioned response that is paired with a specific stimulus. It is essentially equivalent to a signal. The Russian physiology, physiologist Ivan Pavlov studied classical conditioning with detailed experiments with dogs, and published the experimental results in 1897. In the study of digestion, Pavlov observed that the experimental dogs salivated when fed red meat. Pavlovian conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified, either by reinforcement or by Punishment (psychology), punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |