|
Porifera
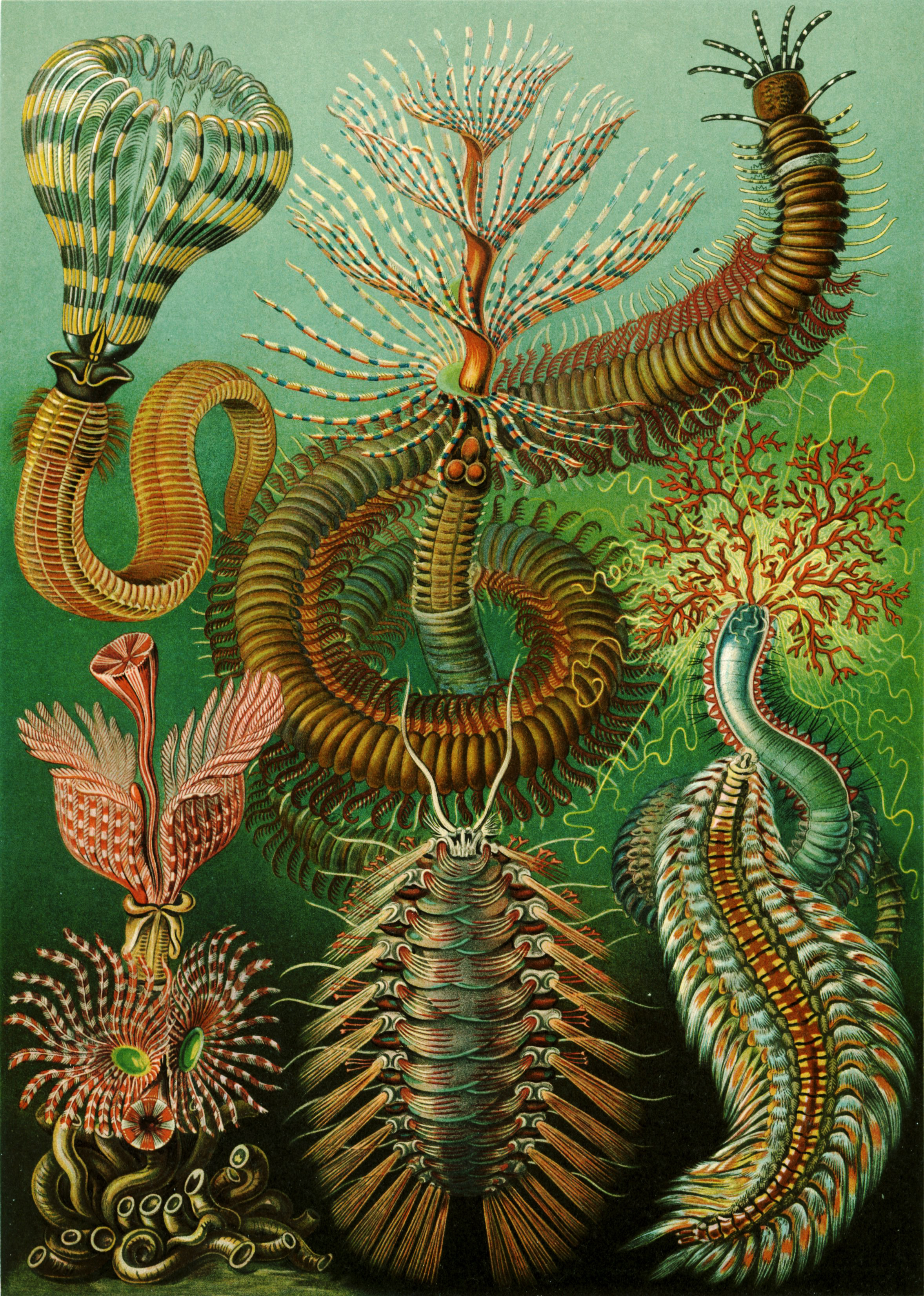
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important sponge reef , reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cell (biology) , cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can cellular differentiation , transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous system , nervous, digestive system , digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demospongiae
Demosponges or common sponges are sponges of the class Demospongiae (from + ), the most diverse group in the phylum Porifera which include greater than 90% of all extant sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (according to the World Porifera Database). Being siliceous sponges, they are predominantly leuconoid in structure with an endoskeleton made of a meshwork of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges. Some species, in particular from the Antarctic, obtain the silica for spicule-building from the ingestion of diatoms. The many diverse orders in this class include all of the large sponges. About 311 million years ago, in the Late Carboniferous, the order Spongillida split from the marine sponges, and is the only sponges to live in freshwater environments. Some species are brightly colored, with great va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
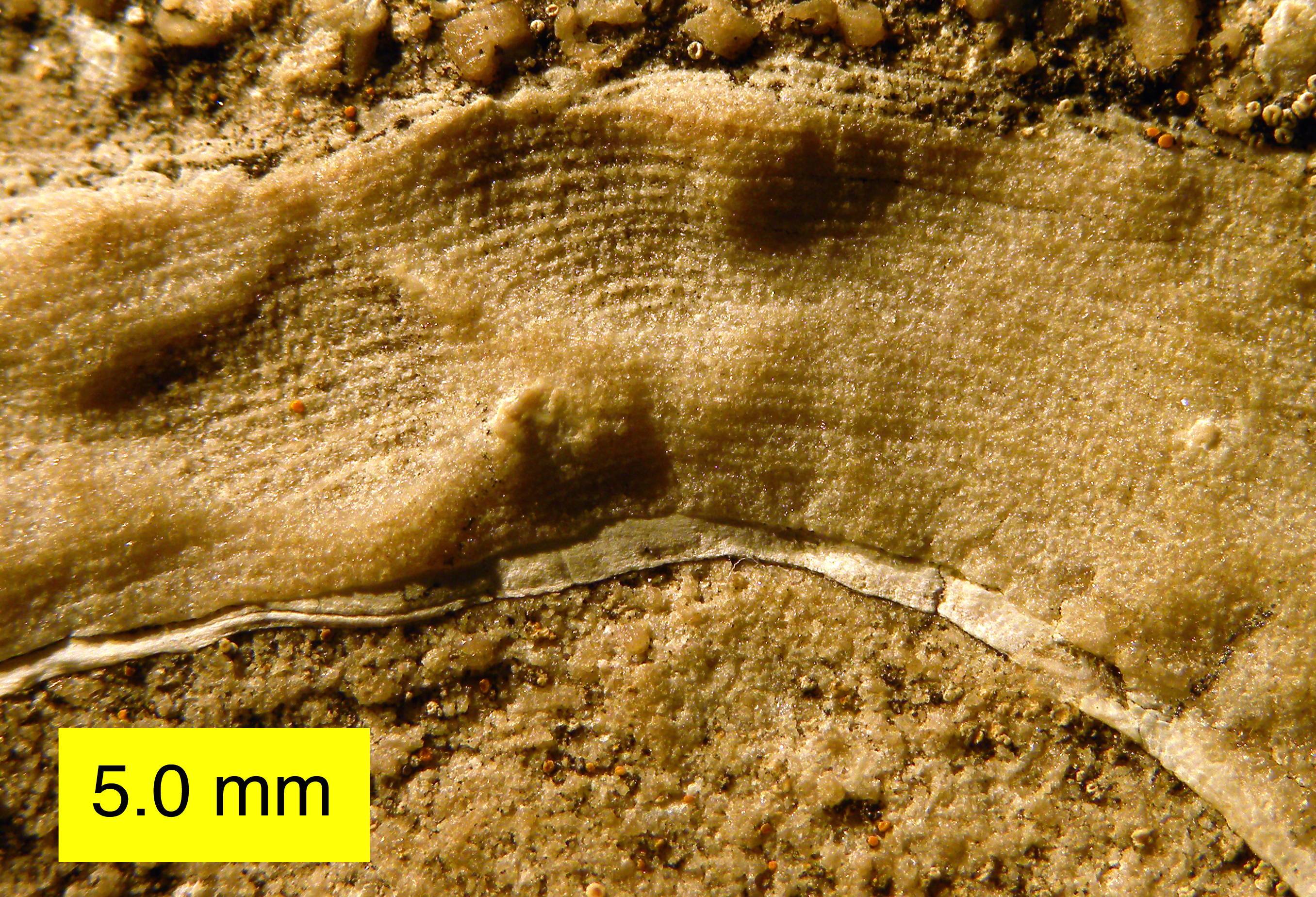
Stromatoporoidea
Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian.Stock, C.W. 2001, Stromatoporoidea, 1926–2000: ''Journal of Paleontology'', v. 75, p. 1079–1089. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking Sponge spicule, spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms. Externally, some species have raised bumps (mamelons) and star-shaped crevices (astrorhizae), which together help vent exhalant water away from the living surface. Internally, stromatoporoids have a mesh-like skeletal system combining extensive horizontal layers (laminae), vertical rods (pillars), and boxy spaces (galleries), along with other features. The most common growth forms range from laminar (flattened) to domical (dome-shaped). Spheroidal, finger-like, or tree-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parazoa
Parazoa (Parazoa, gr. Παρα-, para, "next to", and ζωα, zoa, "animals") is an obsolete subkingdom that is located at the base of the phylogenetic tree of the animal kingdom in opposition to the subkingdom Eumetazoa; they group together the most primitive forms, characterized by not having proper tissues or where, in any case, these tissues are only partially differentiated. It generally includes a single phylum, Porifera, which lack muscles, nerves and internal organs, which in many cases resembles a cell colony rather than a multicellular organism itself. All other animals are eumetazoans and agnotozoans (Agnotozoans are possibly paraphyletic or even nonexistent in studies), which do have differentiated tissues. On occasion, Parazoa reunites Porifera with Archaeocyatha, a group of extinct sponges sometimes considered a separate phylum. In other cases, Placozoa is included, depending on the authors. Porifera and Archaeocyatha Porifera and Archaeocyatha show similari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Invertebrates
Marine invertebrates are invertebrate animals that live in marine habitats, and make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans. It is a polyphyletic blanket term that contains all marine animals except the marine vertebrates, including the non-vertebrate members of the phylum Chordata such as lancelets, sea squirts and salps. As the name suggests, marine invertebrates lack any mineralized tissue, mineralized axial skeleton, axial endoskeleton, i.e. the vertebral column, and some have evolved a rigid seashell, shell, test (biology), test or exoskeleton for protection and/or aquatic locomotion, locomotion, while others rely on hydroskeleton, internal fluid pressure to support their bodies. Marine invertebrates have a large variety of body plans, and have been categorized into over 30 phyla. Evolution The earliest animals were marine invertebrates, that is, vertebrates came later. Animals are multicellular eukaryotes, and are distinguished from plants, algae, and fungi by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biology), fission or budding, placozoans are described as "the simplest animals on Earth." Structural and molecular analyses have supported them as among the most basal animals, thus, constituting a primitive metazoan phylum. The first known placozoan, ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', was discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921).F. E. Schulze "''Trichoplax adhaerens'' n. g., n. s.", ''Zoologischer Anzeiger'' (Elsevier, Amsterdam and Jena) 6 (1883), p. 92. Describing the uniqueness, another German, Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), erected a new phylum, Placozoa, for it in 1971. Remaining a monotypic phylum for over a century, new species began to be added since 2018. So far, three other extant species have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeocyatha
Archaeocyatha (), 'ancient cups') is a taxon of extinct, Sessility (zoology), sessile, reef-building Marine (ocean), marine Sponge, sponges that lived in warm tropical and subtropical waters during the Cambrian Period. It is believed that the centre of the Archaeocyatha origin is now located in East Siberia, where they are first known from the beginning of the Tommotian Age of the Cambrian, 525 million years ago (mya (unit), mya). In other regions of the world, they appeared much later, during the Atdabanian, and quickly diversified into over a hundred Family (biology), families. They became the planet's first reef-building animals and are an index fossil for the Lower Cambrian worldwide. Preservation The remains of Archaeocyatha are mostly preserved as carbonate structures in a limestone Matrix (geology), matrix. This means that the fossils cannot be chemically or mechanically isolated, save for some specimens that have already eroded out of their matrices, and their morph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexactinellida
Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe that glass sponges are the longest-lived animals on earth; these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years. Biology Glass sponges are relatively uncommon and are mostly found at depths from below sea level. Although the species '' Oopsacas minuta'' has been found in shallow water, others have been found much deeper. They are found in all oceans of the world, although they are particularly common in Antarctic and Northern Pacific waters. They are more-or-less cup-shaped animals, ranging from in height, with sturdy skeletons made of glass-like silica spicules, fused to form a lattice. In some glass sponges such as members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteractinida
Heteractinida is an extinct grade of Paleozoic (Cambrian–Permian) sponges, sometimes used as a class or order. They are most commonly considered paraphyletic with respect to Calcarea (calcareous sponges), though some studies instead argue that they are paraphyletic relative to Hexactinellida (glass sponges). Heteractinids can be distinguished by their six-pronged (snowflake-shaped) spicules, whose symmetry historically suggested a relationship with the triradial calcarean sponges. The sponge-like Cambrian Hetairacyathidae may be related to heteractinids, though most instead consider hetairacyathids to be closer to archaeocyaths and radiocyaths.''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' Part E, Revised. Porifera, Volumes 4 & 5: Hypercalcified Porifera, Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea & Archaeocyatha, liii + 1223 p., 665 figs., 2015, availablhere . An example of a species in the Heteractinida class is the Gondekia Lancifer; the Gondekia lancifer specimen is only the second articul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoscleromorpha
Homosclerophorida is an order of marine sponges. It is the only order in the monotypic class Homoscleromorpha. The order is composed of two families: Plakinidae and Oscarellidae. Taxonomy Homoscleromorpha is phylogenetically well separated from Demospongiae. Therefore, it has been recognized as the fourth class of sponges. It has been suggested that Homoscleromorpha are more closely related to eumetazoans than to the other sponge groups, rendering sponges paraphyletic.Sperling, Pisani and Peterson 2007, cited in: The Cambrian Explosion p. 80, Erwin and Valentine 2013 This view has not been supported by later work using larger datasets and new techniques for phylogenetic inference, which tend to support sponges as monophyletic, with Homoscleromorpha grouping together with Calcarea. On the basis of molecular and morphological evidence, the two families Plakinidae and Oscarellidae have been reinstated. There are 136 species in this group divided into 10 genera. The spiculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cribricyatha
Cribricyatha is an extinct class of sponge-like animals which lived in the early to mid-Cambrian Period ( Tommotian to Botomian). Description Cribricyatha were cup-shaped filter feeders similar to archaeocyathan sponges, with a skeleton composed of magnesium-rich calcite microgranules. The base is narrow, broadening upwards into a solid conical or semi-conical shell. In horizontal cross-section, the cup may be circular, elliptical, cardioid (heart-shaped), or quadrate (square-shaped).''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' Part E, Revised. Porifera, Volumes 4 & 5: Hypercalcified Porifera, Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea & Archaeocyatha, liii + 1223 p., 665 figs., 2015, availablhere . All cribricyaths can be characterized by a series of peripterates, ribbon-like crests ringing around the outer surface of the shell. In cribricyaths of the order Cribricyathida, the peripterates may be supplemented by baculi, low ridges running parallel to the main shaft of the shell. Internally, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetazoa
Eumetazoa (), also known as Epitheliozoa or Histozoa, is a proposed basal animal subkingdom as a sister group of Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen as a eumetazoan in the ParaHoxozoa. The competing hypothesis is the Myriazoa clade. The subkingdom Parazoa and Agnotozoa are the other taxa, and agnotozoa may be fake or even nonexistent at studies. Parazoa or Agnotozoa are a main sister group to eumetazoans, forming clade Blastozoa/Diploblastozoa. Alternatively, Parazoa was considered as a sister group to Agnotozoa(now considered polyphyletic). Several other extinct or obscure life forms, such as ''Iotuba'' and '' Thectardis'', appear to have emerged in the group. Characteristics of eumetazoans include true tissues organized into germ layers, the presence of neurons and muscles, and an embryo that goes through a gastrula stage. Some phylogenists once speculated the sponges and eumetazoans evolved sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |