|
Pentagramma Mirificum
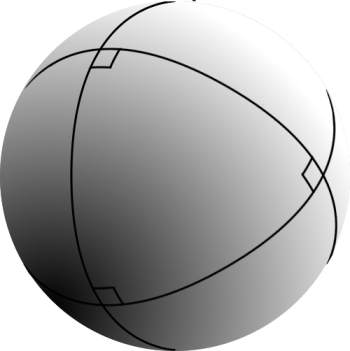
''Pentagramma mirificum'' (Latin for "miraculous pentagram") is a star polygon on a sphere, composed of five great circle arcs, all of whose internal angles are right angles. This shape was described by John Napier in his 1614 book '' Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio'' (''Description of the Admirable Table of Logarithms'') along with rules that link the values of trigonometric functions of five parts of a right spherical triangle (two angles and three sides). The properties of ''pentagramma mirificum'' were studied, among others, by Carl Friedrich Gauss. Geometric properties On a sphere, both the angles and the sides of a triangle (arcs of great circles) are measured as angles. There are five right angles, each measuring \pi/2, at A, B, C, D, and E. There are ten arcs, each measuring \pi/2: PC, PE, QD, QA, RE, RB, SA, SC, TB, and TD. In the spherical pentagon PQRST, every vertex is the pole of the opposite side. For instance, point P is the pole of equator RS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Right Triangle
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, sometimes called an orthogonal triangle or rectangular triangle, is a triangle in which two sides are perpendicular, forming a right angle ( turn or 90 degrees). The side opposite to the right angle is called the '' hypotenuse'' (side c in the figure). The sides adjacent to the right angle are called ''legs'' (or ''catheti'', singular: '' cathetus''). Side a may be identified as the side ''adjacent'' to angle B and ''opposite'' (or ''opposed to'') angle A, while side b is the side adjacent to angle A and opposite angle B. Every right triangle is half of a rectangle which has been divided along its diagonal. When the rectangle is a square, its right-triangular half is isosceles, with two congruent sides and two congruent angles. When the rectangle is not a square, its right-triangular half is scalene. Every triangle whose base is the diameter of a circle and whose apex lies on the circle is a right triangle, with the right angle at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arthur Cayley
Arthur Cayley (; 16 August 1821 – 26 January 1895) was a British mathematician who worked mostly on algebra. He helped found the modern British school of pure mathematics, and was a professor at Trinity College, Cambridge for 35 years. He postulated what is now known as the Cayley–Hamilton theorem—that every square matrix is a root of its own characteristic polynomial, and verified it for matrices of order 2 and 3. He was the first to define the concept of an abstract group, a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws, as opposed to Évariste Galois' concept of permutation groups. In group theory, Cayley tables, Cayley graphs, and Cayley's theorem are named in his honour, as well as Cayley's formula in combinatorics. Early life Arthur Cayley was born in Richmond, London, England, on 16 August 1821. His father, Henry Cayley, was a distant cousin of George Cayley, the aeronautics engineer innovator, and descended from an ancient Yorkshire family. He settled i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but for Perimeter of an ellipse, its perimeter (also known as circumference), Integral, integration is required to obtain an exact solution. The largest and smallest diameters of an ellipse, also known as its width and height, are typically denoted and . An ellipse has four extreme points: two ''Vertex (geometry), vertices'' at the endpoints of the major axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conic Section
A conic section, conic or a quadratic curve is a curve obtained from a cone's surface intersecting a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though it was sometimes considered a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a '' focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of degree 2; that is, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Five Points Determine A Conic
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean and projective geometry, five points determine a conic (a degree-2 plane curve), just as two (distinct) Point (geometry), points determine a line (geometry), line (a degree-1 plane curve). There are additional subtleties for conics that do not exist for lines, and thus the statement and its proof for conics are both more technical than for lines. Formally, given any five points in the plane in general linear position, meaning no three collinear, there is a unique conic passing through them, which will be non-Degenerate conic, degenerate; this is true over both the Euclidean plane and any Pappian plane, pappian projective plane. Indeed, given any five points there is a conic passing through them, but if three of the points are collinear the conic will be degenerate (reducible, because it contains a line), and may not be unique; see Degenerate conic#Points to define, further discussion. Proofs This result can be proven numerous different ways; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gnomonic Projection
A gnomonic projection, also known as a central projection or rectilinear projection, is a perspective projection of a sphere, with center of projection at the sphere's center, onto any plane not passing through the center, most commonly a tangent plane. Under gnomonic projection every great circle on the sphere is projected to a straight line in the plane (a great circle is a geodesic on the sphere, the shortest path between any two points, analogous to a straight line on the plane). More generally, a gnomonic projection can be taken of any -dimensional hypersphere onto a hyperplane. The projection is the -dimensional generalization of the trigonometric tangent which maps from the circle to a straight line, and as with the tangent, every pair of antipodal points on the sphere projects to a single point in the plane, while the points on the plane through the sphere's center and parallel to the image plane project to points at infinity; often the projection is considered as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a ''center of rotation''. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientation (geometry), orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis, rotation around a axis. The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or ''autorotation''). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal ''spin axis'' can be called a ''pole''; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or ''orbit''), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and professor of astronomy from 1807 until his death in 1855. While studying at the University of Göttingen, he propounded several mathematical theorems. As an independent scholar, he wrote the masterpieces '' Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'' and ''Theoria motus corporum coelestium''. Gauss produced the second and third complete proofs of the fundamental theorem of algebra. In number theory, he made numerous contributions, such as the composition law, the law of quadratic reciprocity and the Fermat polygonal number theorem. He also contributed to the theory of binary and ternary quadratic forms, the construction of the heptadecagon, and the theory of hypergeometric series. Due to Gauss' extensive and fundamental contributions to science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trigonometric Functions
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena through Fourier analysis. The trigonometric functions most widely used in modern mathematics are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent functions. Their multiplicative inverse, reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant, and the cotangent functions, which are less used. Each of these six trigonometric functions has a corresponding Inverse trigonometric functions, inverse function, and an analog among the hyperbolic functions. The oldest definitions of trigonometric functions, related to right-an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |