|
Palagonite
Palagonite is an alteration product from the interaction of water with volcanic glass of chemical composition similar to basalt. Palagonite can also result from the interaction between water and basalt melt. The water flashes to steam on contact with the hot lava and the small fragments of lava react with the steam to form the light-colored palagonite tuff cones common in areas of basaltic eruptions in contact with water. An example is found in the pyroclastic cones of the Galapagos Islands. Charles Darwin recognized the origin of these cones during his visit to the islands. Palagonite can also be formed by a slower weathering of lava into palagonite, resulting in a thin, yellow-orange rind on the surface of the rock. The process of conversion of lava to palagonite is called ''palagonitization.'' Palagonite soil is a light yellow-orange dust, comprising a mixture of particles ranging down to sub-micrometer sizes, usually found mixed with larger fragments of lava. The color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palagonite Layers At Moya Beach (Mayotte)
Palagonite is an alteration product from the interaction of water with volcanic glass of chemical composition similar to basalt. Palagonite can also result from the interaction between water and basalt melt. The water flashes to steam on contact with the hot lava and the small fragments of lava react with the steam to form the light-colored palagonite tuff cones common in areas of basaltic eruptions in contact with water. An example is found in the pyroclastic cones of the Galapagos Islands. Charles Darwin recognized the origin of these cones during his visit to the islands. Palagonite can also be formed by a slower weathering of lava into palagonite, resulting in a thin, yellow-orange rind on the surface of the rock. The process of conversion of lava to palagonite is called ''palagonitization.'' Palagonite soil is a light yellow-orange dust, comprising a mixture of particles ranging down to sub-micrometer sizes, usually found mixed with larger fragments of lava. The color is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
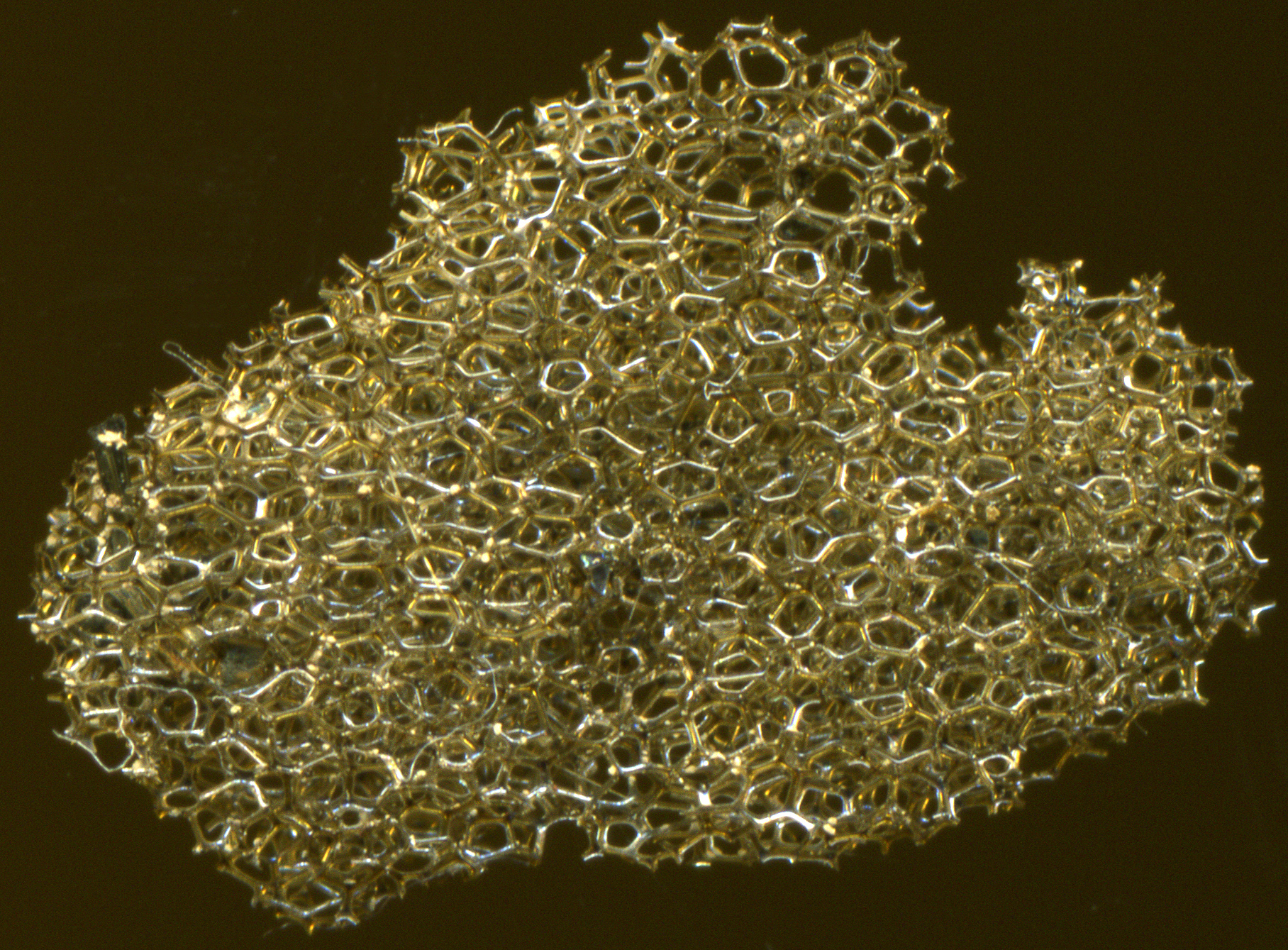
Sideromelane
Sideromelane is a vitreous basaltic volcanic glass, usually occurring in palagonite tuff, for which it is characteristic. It is a less common form of tachylite, with which it usually occurs together; however it lacks the iron oxide crystals dispersed in the glass, and therefore appears transparent and pure, with yellow-brown color, instead of tachylite opaque black. It forms at higher temperatures and with more rapid chilling. Presence of sideromelane indicates higher temperature of the lava, and solidifying of the flow closer to the vent, probably by rapid quenching in a wet environment. Sideromelane often forms during explosions of submarine volcanoes and subglacial volcanoes, and often occurs as fragments embedded in a palagonite matrix, forming hyaloclastite deposits. Sideromelane is a mafic A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones. Stratocone Stratocones are large cone-shaped volcanoes made up of lava flows, explosively erupted pyroclastic rocks, and igneous intrusives that are typically centered around a cylindrical vent. Unlike shield volcanoes, they are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, often alternating, explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions. Some have collapsed craters called calderas. The central core of a stratocone is commonly dominated by a central core of intrusive rocks that range from around to over several kilometers in diameter. This central core is surrounded by multiple generations of lav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Glass
Volcanic glass is the amorphous (uncrystallized) product of rapidly cooling magma. Like all types of glass, it is a state of matter intermediate between the closely packed, highly ordered array of a crystal and the highly disordered array of liquid. Volcanic glass may refer to the interstitial material, or matrix, in an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock, or to any of several types of vitreous igneous rocks. Origin Volcanic glass is formed when magma is rapidly cooled. Magma rapidly cooled to below its normal crystallization temperature becomes a supercooled liquid, and, with further rapid cooling, this becomes an amorphous solid. The change from supercooled liquid to glass occurs at a temperature called the glass transition temperature, which depends on both cooling rate and the amount of water dissolved in the magma. Magma rich in silica and poor in dissolved water is most easily cooled rapidly enough to form volcanic glass. As a result, rhyolite magmas, which are high in si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and electronic structure of matter to be investigated at the atomic, molecular and macro scale, and over astronomical distances. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Current applications of spectroscopy include biomedical spectroscopy in the areas of tissue analysis and medical imaging. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geology, geological, geophysical and geochemistry, geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin language, Latin word ''Vulcan (mythology), vulcan''. Vulcan was the ancient Roman mythology, Roman god of fire. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, especially active ones, to observe volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as Volcanic ash, ash or pumice), Rock (geology), rock and lava samples. One major focus of enquiry is the prediction of eruptions; there is currently no accurate way to do this, but predicting or forecasting eruptions, like predicting earthquakes, could save many lives. Modern volcanology image:Icelandic tephra.JPG, Volcanologist examining tephra horizons in south- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rocks
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main Rock (geology)#Classification, rock types, the others being sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from Partial melting, partial melts of existing rocks in either a Terrestrial planet, planet's mantle (geology), mantle or crust (geology), crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive (geology), extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form Volcanic glass, natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water On Mars
Although very small amounts of liquid water may occur transiently on the surface of Mars, limited to traces of dissolved moisture from the atmosphere and thin films, large quantities of ice are present on and under the surface. Small amounts of water vapor are present in the atmosphere, and liquid water may be present under the surface. In addition, a large quantity of liquid water was likely present on the surface in the distant past. Currently, ice is mostly present in polar permafrost. More than 5 million km3 of ice have been detected at or near the surface of Mars, enough to cover the planet to a depth of . Even more ice might be locked away in the deep subsurface.Carr, 2006, p. 173. The chemical signature of water vapor on Mars was first unequivocally demonstrated in 1963 by spectroscopy using an Earth-based telescope. In 2008 and 2013, ice was detected in soil samples taken by the Phoenix lander and ''Curiosity'' rover. In 2018, radar findings suggested the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martian Regolith Simulant
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, has appeared as a setting in works of fiction since at least the mid-1600s. Trends in the planet's portrayal have largely been influenced by advances in planetary science. It became the most popular celestial object in fiction in the late 1800s, when it became clear that there was no life on the Moon. The predominant genre depicting Mars at the time was utopian fiction. Around the same time, the mistaken belief that there are canals on Mars emerged and made its way into fiction, popularized by Percival Lowell's speculations of an ancient civilization having constructed them. ''The War of the Worlds'', H. G. Wells's novel about an alien invasion of Earth by sinister Martians, was published in 1897 and went on to have a major influence on the science fiction genre. Life on Mars appeared frequently in fiction throughout the first half of the 1900s. Apart from enlightened as in the utopian works from the turn of the century, or evil as in the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which Paleoecology, paleoenvironmental or Archaeology, archaeological records can be placed. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |