|
Photosensor
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical communication to scientific research and industrial automation. Photodetectors can be classified by their mechanism of detection, such as the photoelectric effect, photochemical reactions, or thermal effects, or by performance metrics like spectral response. Common types include photodiodes, phototransistors, and photomultiplier tubes, each suited to specific uses. Solar cells, which convert light into electricity, are also a type of photodetector. This article explores the principles behind photodetectors, their various types, applications, and recent advancements in the field. History The development of photodetectors began with the discovery of the photoelectric effect by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, later explained by Albert Einstein in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into signal (electrical engineering), signals, small bursts of electric current, current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronics, electronic imaging devices of both analogue electronics, analog and digital electronics, digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermography, thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technological change, technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Current Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units ("dB gain"). A gain greater than one (greater than zero dB), that is, amplification, is the defining property of an active device or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one. The term ''gain'' alone is ambiguous, and can refer to the ratio of output to input voltage (''voltage gain''), current (''current gain'') or electric power (''power gain''). In the field of audio and general purpose amplifiers, especially operational amplifiers, the term usually refers to voltage gain, but in radio frequency amplifiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
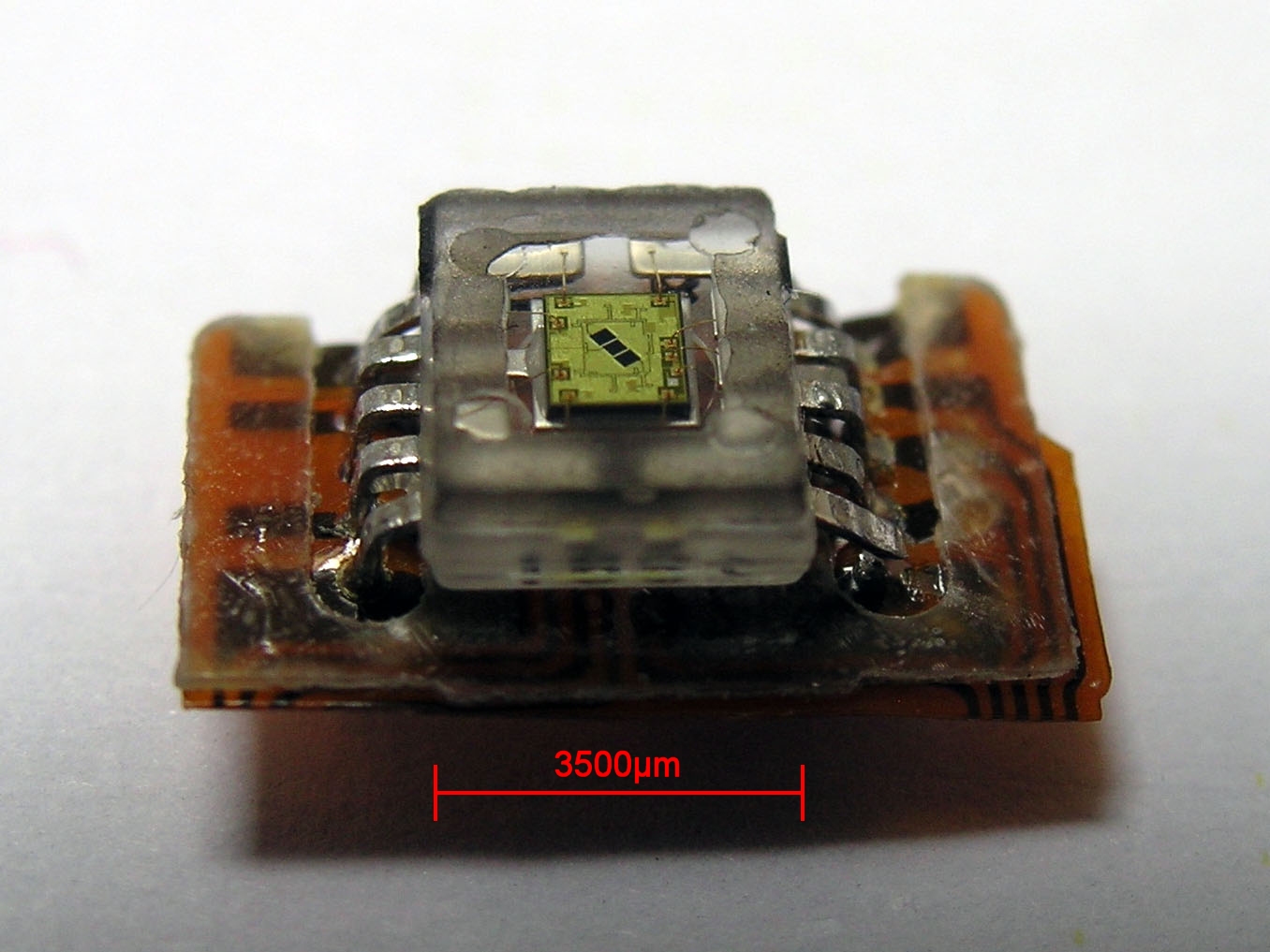
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers. Principle of operation A photodiode is a PIN diode, PIN structure or p–n junction. When a photon of sufficient energy strikes the diode, it creates an electron–electron hole, hole pair. This mechanism is also known as the inner photoelectric effect. If the absorption occurs in the junction's depletion region, or one diffusion length away from it, these carriers are swept from the junction by the built-in electric field of the depletion region. Thus holes move toward the anode, and electrons toward the cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Specific Detectivity
Specific detectivity, or ''D*'', for a photodetector is a figure of merit used to characterize performance, equal to the reciprocal of noise-equivalent power (NEP), normalized per square root of the sensor's area and frequency bandwidth (reciprocal of twice the integration time). Specific detectivity is given by D^*=\frac, where A is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector, \Delta f is the bandwidth, and NEP the noise equivalent power in units It is commonly expressed in ''Jones'' units (cm \cdot \sqrt/ W) in honor of Robert Clark Jones who originally defined it.R. C. Jones, "Proposal of the detectivity D** for detectors limited by radiation noise," ''J. Opt. Soc. Am.'' 50, 1058 (1960), ) Given that noise-equivalent power can be expressed as a function of the responsivity \mathfrak (in units of A/W or V/W) and the noise spectral density S_n (in units of A/Hz^ or V/Hz^) as NEP=\frac, it is common to see the specific detectivity expressed as D^*=\frac. It is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arises when the brain receives and perceives a sound. Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate (e.g., music or speech) or unintended. In contrast, noise in electronics may not be audible to the human ear and may require instruments for detection. In audio engineering, noise can refer to the unwanted residual electronic noise signal that gives rise to acoustic noise heard as a hiss. This signal noise is commonly measured using A-weighting or ITU-R 468 weighting. In experimental sciences, noise can refer to any random fluctuations of data that hinders perception of a signal. Measurement Sound is measured based on the amplitude and frequency of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Noise-equivalent Power
Noise-equivalent power (NEP) is a measure of the sensitivity of a photodetector or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio of one in a one hertz output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time.The factor of one half is explained by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. The units of NEP are watts per square root hertz. The NEP is equal to the noise amplitude spectral density (expressed in units of \mathrm/\sqrt or \mathrm/\sqrt) divided by the responsivity Responsivity is a measure of the input–output Gain (electronics), gain of a detector system. In the specific case of a photodetector, it measures the electrical output per optical input. A photodetector's responsivity is usually expressed in un ... (expressed in units of \mathrm/\mathrm or \mathrm/\mathrm, respectively). The fundamental equation is SNR = P/NEP. A smaller NEP corresponds to a more sensitive detector. For exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Responsivity
Responsivity is a measure of the input–output Gain (electronics), gain of a detector system. In the specific case of a photodetector, it measures the electrical output per optical input. A photodetector's responsivity is usually expressed in units of amperes or volts per watt of incident radiant flux, radiant power. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the Derivative, local slope. Many common photodetectors respond linearly as a function of the incident power. Responsivity is a function of the wavelength of the incident Electromagnetic radiation, radiation and of the sensor's properties, such as the bandgap of the material of which the photodetector is made. One simple expression for the responsivity ''R'' of a photodetector in which an optical signal is converted into an electric current (known as a photocurrent) is : R=\eta\frac\approx\eta\frac where \eta is the quantum efficiency (the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron Hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle denoting the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or crystal structure, atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or crystal lattice the negative charge of the electrons is balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, the absence of an electron leaves a net positive charge at the hole's location. Holes in a metal or semiconductor crystal lattice can move through the lattice as electrons can, and act similarly to electric charge, positively-charged particles. They play an important role in the operation of semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes (including light-emitting diodes) and integrated circuits. If an electron is excited into a higher state it leaves a hole in its old state. This meaning is used in Auger electron spectroscopy (and other x-ray techniques), in computational chemistry, and to explai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quantum Efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction. This article deals with the term as a measurement of a device's electrical sensitivity to light. In a charge-coupled device (CCD) or other photodetector, it is the ratio between the number of charge carriers collected at either terminal and the number of photons hitting the device's photoreactive surface. As a ratio, QE is dimensionless, but it is closely related to the responsivity, which is expressed in amps per watt. Since the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength, QE is often measured over a range of different wavelengths to characterize a device's efficiency at each photon energy level. For typical semiconductor photodetectors, QE drops to zero for photons whose energy is below the band gap. A photographic film typically has a QE of much less than 10%, while CCD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Figure Of Merit
A figure of merit (FOM) is a performance metric that characterizes the performance of a device, system, or method, relative to its alternatives. Examples *Absolute alcohol content per currency unit in an alcoholic beverage *accurizing, Accuracy of a rifle *Audio amplifier figures of merit such as gain or efficiency *Battery life of a laptop computer New York Times, June 25, 2009 *Calories per serving *Clock rate of a CPU is often given as a figure of merit, but is of limited use in comparing between different architectures. FLOPS may be a better figure, though these too are not completely representative of the performance of a CPU. *Contrast ratio of an LCD *Frequency response of a Loudspeaker, speaker *Fill factor (solar cell), Fill factor of a solar cell *Image resolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antimony Selenide
Antimony triselenide is the chemical compound with the formula . The material exists as the sulfosalt mineral antimonselite ( IMA symbol: Atm), which crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. In this compound, antimony has a formal oxidation state +3 and selenium −2. The bonding in this compound has covalent character as evidenced by the black color and semiconducting properties of this and related materials. The low-frequency dielectric constant (ε0) has been measured to be 133 along the ''c'' axis of the crystal at room temperature, which is unusually large. Its band gap is 1.18 eV at room temperature. The compound may be formed by the reaction of antimony with selenium Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elem ... and has a melting point of 885 K. Applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |