|
Plexin
A plexin is a protein which acts as a receptor for semaphorin family signaling proteins. It is classically known for its expression on the surface of axon growth cones and involvement in signal transduction to steer axon growth away from the source of semaphorin. Plexin also has implications in development of other body systems by activating GTPase enzymes to induce a number of intracellular biochemical changes leading to a variety of downstream effects. Structure Extracellular All plexins have an extracellular SEMA domain at their N-terminus. This is a structural motif common among all semaphorins and plexins and is responsible for this binding of semaphorin dimers, which are the native conformation for these ligands in vivo. This is followed by alternating plexin, semaphorin, and integrin (PSI) domains and immunoglobulin-like, plexin, and transcription factors (IPT) domains. Each of these is named for the proteins in which their structure is conserved. Collectively, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLXNB1
Plexin B1 is a protein of the plexin family that in humans is encoded by the ''PLXNB1'' gene. Function Within neural tissues, the plexin A plexin is a protein which acts as a receptor for semaphorin family signaling proteins. It is classically known for its expression on the surface of axon growth cones and involvement in signal transduction to steer axon growth away from the sour ... family serves as transmembrane receptors for Semaphorins. Outside of neural tissues, Plexin B1 is implicated in the control of cell migration. Interactions PLXNB1 has been shown to interact with ARHGEF12, Rnd1 and ARHGEF11. References * Chapoval SP, Hritzo M, Qi X, Tamagnone L, Golding A and Keegan AD. "Semaphorin 4A Stabilizes Human Regulatory T Cell Phenotype via Plexin B1". ImmunoHorizons, February 1, 2019, 3 (2) 71-87; Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLXNA4A
Plexin-A4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PLXNA4'' gene. Function Plexin A4 binds to neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) and neuropilin 2 ( Nrp2) and transduces signals from Sema3A, Sema6A, and Sema6B. These Nrp-plexin and semaphorin complexes initiate cascades that regulate diverse processes such as axon pruning and repulsion, dendritic attraction and branching, regulation of cell migration, vascular remodeling, and growth cone collapse. Both upregulation and downregulation of Plexin A4 has been observed following neural injury suggesting a dynamic role for Sema3A and Plexin A4 in neural maintenance and regeneration. Additionally, Sema3A and therefore its receptor, Plexin A4, have been implicated as possible components of fast-fatigable muscle fiber denervation in ALS. Structure Plexin A4 has ~1890 amino acids that include a likely signal sequence, transmembrane domain, and 12 extracellular N-linked glycosylation sites. It also contains domains consistent with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semaphorin
Semaphorins are a class of secreted and membrane proteins that were originally identified as axonal growth cone guidance molecules. They primarily act as short-range inhibitory signals and signal through multimeric receptor (biochemistry), receptor complexes. Semaphorins are usually cues to deflect axons from inappropriate regions, especially important in the nervous system, neural system development. The major class of proteins that act as their receptors are called plexins, with Neuropilin, neuropilins as their co-receptors in many cases. The main receptors for semaphorins are plexins, which have established roles in regulating Rho-family GTPases. Recent work shows that plexins can also influence RRAS, R-Ras, which, in turn, can regulate integrins. Such regulation is probably a common feature of semaphorin signalling and contributes substantially to our understanding of semaphorin biology. Every semaphorin is characterised by the expression of a specific region of about 500 amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLXNA1
Plexin-A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PLXNA1'' gene. Interactions Plexin A1 has been shown to interact with AKT1 RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AKT1'' gene. This enzyme belongs to the AKT subfamily of serine/threonine kinases that contain SH2 (Src homology 2-like) protein domains. It .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLXNA2
Plexin-A2 is a protein that in humans is coded by the ''PLXNA2'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the plexin-A family of semaphorin co-receptors. Semaphorins are a large family of secreted or membrane-bound proteins that mediate repulsive effects on axon pathfinding during nervous system development. A subset of semaphorins are recognized by plexin-A/neuropilin transmembrane receptor complexes, triggering a cellular signal transduction cascade that leads to axon repulsion. This plexin-A family member is thought to transduce signals from semaphorin-3A and -3C. In some studies, the PLXNA2 gene is associated with schizophrenia. and anxiety Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response .... PLXNA2 is a candidate gene for intellectual disability and possibly facial dysmorphism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLXNA3
Plexin-A3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PLXNA3'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology Modeling
Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "''target''" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the "''template''"). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of a sequence alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure. Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure. It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in response to the binding of membrane-impermeable peptide hormones to the external cell surface. Through protein kinases activation, cGMP can relax smooth muscle. cGMP concentration in urine can be measured for kidney function and diabetes detection. History Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) research began after cGMP and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) were identified as cellular components and potentially involved with cellular regulation. Upon the synthesis of cGMP in 1960, progress rapidly spread in the understanding of regulation and effects of cGMP. Earl W. Sutherland received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his work with cAMP and secondary messengers. This award sparked extensive research into cAMP, while cGMP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
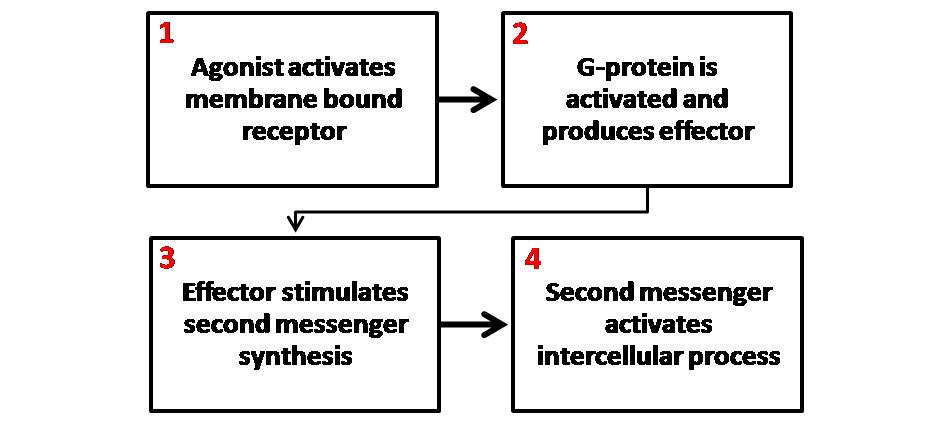
Secondary Messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first messe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases. A typical G-protein is active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP (i.e. when the GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP). The GDP can then be replaced by free GTP. Therefore, a G-protein can be switched on and off. GTP hydrolysis is accelerated by GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), while GTP exchange is catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). Activation of a GEF typically activates its cognate G-protein, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |