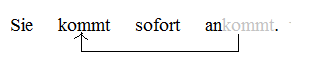|
Phrasal Verb
In the traditional grammar of Modern English, a phrasal verb typically constitutes a single semantic unit consisting of a verb followed by a particle (e.g., ''turn down'', ''run into,'' or ''sit up''), sometimes collocated with a preposition (e.g., ''get together with'', ''run out of,'' or ''feed off of''). Phrasal verbs ordinarily cannot be understood based upon the meanings of the individual parts alone but must be considered as a whole: the meaning is non- compositional and thus unpredictable. Phrasal verbs are differentiated from other classifications of multi-word verbs and free combinations by the criteria of idiomaticity, replacement by a single verb, ''wh''-question formation and particle movement. Terminology In 1900, Frederick Schmidt referred to particle verbs in the Middle English writings of Reginald Pecock as "phrasal verbs", though apparently without intending it as a technical term. The term was popularized by Logan Pearsall Smith in ''Words and Idioms'' (1925 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Traditional Grammar
Traditional grammar (also known as classical grammar) is a framework for the description of the structure of a language or group of languages. The roots of traditional grammar are in the work of classical Greek and Latin philologists. The formal study of grammar based on these models became popular during the Renaissance. Traditional grammars may be contrasted with more modern theories of grammar in theoretical linguistics, which grew out of traditional descriptions. While traditional grammars seek to describe how particular languages are used, or to teach people to speak or read them, grammar frameworks in contemporary linguistics often seek to explain the nature of language knowledge and ability common to all languages. Traditional grammar is often prescriptive, and may be regarded as unscientific by those working in linguistics. Traditional Western grammars classify words into parts of speech. They describe the patterns for word inflection, and the rules of syntax by whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Preposition Stranding
Preposition stranding or p-stranding is the syntax, syntactic construction in which a so-called ''stranded'', ''hanging'', or ''dangling'' preposition occurs somewhere other than immediately before its corresponding object (grammar), object; for example, at the end of a sentence. The term ''preposition stranding'' was coined in 1964, predated by stranded preposition in 1949. Linguists had previously identified such a construction as a sentence-terminal preposition or as a preposition at the end. Preposition stranding is found in English and other Germanic languages, as well as in Vata and Gbadi (languages in the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family), and certain dialects of French language, French spoken in North America. P-stranding occurs in various syntactic contexts, including passive voice, wh-movement, ''wh-''movement, and sluicing. ''Wh-''movement and P-stranding Wh-movement, ''Wh-''movement—which involves ''wh-''words like ''who'', ''what'', ''when'', ''where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Principal Clause
In traditional grammar, an independent clause (or main clause) is a clause that can stand by itself as a ''simple sentence''. An independent clause contains a subject and a predicate and makes sense by itself. Independent clauses can be joined by using a semicolon or by using a comma followed by a coordinating conjunction (''and'', ''but'', ''for'', ''or'', ''nor'', ''so'', ''yet'', etc.). Examples In the following example sentences, independent clauses are underlined, and conjunctions are in bold. Single independent clauses: *I have enough money to buy an ice cream cone. *My favourite flavour is chocolate. *Let's go to the shop. Multiple independent clauses: *I have enough money to buy an ice cream cone; my favourite flavour is chocolate. *I have enough money to buy an ice cream cone, so let's go to the shop. See also *Comma splice *Conditional sentence *Dependent clause *Relative clause A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase and uses some gramm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
West Germanic Languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English language, English, the Low German, Low German languages, and the Frisian languages; Istvaeonic, which encompasses Dutch language, Dutch and its close relatives; and Irminonic, which includes German language, German and its close relatives and variants. English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish language, Yiddish, Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Separable Verb
A separable verb is a verb that is composed of a lexical core and a separable particle. In some sentence positions, the core verb and the particle appear in one word, whilst in others the core verb and the particle are separated. The particle is traditionally referred to as a "separable prefix". German language, German, Dutch language, Dutch, Yiddish, Afrikaans language, Afrikaans and Hungarian language, Hungarian are notable for having many separable verbs. Examples The German verb ''ankommen'' is a separable verb, and is used here as the first illustration: The first two examples, sentences a and b, contain the "simple" tenses. In matrix declarative clauses that lack auxiliary verbs, the verb and its particle ''an-'' (both in bold) are separated, the verb appearing in V2 position and the particle appearing in clause-final position. The second two examples, sentences c and d, contain the so-called "complex tenses"; they show that when an auxiliary verb appears, the separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old English Language
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman (a type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers became dominant in England, their language re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Particle (grammar)
In grammar, the term ''particle'' (abbreviated ) has a traditional meaning, as a part of speech that cannot be inflected, and a modern meaning, as a function word (functor) associated with another word or phrase in order to impart meaning. Although a particle may have an intrinsic meaning and may fit into other grammatical categories, the fundamental idea of the particle is to add context to the sentence, expressing a mood or indicating a specific action. In English, for example, the phrase "oh well" has no purpose in speech other than to convey a mood. The word "up" would be a particle in the phrase "look up" (as in "look up this topic"), implying that one researches something rather than that one literally gazes skywards. Many languages use particles in varying amounts and for varying reasons. In Hindi, they may be used as honorifics, or to indicate emphasis or negation. In some languages, they are clearly defined; for example, in Chinese, there are three types of (; ): ''struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation, also known as nouning, is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head (linguistics), head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivation (linguistics), derivational affix (e.g., the noun "legalization" from the verb "legalize"), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion (word formation), conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation. English language, English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural language, natural part of language, but some insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Compound (linguistics)
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or Sign language, sign) that consists of more than one Word stem, stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make a longer word or sign. Consequently, a compound is a unit composed of more than one stem, forming words or signs. If the joining of the words or signs is orthographically represented with a hyphen, the result is a hyphenated compound (e.g., ''must-have'', ''hunter-gatherer)''. If they are joined without an intervening space, it is a closed compound (e.g., ''footpath'', ''blackbird''). If they are joined with a space (e.g. ''school bus, high school, lowest common denominator''), then the result – at least in English – may be an open compound. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phrasal Verb Trees 2
In grammar, a phrasecalled expression in some contextsis a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a constituent. There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as " all rights reserved", "economical with the truth", " kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single word, which plays a particular role within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |