|
Palaestra
A palaestra ( or ; also (chiefly British) palestra; ) was any site of a Greek wrestling school in antiquity. Events requiring little space, such as boxing and wrestling, occurred there. ''Palaistrai'' functioned both independently and as a part of public Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasia; a palaestra could exist without a gymnasium, but no gymnasium existed without a palaestra. Etymology Compare ancient Greek ''palaiein'' - "to wrestle" and ''palē'' - "wrestling". A palaestrophylax or palaistrophulax () was the guardian or the director of a Palaestra. The spelling is notable because it is usually spelled ''palestra'' in the United Kingdom, while in the United States, it is spelled ''palaestra''. This is a reverse of the usual rule for such words, where the ''ae''/''oe'' is used in British spelling but appears as ''e'' in American spelling. Architecture Greek The Architecture of Ancient Greece, architecture of the palaestra, although allowing for some variation, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaestra At Olympia
The palaestra at Olympia (Greek παλαίστρ-α, -αι, "wrestling ground or grounds," Latin palaestr-a, -ae, with Greek ἐν Όλυμπία, Latin in Olympia) is the ground or grounds in Olympia, Greece, ancient Olympia where πάλη, Doric πάλα, "wrestling," was taught and performed for training purposes; i.e., "wrestling-school." Two other martial arts were taught there: Greek πυγμή (pygme), Latin pugnus, "fist, boxing," and Greek παγκράτιον, Latin pancration or pancratium, "any method," which was free-style, or hand-to-hand, including grappling, kicking, punching, or any unarmed method whatever, no holds barred. The latter was sometimes deadly, or disfiguring (with permission), which indicates that the arts were ephebic, or "soldier" training for prospective citizens of the city-state sponsoring the school, such as Elis, but here combined with prospective candidacy for contention in the games. Be that as it may, none of the games were conducted withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaestra At Delphi
The palaestra at Delphi is part of a gymnasium at the sanctuary. It is the oldest existing gymnasium from the Greek world, dating to the second half of the fourth century B.C. It was built on two terraces, with the palaestra and baths on the lower terrace. The frequent earthquakes and landslides at Delphi have damaged the palaestra the most seriously of all of the gymnasium areas. The palaestra is small, measuring thirty-two metres square. The central court is 14 metres square with an Ionic peristyle in blue limestone. The eastern wall of the palaestra is formed by the retaining wall for the terrace above. Several rooms open onto the north and west sides of the court. There are three rooms of identical dimensions (8 X 5.80 meters) along the north side of the palaestra. The middle of the three rooms was faced with two columns ''in antis'' and divided by a wall pierced with a door. Along the west side of the building there are also three rooms. The large room in the northw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Baths
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large Roman Empire, imperial public bath, bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed in great numbers throughout Rome. Most Roman cities had at least one – if not many – such buildings, which were centers not only for bathing, but socializing and reading as well. Bathhouses were also provided for wealthy private Roman villa, villas, domus, town houses, and castra, forts. They were supplied with water from an adjacent river or stream, or within cities by aqueduct (watercourse), aqueduct. The water would be heated by fire then channelled into the caldarium (hot bathing room). The design of baths is discussed by Vitruvius in ''De architectura'(V.10) Terminology '','' '','' '','' and may all be translated as 'bath' or 'baths', though Latin sources distinguish among these terms. or , derived from the Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (ancient Greece)
The gymnasium () in Ancient Greece functioned as a training facility for competitors in public games. It was also a place for socializing and engaging in intellectual pursuits. The name comes from the Ancient Greek term '' gymnós'', meaning "naked" or "nude". Only adult male citizens were allowed to use the gymnasia. Athletes competed nude, a practice which was said to encourage aesthetic appreciation of the male body, and to be a tribute to the gods. Gymnasia and palaestrae (wrestling schools) were under the protection and patronage of Heracles, Hermes and, in Athens, Theseus. Etymology The word ''gymnasium'' is the latinisation of the Greek noun γυμνάσιον (''gymnasion''), "public place for physical exercises; exercise area", in pl. "bodily exercises" and generally "school", which in turn is derived from the common Greek adjective (''gymnos'') meaning "naked" or "nude", by way of the related verb γυμνάζω (''gymnazo''), whose meaning is "to train naked", "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conisterium
A conisterium (or conisterion) () was an apartment in Greek and Roman gymnasiums. It was where sand or dust was stored, for use by wrestlers after they had been anointed with oil. They would either sprinkle it on themselves, or a slave would do it. The purpose of this was so that during a fight, the oil or sweat would not prevent a wrestler from having a good grip on his opponent. After a fight, or exercise, the powder was rubbed off with strigils, before the wrestler had a bath. The conisterium was built after the ''coryceum'' and next to a cold bath called ''frigida lavatio''. Conisteriums were also found in palaestras. In the palaestra of Vitruvius Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ..., for instance, the gymnasium chambers were built on the right side while the ''ela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaulos (architecture)
A ''diaulos'' (from Gr. δι-, "double", and αὐλός, "pipe"), in ancient Greek architecture, was a peristyle round the great court of the palaestra, described by Vitruvius, which measured two stadia (.) in length, on the south side this peristyle had two rows of columns, so that in stormy weather the rain might not be driven into the inner part."DIAULOS.—The peristyle round the great court of the Palaestra described by Vitruvius" . Vitruvius says that the ''diaulos'' should contain "spacious exedrae... with seats, so that philosophers, orators, and everyone else who delights in study will be able to sit and hold discussions." The double (south) portico should contain a large exedra, on one side a punching bag, a dust bath, and a cold water sink (''loutron''), on the other side an oiling room, a cold bath (''frigidarium''), and a passage to the stream room, sauna, and hot-water washing area. See also * Glossary of architecture * Palaestra at Delphi * Palaestra at Olympia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympia, Greece
Olympia ( ; ), officially Archaia Olympia ( ), is a small town in Elis (regional unit), Elis on the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, famous for the nearby archaeological site of the same name. The site was a major Panhellenic sanctuary, Panhellenic religious sanctuary of ancient Greece, where the ancient Olympic Games were held every Olympiad, four years throughout classical antiquity, from the 8th century BC to the 4th century AD. They were Olympic Games, restored on a global basis in 1894 in honor of the ideal of peaceful international contention for excellence. The sacred precinct, named the Altis, was primarily dedicated to Zeus, although other gods were worshipped there. The games conducted in his name drew visitors from all over the Greek world as one of a group of such "Panhellenic" centres, which helped to build the identity of the ancient Greeks as a nation. Despite the name, it is nowhere near Mount Olympus in northern Greece, where the twelve Olympians, the major deit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks considered the centre of the world to be in Delphi, marked by the stone monument known as the Omphalos of Delphi (navel). According to the Suda, Delphi took its name from the Delphyne, the she-serpent (''Drakaina (mythology), drakaina'') who lived there and was killed by the god Apollo (in other accounts the serpent was the male serpent (''drakon'') Python (mythology), Python). The sacred precinct occupies a delineated region on the south-western slope of Mount Parnassus. It is now an extensive archaeological site, and since 1938 a part of Mount Parnassus, Parnassos National Park. The precinct is recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in having had a great influence in the ancient world, as evidenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenes, whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. Ancient Greek architecture is best known for its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway ('' propylon''), the public square (''agora'') surrounded by storied colonnade (''stoa''), the town council building (''bouleuterion''), the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Muslim Conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that expanded rapidly under the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate, culminating in Muslim rule being established on three continents (Asia, Africa, and Europe) over the next century. According to historian James Buchan: "In speed and extent, the first Arab conquests were matched only by those of Alexander the Great, and they were more lasting." At their height, the territory that was conquered by the Arab Muslims stretched from Iberian Peninsula, Iberia (at the Pyrenees) in the west to Indian subcontinent, India (at Sind (caliphal province), Sind) in the east; Muslim control spanned Sicily, most of the Middle East and North Africa, and the Caucasus and Central Asia. Among other drastic changes, the early Muslim conquests brought about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
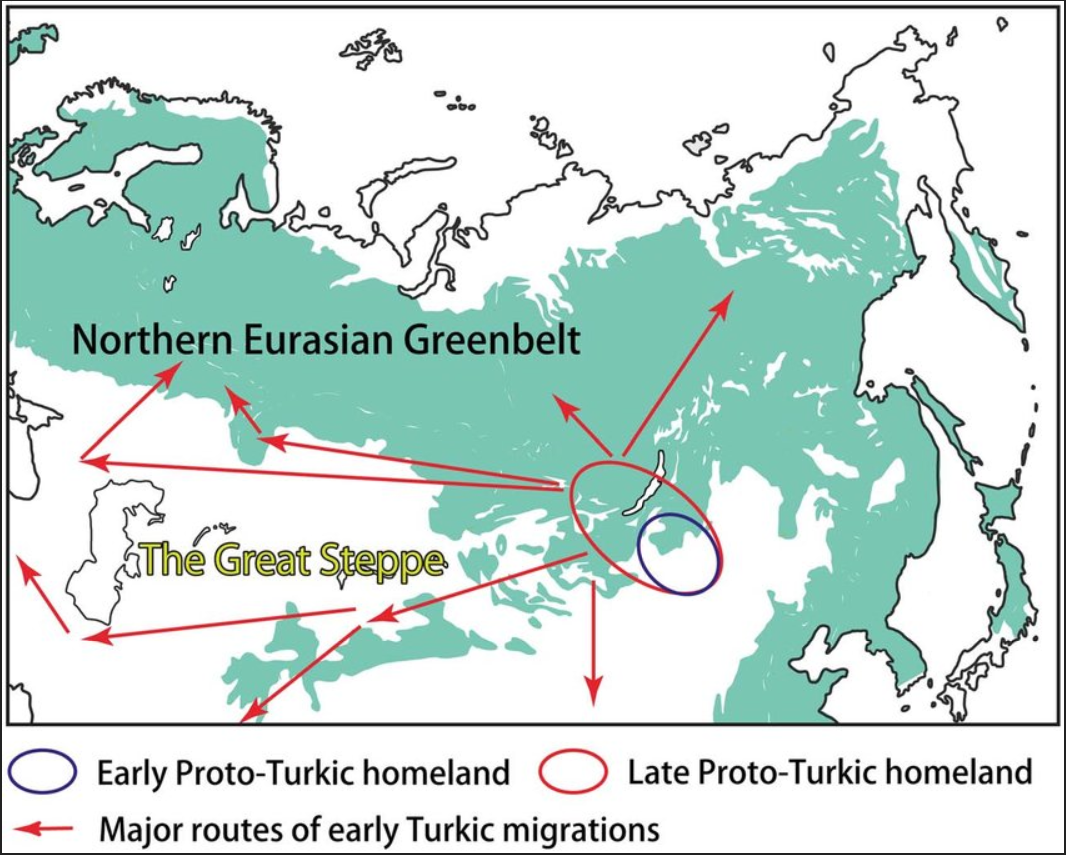
Turkic Migration
The Turkic migrations were the spread of Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes and Turkic languages across Eurasia between the 4th and 11th centuries. In the 6th century, the Göktürks overthrew the Rouran Khaganate in what is now Mongolia and expanded in all directions, spreading Turkic culture throughout the Eurasian steppes. Although Göktürk empires came to an end in the 8th century, they were succeeded by numerous Turkic empires such as the Uyghur Khaganate, Kara-Khanid Khanate, Khazars, and the Cumans. Some Turks eventually settled down into sedentary societies such as the Qocho and Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom, Ganzhou Uyghurs. The Seljuq dynasty invaded Anatolia starting in the 11th century, resulting in permanent Turkic settlement and presence there. Modern nations with large Turkic populations include Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan, and Turkic populations also exist within other nations, such as Chuvashia, Bashkortostan, Tatarstan and the Sakha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Imperial Period
The Roman imperial period is the expansion of political and cultural influence of the Roman Empire. The period begins with the reign of Augustus (), and it is taken to end variously between the late 3rd and the late 4th century, with the beginning of late antiquity. Despite the end of the "Roman imperial period", the Roman Empire continued to exist under the rule of the Roman emperors into Late Antiquity and beyond, except in the Western Empire, over which the Romans' political and military control was lost in the course of the 5th-century fall of the Western Roman Empire. Periodization In historiography, the "imperial period" is by convention taken to last from 27 BCE to CE 284. In archaeology, on the other hand, the term is usually taken to cover the period of c. CE 1 to 375 (the latter being a conventional date for the onset of the Migration Period). This follows (1955), who used a periodization of "early imperial period" () B1 to B2 and "late imperial period" () C1 to C3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |