|
Pituitary Gigantism
Gigantism (, ''gígas'', "giant", plural γίγαντες, ''gígantes''), also known as giantism, is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average. In humans, this condition is caused by over-production of growth hormone in childhood. It is a rare disorder resulting from increased levels of growth hormone before the fusion of the growth plate which usually occurs at some point soon after puberty. This increase is most often due to abnormal tumor growths on the pituitary gland. Gigantism should not be confused with acromegaly, the adult form of the disorder, characterized by somatic enlargement specifically in the extremities and face. Cause Gigantism is characterized by an excess of growth hormone (GH). The excess of growth hormone that brings about gigantism is virtually always caused by pituitary growths (adenomas). These adenomas are on the anterior pituitary gland. They can also cause overproduction of GH's hypothalamic precursor known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Wadlow
Robert Pershing Wadlow (February 22, 1918 July 15, 1940), also known as the Alton Giant and the Giant of Illinois, was an American man. He is the list of tallest people, tallest person in recorded history for whom there is irrefutable evidence. Wadlow was born and raised in Alton, Illinois, a small city near St. Louis, Missouri. Wadlow's height was while his weight reached at his death at age 22. His great size and his continued growth in adulthood were due to hypertrophy of his pituitary gland, which results in an abnormally high level of Growth hormone, human growth hormone (HGH). Early life Wadlow was born in Alton, Illinois, on February 22, 1918, to Harold Franklin and Addie May (Johnson) Wadlow, and was the oldest of five children. He was taller than his father by age 8, and in elementary school a special desk was made for him. He was involved in a school German and Camera club before his graduation. By the time of his graduation from Alton Community Unit School Distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
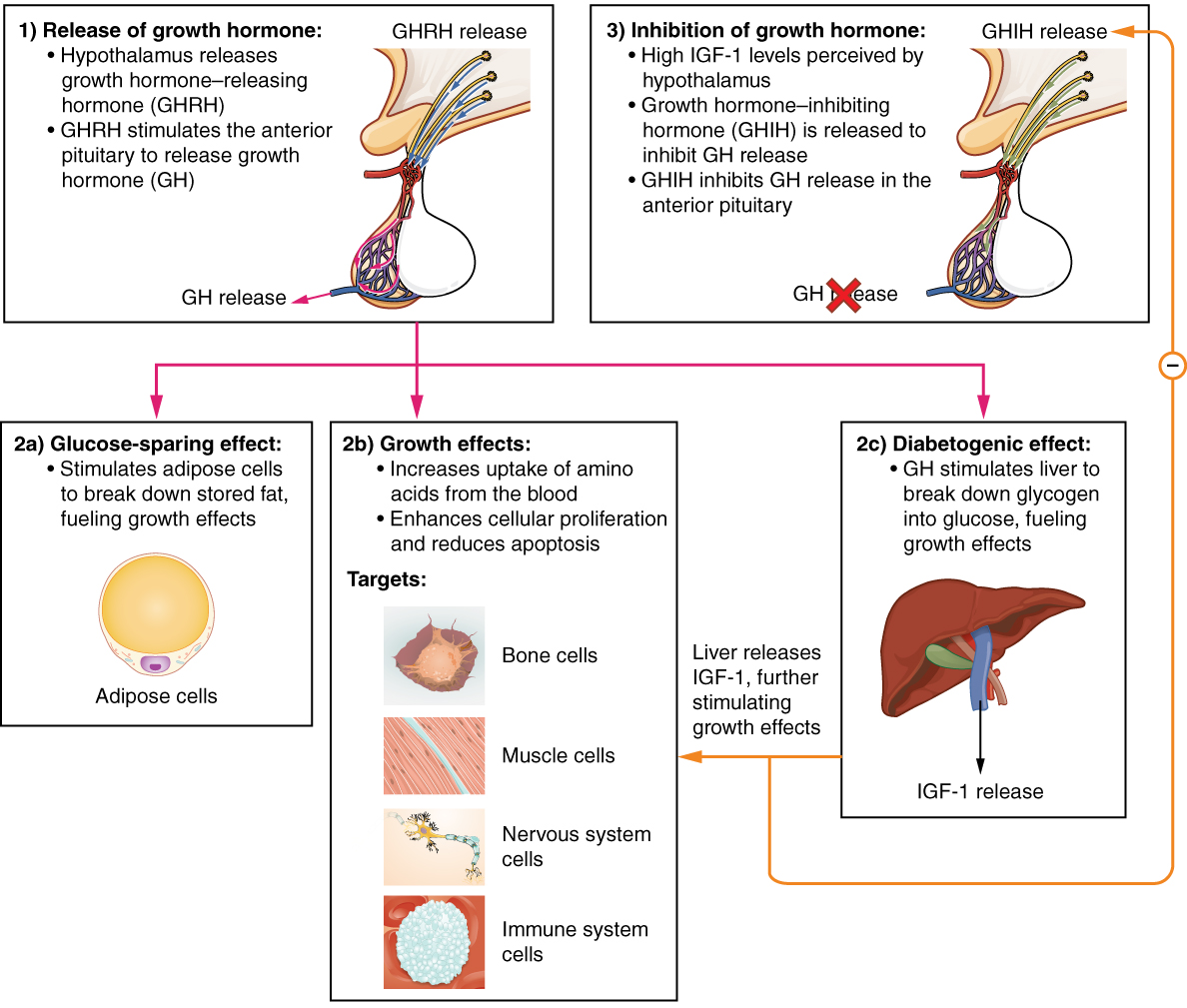
Growth Hormone–releasing Hormone
Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), also known as somatocrinin among other names in its endogenous form and as somatorelin (INN) in its pharmaceutical form, is a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a 44-amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. GHRH first appears in the human hypothalamus between 18 and 29 weeks of gestation, which corresponds to the start of production of growth hormone and other somatotropes in fetuses. Nomenclature * Endogenous: ** somatocrinin ** somatoliberin ** growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH or GH-RH; HGNC symbol is GHRH) ** growth hormone–releasing factor (GHRF or GRF) ** somatotropin-releasing hormone (SRH) ** somatotropin-releasing factor (SRF) * Pharmaceutical: ** somatorelin (INN) Origin GHRH is released from neurosecretory nerve terminals of these arcuate neurons, and is carried by the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland, where it stimulates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIP (gene)
AH receptor-interacting protein (AIP) also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein, immunophilin homolog ARA9, or HBV X-associated protein 2 (XAP-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AIP'' gene. The protein is a member of the FKBP family. Function AIP may play a positive role in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signalling possibly by influencing its receptivity for ligand and/or its nuclear targeting. AIP is the cellular negative regulator of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein. Further, it's been known to suppress antiviral signaling and the induction of type I interferon by targeting IRF7, a key player in the antiviral signal pathways. AIP consists of an N-terminal FKBP52 like domain and a C-terminal TPR domain. Mutations and role in disease AIP mutations may be the cause of a familial form of acromegaly, familial isolated pituitary adenoma (FIPA). Somatotropinomas (i.e. GH-producing pituitary adenomas), sometimes associated with prolact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination, retrotransposition event, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and replication slippage. Mechanisms of duplication Ectopic recombination Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes. The products of this recombination are a duplication at the site of the exchange and a reciprocal deletion. Ectopic recombina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarfism And Gigantism
Dwarfism is a condition of people and animals marked by unusually small size or short stature. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dwarfism is . ''Disproportionate dwarfism'' is characterized by either short limbs or a short torso. In cases of ''proportionate dwarfism'', both the limbs and torso are unusually small. Intelligence is usually normal, and most people with it have a nearly normal life expectancy. People with dwarfism can usually bear children, although there are additional risks to the mother and child depending upon the underlying condition. The most common and recognizable form of dwarfism in humans (comprising 70% of cases) is achondroplasia, a genetic disorder whereby the limbs are diminutive. Growth hormone deficiency is responsible for most other cases. There are many other less common causes. Treatment of the condition depends on the underlying cause. Those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnal Variation
A chronotype is the behavioral manifestation of an underlying circadian rhythm's myriad of physical processes. A person's chronotype is the propensity for the individual to sleep at a particular time during a 24-hour period. ''Eveningness'' (delayed sleep period; most active and alert in the evening) and ''morningness'' (advanced sleep period; most active and alert in the morning) are the two extremes with most individuals having some flexibility in the timing of their sleep period. However, across development there are changes in the propensity of the sleep period with pre-pubescent children preferring an advanced sleep period, adolescents preferring a delayed sleep period and many elderly preferring an advanced sleep period. Humans are normally diurnal creatures that are active in the daytime. As with most other diurnal animals, human activity-rest patterns are endogenously regulated by biological clocks with a circadian (~24-hour) period. Chronotypes have also been investigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upstream And Downstream (DNA)
In molecular biology and genetics, upstream and downstream both refer to relative positions of genetic code in DNA or RNA. Each strand of DNA or RNA has a 5' end and a 3' end, so named for the carbon position on the deoxyribose (or ribose) ring. By convention, upstream and downstream relate to the 5' to 3' direction respectively in which RNA transcription takes place. Upstream is toward the 5' end of the RNA molecule, and downstream is toward the 3' end. When considering double-stranded DNA, upstream is toward the 5' end of the coding strand for the gene in question and downstream is toward the 3' end. Due to the anti-parallel nature of DNA, this means the 3' end of the template strand is upstream of the gene and the 5' end is downstream. Some genes on the same DNA molecule may be transcribed in opposite directions. This means the upstream and downstream areas of the molecule may change depending on which gene is used as the reference. The terms upstream and downstream are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in tertiary structure, molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has Anabolism, anabolic effects in adults. In the 1950s IGF-1 was called "sulfation factor" because it stimulated sulfation of cartilage in vitro, and in the 1970s due to its effects it was termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" (NSILA). IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is Genetic code, encoded by the ''IGF1'' gene. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular reaction, intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 has a molecular weight of 7,649 Dalton (unit), daltons. In dogs, an ancient mutation in IGF1 is the primary cause of the Toy dog, toy phenotype. IGF-1 is produced primarily by the liver. Production is stimulated by growth hormone (GH). Most of IGF-1 is bound to one of 6 binding proteins (IGF-BP). IGFBP-1 is regulated by insulin. IGF-1 is pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the Teenager (word), teenage years, but its physical, psychological or cultural expressions may begin earlier or end later. Puberty typically begins during preadolescence, particularly in females. Physical growth (particularly in males) and cognitive development can extend past the teens. Age provides only a rough marker of adolescence, and scholars have not agreed upon a precise definition. Some definitions start as early as 10 and end as late as 30. The World Health Organization definition officially designates adolescence as the phase of life from ages 10 to 19. Biological development Puberty in general Puberty is a period of several years in which rapid physical growth and psycholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |