|
Polysomnographies
Polysomnography (PSG) is a multi-parameter type of sleep study and a diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. The test result is called a polysomnogram, also abbreviated PSG. The name is derived from Greek and Latin roots: the Greek πολύς (''polus'' for "many, much", indicating many channels), the Latin ''somnus'' ("sleep"), and the Greek γράφειν (''graphein'', "to write"). Type I polysomnography is a sleep study performed overnight with the patient continuously monitored by a credentialed technologist. It records the physiological changes that occur during sleep, usually at night, though some labs can accommodate shift workers and people with circadian rhythm sleep disorders who sleep at other times. The PSG monitors many body functions, including brain activity (EEG), eye movements ( EOG), muscle activity or skeletal muscle activation ( EMG), and heart rhythm (ECG). After the identification of the sleep disorder sleep apnea in the 1970s, breathing functions, respiratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sleep Disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders, including those caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep without any obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, which is the most common sleep disorder. Other sleep disorders include sleep apnea, narcolepsy, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of the sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding (bruxism) and night terrors. Managing sleep disturbances that are seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
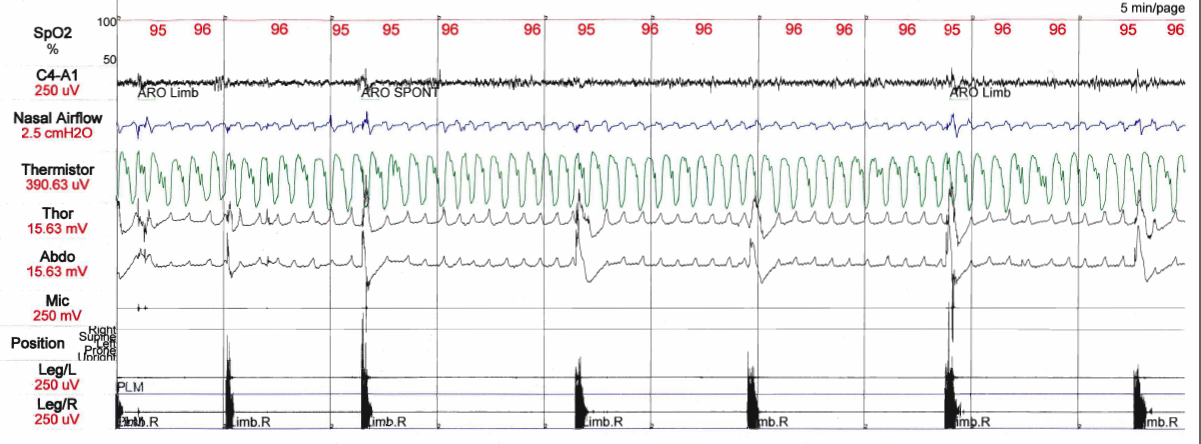
Periodic Limb Movement Disorder
Periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD) is a sleep disorder where the patient moves Limb (anatomy), limbs involuntarily and periodically during sleep, and has symptoms or problems related to the movement. PLMD should not be confused with restless legs syndrome (RLS), which is characterized by a voluntary response to an urge to move legs due to discomfort. PLMD on the other hand is involuntary, and the patient is often unaware of these movements altogether. Periodic limb movements (PLMs) occurring during daytime period can be found but are considered as a symptom of RLS; only PLMs during sleep can suggest a diagnosis of PLMD. Periodic limb movement disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of frequent limb movements while sleeping. It mostly happens in the lower parts of the body like the toes, ankles, knees and hips. It can also, in some cases, appear in the upper extremities of the body. These movements can lead the patient to wake up, and if so, sleep interruption can be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Idiopathic Hypersomnia
Idiopathic hypersomnia (IH) is a neurological disorder which is characterized primarily by excessive sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS). Idiopathic hypersomnia was first described by Bedrich Roth in 1976, and it can be divided into two forms: polysymptomatic and monosymptomatic. The condition typically becomes evident in early adulthood and most patients diagnosed with IH will have had the disorder for many years prior to their diagnosis. , an FDA-approved medication exists for IH called Xywav, which is an oral solution of calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium oxybates; in addition to several off-label treatments (primarily FDA-approved narcolepsy medications). Idiopathic hypersomnia may also be referred to as IH, IHS, or primary hypersomnia, and belongs to a group of sleep disorders known as central hypersomnias, central disorders of hypersomnolence, or hypersomnia of brain origin. ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', Fourth Edition (DSM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles, and specifically impacts REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. The symptoms of narcolepsy include excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep-related hallucinations, sleep paralysis, disturbed nocturnal sleep (DNS), and cataplexy. People with narcolepsy typically have poor quality of sleep. There are two recognized forms of narcolepsy, narcolepsy type 1 and type 2. Narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) can be clinically characterized by symptoms of EDS and cataplexy, and/or will have cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin levels of less than 110 pg/ml. Cataplexy are transient episodes of aberrant tone, most typically loss of tone, that can be associated with strong emotion. In pediatric-onset narcolepsy, active motor phenomena are not uncommon. Cataplexy may be mistaken for syncope, tics, or seizures. Narcolepsy type 2 (NT2) does not have features of cataplexy, and CSF orexin levels are normal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parasomnia
Parasomnias are a category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal movements, behaviors, emotions, perceptions, and dreams that occur while falling asleep, sleeping, between sleep stages, or during arousal from sleep. Parasomnias are dissociated sleep states which are partial arousals during the transitions between wakefulness, NREM sleep, and REM sleep, and their combinations. Classification The newest version of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD, 3rd. Ed.) uses State Dissociation as the paradigm for parasomnias. Unlike before, where wakefulness, non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep were considered exclusive states, research has shown that combinations of these states are possible and thus, may result in unusual unstable states that could eventually manifest as parasomnias or as altered levels of awareness. Although the previous definition is technically correct, it contains flaws. The consideration of the State Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, is an Organ (anatomy), organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by Peristalsis, peristaltic contractions, from the Human pharynx, pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a :wiktionary:fibromuscular, fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and human heart, heart, passes through the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''esophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, "I carry") + ἔφαγον ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arousal
Arousal is the physiology, physiological and psychology, psychological state of being awoken or of Five senses, sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the human brain, brain, which mediates wakefulness, the autonomic nervous system, and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of sensory alertness, desire, mobility, and reactivity. Arousal is mediated by several neural systems. Wakefulness is regulated by the ARAS, which is composed of projections from five major neurotransmitter systems that originate in the brainstem and form connections extending throughout the Cerebral cortex, cortex; activity within the ARAS is regulated by neurons that release the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin and histamine. Activation of these neurons produces an increase in cortical activity and subsequently alertness. Arousal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sleep Onset Latency
In sleep science, sleep onset latency (SOL) is the length of time that it takes to accomplish the transition from full wakefulness to sleep, normally to the lightest of the non-REM sleep stages. Sleep latency studies Pioneering Stanford University sleep researcher William C. Dement reports the early development of the concept, and of the first test for it, the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT), in his book ''The Promise of Sleep''. Dement and colleagues including Mary Carskadon had been seeking an objective measure of daytime sleepiness to help assess the effects of sleep disorders. In the course of evaluating experimental results, they realized that the amount of time it took to fall asleep in bed was closely linked to the subjects' own self-evaluated level of sleepiness. "This may not seem like an earthshaking epiphany, but conceiving and developing an objective measure of sleepiness was perhaps one of the most important advances in sleep science," Dement and coauthor Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
REM Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals (including humans) and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly. The core body and brain temperatures increase during REM sleep and skin temperature decreases to lowest values. The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seem to originate in the brain stem, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and duration for satisfactory sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in males and can cause psychological distress due to its impact on self-image and sexual relationships. The majority of ED cases are attributed to physical risk factors and predictive factors. These factors can be categorized as vascular, neurological, local penile, hormonal, and drug-induced. Notable predictors of ED include aging, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, high blood pressure, obesity, Dyslipidemia, abnormal lipid levels in the blood, hypogonadism, smoking, Depression (mood), depression, and Adverse drug reactions, medication use. Approximately 10% of cases are linked to psychosocial factors, encompassing conditions such as depressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nocturnal Penile Tumescence
Nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) is a spontaneous erection of the penis during sleep or when waking up. Along with nocturnal clitoral tumescence, it is also known as sleep-related erection. Colloquially, the term morning wood, or less commonly, morning glory is also used, although this is more commonly used to refer specifically to an erection ''beginning'' during sleep and persisting into the period just after waking. Men without physiological erectile dysfunction or severe depression experience nocturnal penile tumescence, usually three to five times during a period of sleep, typically during rapid eye movement sleep. Nocturnal penile tumescence is believed to contribute to penile health. Mechanism The cause of nocturnal penile tumescence is not known with certainty. In a wakeful state, in the presence of mechanical stimulation with or without an arousal, erection is initiated by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system with minimal input from the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |