|
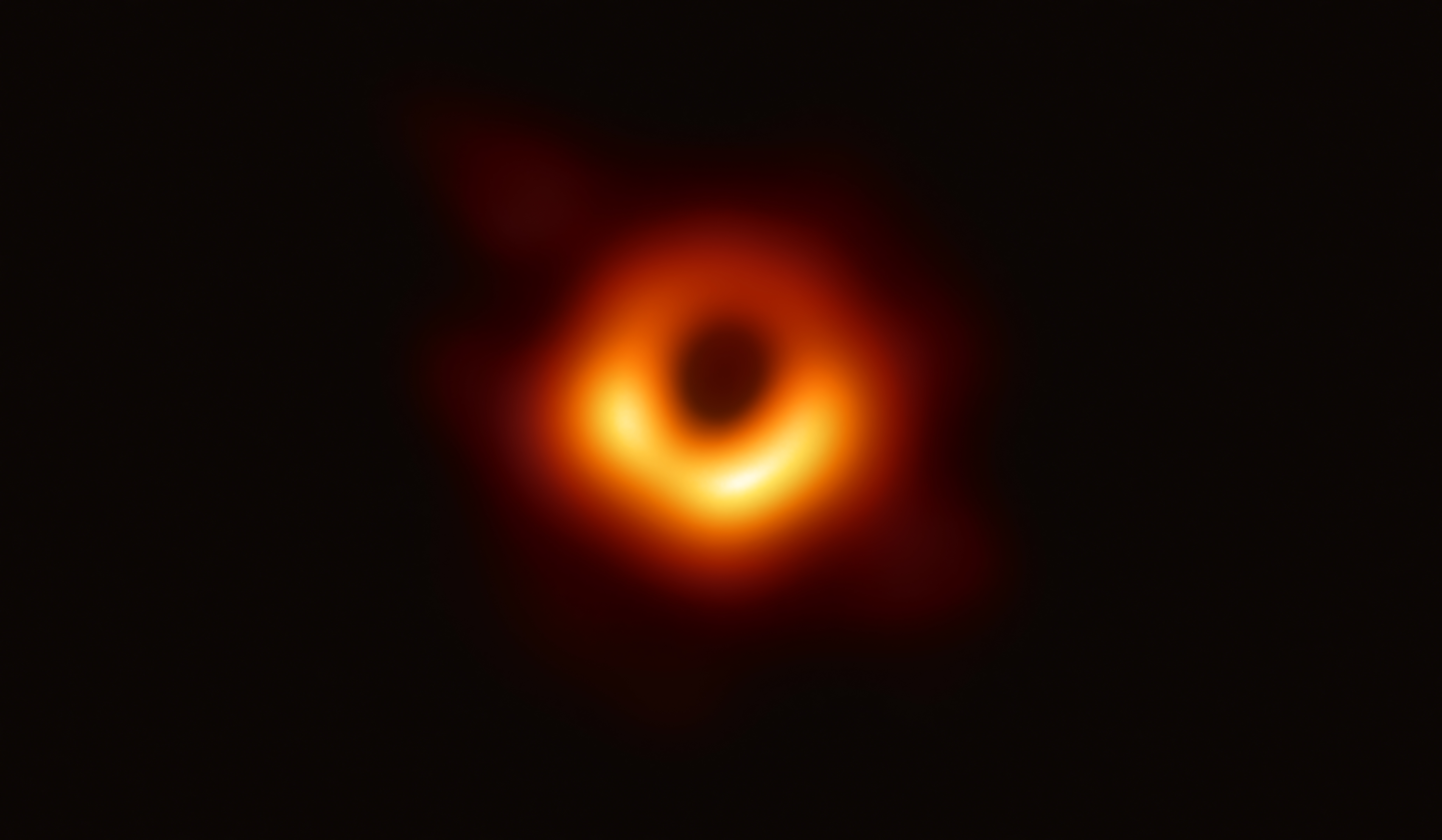
Photon Ring
A photon sphere, or photon ring or photon circle, arises in a neighbourhood of the event horizon of a black hole where gravity is so strong that emitted photons will not just bend around the black hole but also return to the point where they were emitted from and consequently display boomerang-like properties. As the source emitting photons falls into the gravitational field towards the event horizon the shape of the trajectory of each boomerang photon changes, tending to a more circular form. At a critical value of the radial distance from the singularity the trajectory of a boomerang photon will take the form of a non-stable circular orbit, thus forming a photon circle and hence in aggregation a photon sphere. The circular photon orbit is said to be the last photon orbit. The radius of the photon sphere, which is also the lower bound for any circular orbit, is, for a Schwarzschild black hole, : r = \frac = \frac, where is the gravitational constant, is the mass of the blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole Shadow
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of visible spectrum, visible light. It is an achromatic color, without Colorfulness#Chroma, chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figurative language, figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''Psychologie de la couleur – effets et symboliques'', pp. 105–26. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages versus the Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame-dragging
Frame-dragging is an effect on spacetime, predicted by Albert Einstein's General relativity, general theory of relativity, that is due to non-static stationary distributions of mass–energy. A stationary Field (physics), field is one that is in a steady state, but the masses causing that field may be non-static — rotating, for instance. More generally, the subject that deals with the effects caused by mass–energy currents is known as gravitoelectromagnetism, which is analogous to the magnetism of classical electromagnetism. The first frame-dragging effect was derived in 1918, in the framework of general relativity, by the Austrian physicists Josef Lense and Hans Thirring, and is also known as the Lense–Thirring effect. They predicted that the rotation of a massive object would distort the Metric tensor (general relativity), spacetime metric, making the orbit of a nearby test particle precess. This does not happen in Newtonian mechanics for which the gravitational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy, elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo that contains several trillion stars. One of the List of largest galaxies, largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters—about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way—and a jet of energetic plasma (physics), plasma that originates at the core and extends at least , traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers. The French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, and cataloged it as a nebula. M87 is about from Earth and is the second-brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, having many satellite galaxies. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermassive Black Hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical objects that have undergone gravitational collapse, leaving behind spheroidal regions of space from which nothing can escape, including light. Observational evidence indicates that almost every large galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its center. For example, the Milky Way galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its center, corresponding to the radio source Sagittarius A*. Accretion of interstellar gas onto supermassive black holes is the process responsible for powering active galactic nuclei (AGNs) and quasars. Two supermassive black holes have been directly imaged by the Event Horizon Telescope: the black hole in the giant elliptical galaxy Messier 87 and the black hole at the Milky Way's center (Sagittarius A*). Descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
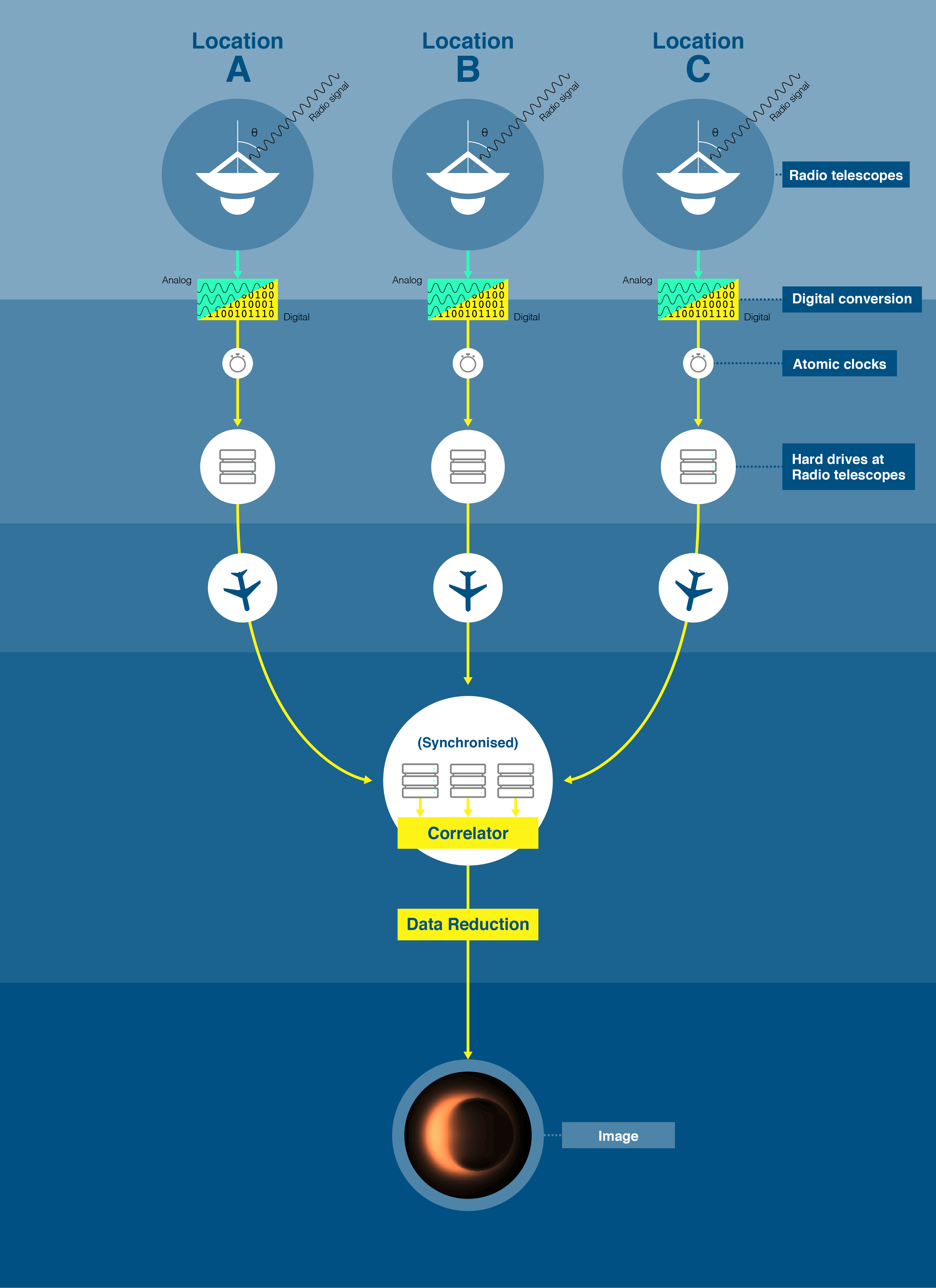
Event Horizon Telescope
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a Astronomical interferometer, telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A*, at Galactic Center, the center of the Milky Way. The Event Horizon Telescope project is an international collaboration that was launched in 2009 after a long period of theoretical and technical developments. On the theory side, work on the photon orbit and first simulations of what a black hole would look like progressed to predictions of VLBI imaging for the Galactic Cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyer–Lindquist Coordinates
In the mathematical description of general relativity, the Boyer–Lindquist coordinates are a generalization of the coordinates used for the metric of a Schwarzschild black hole that can be used to express the metric of a Kerr black hole. The Hamiltonian for particle motion in Kerr spacetime is separable in Boyer–Lindquist coordinates. Using Hamilton–Jacobi theory one can derive a fourth constant of the motion known as Carter's constant. The 1967 paper introducing Boyer–Lindquist coordinates was a posthumous publication for Robert H. Boyer, who was killed in the 1966 University of Texas tower shooting. Line element The line element for a black hole with a total mass equivalent M, angular momentum J, and charge Q in Boyer–Lindquist coordinates and geometrized units (G=c=1) is : ds^2 = -\frac\left(dt - a \sin^2\theta \,d\phi \right)^2 +\frac\Big(\left(r^2+a^2\right)\,d\phi - a \,dt\Big)^2 + \fracdr^2 + \rho^2 \,d\theta^2 or equivalently : ds^2 = -\left(1-\frac\r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Black Hole
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of general relativity; these equations are highly non-linear, which makes exact solutions very difficult to find. Overview The Kerr metric is a generalization to a rotating body of the Schwarzschild metric, discovered by Karl Schwarzschild in 1915, which described the geometry of spacetime around an uncharged, spherically symmetric, and non-rotating body. The corresponding solution for a ''charged'', spherical, non-rotating body, the Reissner–Nordström metric, was discovered soon afterwards (1916–1918). However, the exact solution for an uncharged, ''rotating'' black hole, the Kerr metric, remained unsolved until 1963, when it was discovered by Roy Kerr.Melia, Fulvio (2009). "Cracking the Einstein code: relativity and the birth of black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Photon Orbits With Orbital Inclination Thumbnail
Kerr may refer to: People *Kerr (surname) *Kerr (given name) Places ;United States *Kerr Township, Champaign County, Illinois *Kerr, Montana, A US census-designated place *Kerr, Ohio, an unincorporated community *Kerr County, Texas Other uses *KERR, A US radio station *Kerr, a brand of food Mason jars and lids *Clan Kerr Clan Kerr () is a Scottish clan whose origins lie in the Scottish Borders. During the Middle Ages, it was one of the prominent border reiver clans along the present-day Anglo-Scottish border and played an important role in the history of th ..., a Scottish clan See also * * * Ker (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic Equation
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the locally shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. It is a generalization of the notion of a " straight line". The noun ''geodesic'' and the adjective '' geodetic'' come from ''geodesy'', the science of measuring the size and shape of Earth, though many of the underlying principles can be applied to any ellipsoidal geometry. In the original sense, a geodesic was the shortest route between two points on the Earth's surface. For a spherical Earth, it is a segment of a great circle (see also great-circle distance). The term has since been generalized to more abstract mathematical spaces; for example, in graph theory, one might consider a geodesic between two vertices/nodes of a graph. In a Riemannian manifold or submanifold, geodesics are characterised by the property of having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzschild Metric
In Einstein's theory of general relativity, the Schwarzschild metric (also known as the Schwarzschild solution) is an exact solution to the Einstein field equations that describes the gravitational field outside a spherical mass, on the assumption that the electric charge of the mass, angular momentum of the mass, and universal cosmological constant are all zero. The solution is a useful approximation for describing slowly rotating astronomical objects such as many stars and planets, including Earth and the Sun. It was found by Karl Schwarzschild in 1916. According to Birkhoff's theorem, the Schwarzschild metric is the most general spherically symmetric vacuum solution of the Einstein field equations. A Schwarzschild black hole or static black hole is a black hole that has neither electric charge nor angular momentum (non-rotating). A Schwarzschild black hole is described by the Schwarzschild metric, and cannot be distinguished from any other Schwarzschild black hole except by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precess
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of about 80–90 degrees to the body's equator. Launching satellites into polar orbit requires a larger launch vehicle to launch a given payload to a given altitude than for a near-equatorial orbit at the same altitude, because it cannot take advantage of the Earth's rotational velocity. Depending on the location of the launch site and the inclination of the polar orbit, the launch vehicle may lose up to 460 m/s of Delta-v, approximately 5% of the Delta-v required to attain Low Earth orbit. Usage Polar orbits are used for Earth-mapping, reconnaissance satellites, as well as for some weather satellites. The Iridium satellite constellation uses a polar orbit to provide telecommunications services. Near-polar orbiting satellites commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |