|
Pekoe
In the tea industry, tea leaf grading is the process of evaluating products based on the quality and condition of the tea leaves themselves. The highest grades for Western and South Asian teas are referred to as "orange pekoe" (abbreviated as "OP"), and the lowest as " fannings" or "dust". Pekoe tea grades are classified into various qualities, each determined by how many of the adjacent young leaves (two, one, or none) were picked along with the leaf buds. Top-quality pekoe grades consist of only the leaf buds, which are picked using the balls of the fingertips. Fingernails and mechanical tools are not used, to avoid bruising. Certain grades of leaf are better suited to certain varieties of tea. For example, most white tea is processed from the buds or shoots of the tea plant. When crushed to make bagged teas, the tea is referred to as "broken", as in "broken orange pekoe" ("BOP"). These lower grades include fannings and dust, which are tiny remnants created in the sorting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fannings
In the tea industry, tea leaf grading is the process of evaluating products based on the quality and condition of the tea leaves themselves. The highest grades for Western and South Asian teas are referred to as "orange pekoe" (abbreviated as "OP"), and the lowest as " fannings" or "dust". Pekoe tea grades are classified into various qualities, each determined by how many of the adjacent young leaves (two, one, or none) were picked along with the leaf buds. Top-quality pekoe grades consist of only the leaf buds, which are picked using the balls of the fingertips. Fingernails and mechanical tools are not used, to avoid bruising. Certain grades of leaf are better suited to certain varieties of tea. For example, most white tea is processed from the buds or shoots of the tea plant. When crushed to make bagged teas, the tea is referred to as "broken", as in "broken orange pekoe" ("BOP"). These lower grades include fannings and dust, which are tiny remnants created in the sorting and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tea Leaf Grading
In the tea industry, tea leaf grading is the process of evaluating products based on the quality and condition of the tea leaves themselves. The highest grades for Western and South Asian teas are referred to as "orange pekoe" (abbreviated as "OP"), and the lowest as " fannings" or "dust". Pekoe tea grades are classified into various qualities, each determined by how many of the adjacent young leaves (two, one, or none) were picked along with the leaf buds. Top-quality pekoe grades consist of only the leaf buds, which are picked using the balls of the fingertips. Fingernails and mechanical tools are not used, to avoid bruising. Certain grades of leaf are better suited to certain varieties of tea. For example, most white tea is processed from the buds or shoots of the tea plant. When crushed to make bagged teas, the tea is referred to as "broken", as in "broken orange pekoe" ("BOP"). These lower grades include fannings and dust, which are tiny remnants created in the sorting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Tea
Black tea (also literally translated as red tea from various East Asian languages) is a type of tea that is more tea processing, oxidized than oolong, yellow tea, yellow, white tea, white, and green tea, green teas. Black tea is generally stronger in flavour than other teas. All five types are made from leaves of the shrub (or small tree) ''Camellia sinensis,'' though ''Camellia taliensis'' is also rarely used. Two principal varieties of the species are used – the small-leaved Chinese variety plant (''C. sinensis'' var. ''sinensis''), used for most other types of teas, and the large-leaved Assamese plant (''C. sinensis'' var. ''assamica''), which was traditionally mainly used for black tea, although in recent years some green and white teas have been produced. First originating in China, the beverage's name there is ''hong cha'' (, "red tea") due to the colour of the oxidized leaves when processed appropriately. Today, the drink is widespread throughout East Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Grading
Food grading involves the inspection, assessment and sorting of various foods regarding quality, freshness, legal conformity and market value.Saravacos, George D.; Maroulis, Zacharias B. (2011''Food Process Engineering Operations'' CRC Press. pp. 198–199. Sivasankar, B. (2002)Processing and Preservation'' PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. pp. 175–177. Food grading is often done by hand, in which foods are assessed and sorted. Machinery is also used to grade foods, and may involve sorting products by size, shape and quality. For example, machinery can be used to remove spoiled food from fresh product. By food type Beef Beef grading in the United States is performed by the United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) Agricultural and Marketing Service. There are eight beef quality grades, with U.S. Prime being the highest grade and U.S. Canner being the lowest grade. Beef grading is a complex process. Beer In beer grading, the letter "X" is used on some beers, and was tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Tea
White tea may refer to one of several styles of tea which generally feature young or minimally processed leaves of the ''Camellia sinensis'' plant. Currently there is no generally accepted definition of white tea and very little international agreement on how it can be defined. Some sources use the term to refer tea that is merely dried with no additional processing. Therefore, white tea is very close to the natural state of the tea plant. Other sources use the term to refer to tea made from the buds and immature tea leaves picked shortly before the buds have fully opened and traditionally allowed to wither and dry under the sun, while others include tea buds and very young leaves which have been steamed or fired before drying. Most definitions agree, however, that white tea is not rolled or oxidized, resulting in a flavor characterized as "lighter" than most green tea, green or traditional black teas. In spite of its name, brewed white tea is pale yellow. Its name derives fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Orange, is the current dynasty, reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the Politics and government of the Netherlands (1581–1795), politics and government of the Netherlands and elsewhere in Europe, particularly since William the Silent organised the Dutch Revolt against Spain, Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an Dutch Republic, independent Dutch state. William III of Orange led the resistance of the Netherlands and Europe to Louis XIV of France and orchestrated the Glorious Revolution in England that established parliamentary rule. Similarly, Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands was instrumental in the Dutch resistance during W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 3103
ISO 3103 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (commonly referred to as ISO), specifying a standardized method for brewing tea, possibly sampled by the standardized methods described in ISO 1839. It was originally laid down in 1980 as BS 6008:1980 by the British Standards Institution, and a revision was published in December, 2019 as ISO/NP 3103. It was produced by ISO Technical Committee 34 (Food products), Sub-Committee 8 (Tea). The abstract states the following: The method consists in extracting of soluble substances in dried tea leaf, contained in a porcelain or earthenware pot, by means of freshly boiling water, pouring of the liquor into a white porcelain or earthenware bowl, examination of the organoleptic properties of the infused leaf, and of the liquor with or without milk, or both. This standard is not meant to define the proper method for brewing tea intended for general consumption, but rather to document a tea brewing proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tea Bags
A tea bag (or teabag) is a small, porous, sealed bag or packet typically containing tea leaves (''Camellia sinensis'') or the leaves of other herbs, which is immersed in water to steep and make an infusion. Originally used only for making tea, they are now made for other tisanes (herbal "teas") as well. Tea bags are commonly made of filter paper or food-grade plastic, or occasionally of silk cotton or silk. The tea bag performs the same function as a tea infuser. Tea bags can be used multiple times until there is no extraction left. Some tea bags have an attached piece of string with a paper label at the top that assists in removing the bag, while also displaying the brand or variety of tea. There are also special tea filters that can be used to pour loose tea into and brew it in a bag in a cup. History Tea bag patents date from 1903, when Roberta Lawson and Mary McLaren, of Milwaukee, Wisconsin, were granted US patent 723287 for a Tea Leaf Holder, which they had filed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
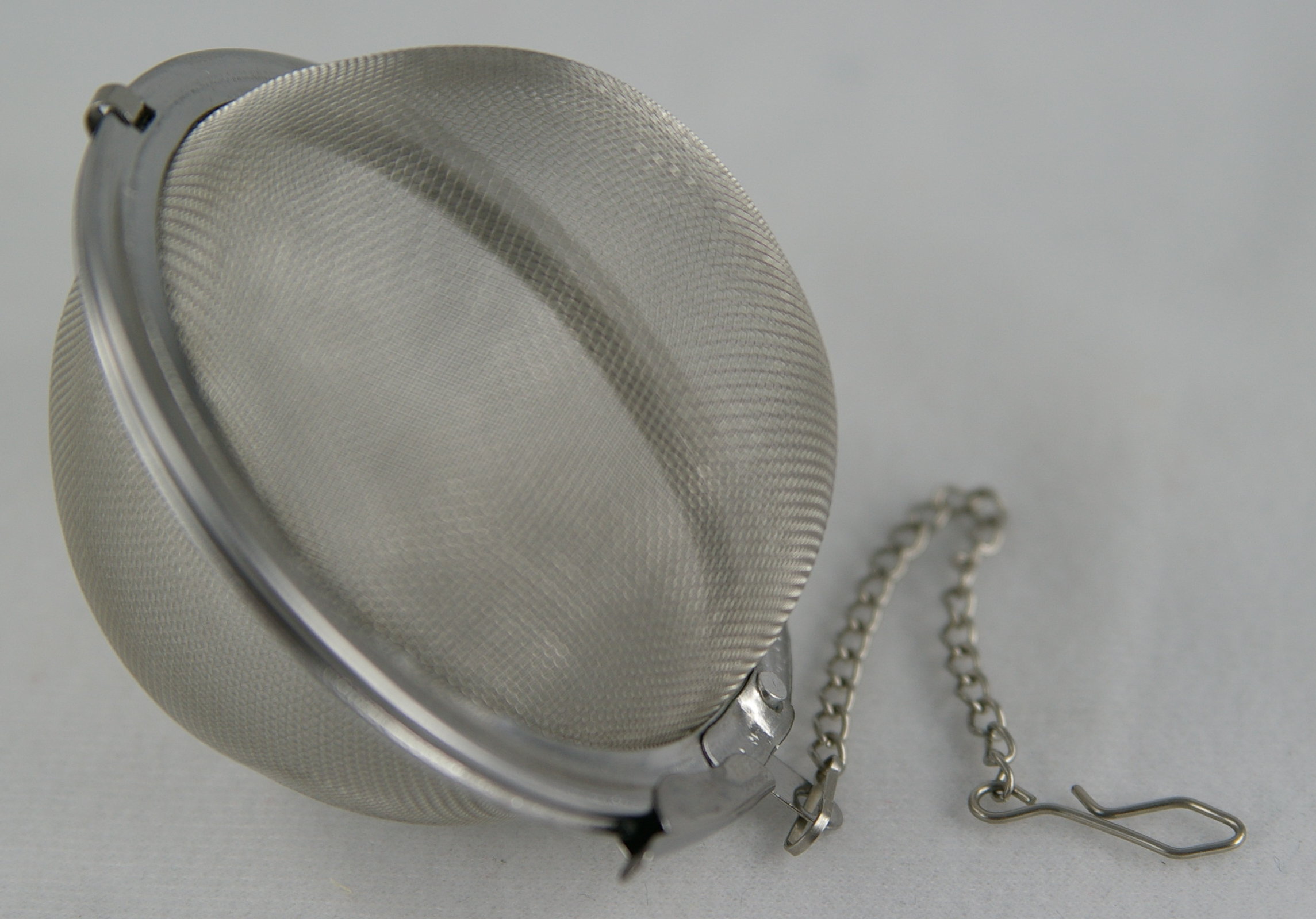
Tea Infuser
A tea infuser is a device in which loose, dried tea leaves are placed for steeping or brewing, in a mug or a teapot full of hot water. It is often called a teaball, tea maker or tea egg. The tea infuser gained popularity in the first half of the 19th century. Tea infusers enable one to easily steep tea from fannings and broken leaf teas. Use A tea infuser performs a similar function as a tea bag, a later American invention. The infuser is generally a small mesh, perforated metal container, or covered spoon that holds tea leaves, in varying sizes, to steep single or multiple servings at once. Common shapes of infusers include spherical, conical and cylindrical. One style of infuser is a split sphere with tong-like handles to open its mesh container. The infuser is placed in a cup or pot of hot or boiling water, allowing the tea to brew without loose tea leaves spilling into the pot or cup. A rod or chain is may be attached to the container of the infuser to simplify retrieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tea Stall
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of south-western China and northern Myanmar. Tea is also made, but rarely, from the leaves of ''Camellia taliensis''. After plain water, tea is the most widely consumed drink in the world. There are many types of tea; some have a cooling, slightly bitter, and astringent flavour, while others have profiles that include sweet, nutty, floral, or grassy notes. Tea has a stimulating effect in humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. An early credible record of tea drinking dates to the third century AD, in a medical text written by Chinese physician Hua Tuo. It was popularised as a recreational drink during the Chinese Tang dynasty, and tea drinking spread to other East Asian countries. Portuguese priests and merchants introduced it to Europe during the 16th century. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating Voorcompagnie, existing companies, it was granted a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be purchased by any citizen of the Dutch Republic and subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). The company possessed quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike Coinage of the Dutch East India Company, its own coins, and establish colonies. Also, because it traded across multiple colonies and countries from both the East and the West, the VOC is sometimes considered to have been the world's first multinational corporation. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |