|
Phlebotomy (modern)
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical laboratory scientists, medical practitioners, some EMTs, paramedics, phlebotomists, dialysis technicians, and other nursing staff. In veterinary medicine, the procedure is performed by veterinarians and veterinary technicians. It is essential to follow a standard procedure for the collection of blood specimens to get accurate laboratory results. Any error in collecting the blood or filling the test tubes may lead to erroneous laboratory results. Venipuncture is one of the most routinely performed invasive procedures and is carried out for any of five reasons: # to obtain blood for diagnostic purposes; # to monitor levels of blood components; # to administer therapeutic treatments including medications, nutrition, or chemotherapy; # to remove b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Venipuncture Using A BD Vacutainer
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous Sampling (medicine)#blood, blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by Medical Laboratory Scientist, medical laboratory scientists, physician, medical practitioners, some EMTs, paramedics, phlebotomists, Kidney dialysis, dialysis technicians, and other nursing staff. In veterinary medicine, the procedure is performed by veterinarians and Paraveterinary worker, veterinary technicians. It is essential to follow a standard procedure for the collection of blood specimens to get accurate laboratory results. Any error in collecting the blood or filling the test tubes may lead to erroneous laboratory results. Venipuncture is one of the most routinely performed invasive procedures and is carried out for any of five reasons: # to obtain blood for diagnostic purposes; # to monitor levels of blood component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autologous Blood Transfusion
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek). The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic tissue) transplanted by such a procedure is called an autograft or autotransplant. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of the same species), syngeneic transplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and xenotransplantation (from other species). A common example is the removal of a piece of bone (usually from the hip) and its being ground into a paste for the reconstruction of another portion of bone. Autotransplantation, although most common with blood, bone, hematopoietic stem cells, or skin, can be used for a wide variety of organs. One of the rare examples is autotransplantation of a kidney from one side of the body to the other. Kid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polycythemia
Polycythemia (also known as polycythaemia) is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called erythrocytosis, and there is significant overlap in the two findings, but the terms are not the same: polycythemia describes any increase in hematocrit and/or hemoglobin, while erythrocytosis describes an increase specifically in the number of red blood cells in the blood. Polycythemia has many causes. It can describe an increase in the number of red blood cells ("absolute polycythemia") or a decrease in the volume of plasma ("relative polycythemia"). Absolute polycythemia can be due to genetic mutations in the bone marrow ("primary polycythemia"), physiologic adaptations to one's environment, medications, and/or other health conditions. Laboratory studies such as serum Erythropoietin, erythropoeitin levels and genetic testing might be helpful t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hemochromatosis
Iron overload is the abnormal and increased accumulation of total iron in the body, leading to organ damage. The primary mechanism of organ damage is oxidative stress, as elevated intracellular iron levels increase free radical formation via the Fenton reaction. Iron overload is often ''primary'' (i.e hereditary haemochromatosis, aceruloplasminemia) but may also be ''secondary'' to other causes (i.e. transfusional iron overload). Iron deposition most commonly occurs in the liver, pancreas, skin, heart, and joints. People with iron overload classically present with the triad of liver cirrhosis, secondary diabetes mellitus, and bronze skin. However, due to earlier detection nowadays, symptoms are often limited to general chronic malaise, arthralgia, and hepatomegaly. Signs and symptoms Organs most commonly affected by hemochromatosis include the liver, heart, and endocrine glands. Hemochromatosis may present with the following clinical syndromes: * liver: chronic liver disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
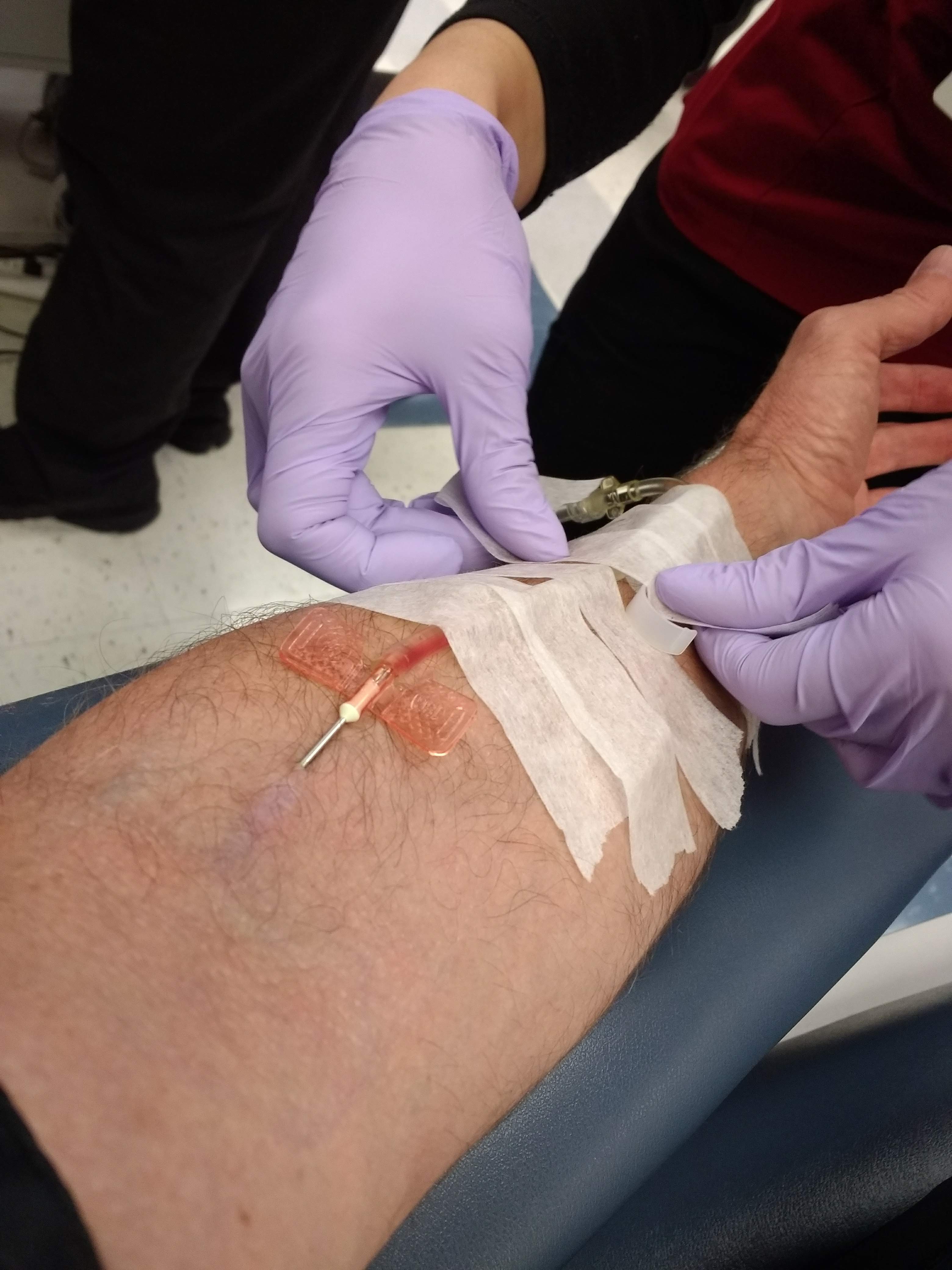
Winged Infusion Needle
Butterfly needle A winged infusion set—also known as "butterfly" or "scalp vein" set—is a device specialized for venipuncture: i.e. for accessing a superficial vein or artery for either intravenous injection or phlebotomy. It consists, from front to rear, of a hypodermic needle, two bilateral flexible "wings", flexible small-bore transparent tubing (often 20–35 cm long), and lastly a connector (often female Luer). This connector attaches to another device: e.g. syringe, vacuum tube holder/hub, or extension tubing from an infusion pump or gravity-fed infusion/ transfusion bag/bottle. Newer models include a slide and lock safety device slid over the needle after use, which helps prevent accidental needlestick injury and reuse of used needles, which can transmit infectious disease such as HIV and viral hepatitis. Use During venipuncture, the butterfly is held by its wings between thumb and index finger. This grasp very close to the needle facilitates precise placem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heelprick
In medicine, some blood tests are conducted on capillary blood obtained by fingerstick (or fingerprick) (or, for neonates, by an analogous heelprick). The site, free of surface arterial flow, where the blood is to be collected is sterilized with a topical germicide, and the skin pierced with a sterile lancet. After a droplet has formed, capillary blood is captured in a capillary tube (usually relying on surface tension). Blood cells drawn from fingersticks have a tendency to undergo hemolysis, especially if the finger is "milked" to obtain more blood. __TOC__ Uses Tests commonly conducted on the capillary blood collected are: * Blood gas test – Fingerstick testing may be used for measuring blood gas tension values, blood pH, and the level and base excess of bicarbonate. * Glucose levels – Diabetics often have a portable blood meter to check on their blood sugar The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fingerstick
In medicine, some blood tests are conducted on capillary blood obtained by fingerstick (or fingerprick) (or, for neonates, by an analogous heelprick). The site, free of surface arterial flow, where the blood is to be collected is sterilized with a topical germicide, and the skin pierced with a sterile lancet. After a droplet has formed, capillary blood is captured in a capillary tube (usually relying on surface tension). Blood cells drawn from fingersticks have a tendency to undergo hemolysis, especially if the finger is "milked" to obtain more blood. __TOC__ Uses Tests commonly conducted on the capillary blood collected are: * Blood gas test – Fingerstick testing may be used for measuring blood gas tension values, blood pH, and the level and base excess of bicarbonate. * Glucose levels – Diabetics often have a portable blood meter to check on their blood sugar. * Lipid profile – Fingerstick testing may be used to find abnormalities in blood lipid (such as choles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Median Antebrachial Vein
The median antebrachial vein, also known as median vein of forearm, is a superficial vein of the (anterior) forearm. It arises from - and drains - the superficial palmar venous arch, ascending superficially along the anterior forearm before ending by opening into the median cubital vein near the junction with the basilic vein within the cubital fossa; alternately, it may fork distal to the elbow and proceed to drain into both aforementioned veins. A bifurcation of the median antebrachial vein produces the (medial) intermediate basilic vein and the (lateral) intermediate cephalic vein; the two veins produced by such a split may replace the median cubital vein In human anatomy, the median cubital vein (or median basilic vein) is a superficial vein of the arm on the anterior aspect of the elbow. It classically shunts blood from the cephalic to the basilic vein at the roof of the cubital fossa. It is ty .... References Veins of the upper limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Basilic Vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial ( ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its course is generally visible through the skin as it travels in the subcutaneous fat and fascia lying superficial to the muscles. The basilic vein terminates by uniting with the brachial veins to form the axillary vein. Anatomy Course As it ascends the medial side of the biceps in the arm proper (between the elbow and shoulder), the basilic vein normally perforates the brachial fascia ( deep fascia) in the middle of the medial bicipital groove, and run upwards medial to the brachial artery to the lower border of teres major, continuing as the axillary vein. Tributaries and anastomoses Near the region anterior to the cubital fossa (in the bend of the elbow joint), the basilic vein usually communicates with the cephalic vein (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cephalic Vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein. Anatomy The cephalic vein is situated within the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Origin The cephalic vein forms at the roof of the anatomical snuffbox at the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand. Course and relations From its origin, it ascends up the lateral aspect of the radius. Near the shoulder, the cephalic vein passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles ( deltopectoral groove) through the clavipectoral triangle, where it empties into the axillary vein. Anastomoses It communicates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cubital Fossa
The cubital fossa, antecubital fossa, chelidon, inside of elbow, or, humorously, wagina, is the area on the anterior side of the upper part between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (antecubital) (Latin ) when in standard anatomical position. The cubital fossa is a triangular area having three borders. Boundaries * superior (proximal) boundary – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus * medial (ulnar) boundary – lateral border of pronator teres muscle originating from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. * lateral (radial) boundary – medial border of brachioradialis muscle originating from the lateral supraepicondylar ridge of the humerus. * apex – it is directed inferiorly, and is formed by the meeting point of the lateral and medial boundaries * superficial boundary (roof) – skin, superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |