|
Pain In Crustaceans
There is a scientific debate which questions whether crustaceans experience pain. It is a complex mental state, with a distinct perceptual quality but also associated with suffering, which is an emotional state. Because of this complexity, the presence of pain in an animal, or another human for that matter, cannot be determined unambiguously using observational methods, but the conclusion that animals experience pain is often inferred on the basis of likely presence of phenomenal consciousness which is deduced from comparative brain physiology as well as physical and behavioural reactions. Definitions of pain vary, but most involve the ability of the nervous system to detect and reflexively react to harmful stimuli by avoiding it, and the ability to subjectively experience suffering. Suffering cannot be directly measured in other animals. Responses to putatively painful stimuli can be measured, but not the experience itself. To address this problem when assessing the capacity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobster 08
Lobsters are malacostracans decapod crustaceans of the family Nephropidae or its synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, which are usually much larger than the others. Highly prized as seafood, lobsters are economically important and are often one of the most profitable commodities in the coastal areas they populate. Commercially important species include two species of ''Homarus'' from the northern Atlantic Ocean and scampi (which look more like a shrimp, or a "mini lobster")—the Northern Hemisphere genus ''Nephrops'' and the Southern Hemisphere genus ''Metanephrops''. Distinction Although several other groups of crustaceans have the word "lobster" in their names, the unqualified term "lobster" generally refers to the clawed lobsters of the family Nephropidae. Clawed lobsters are not closely related to spiny lobsters or slipper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham (; 4 February Dual dating, 1747/8 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. [15 February 1748 Old Style and New Style dates, N.S.] – 6 June 1832) was an English philosopher, jurist, and social reformer regarded as the founder of modern utilitarianism. Bentham defined as the "fundamental axiom" of his philosophy the principle that "it is the greatest happiness of the greatest number that is the measure of right and wrong." He became a leading theorist in Anglo-Americans, Anglo-American philosophy of law, and a political radical whose ideas influenced the development of welfarism. He advocated Individualism, individual and economic freedoms, the separation of church and state, freedom of expression, equal rights for women, the right to divorce, and (in an unpublished essay) the decriminalizing of homosexual acts. He called for the abolitionism, abolition of slavery, capital punishment#Abolition of capital punishment, capital punishment, and physical punishment, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class () is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class ranking between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name – and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'' – was first introduced by French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in the classification of plants that appeared in his '' Eléments de botanique'' of 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, recent research has suggested that classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants may be considered as an alternative. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing to the substantial risks and high chances of overdose, misuse, and addiction in the absence of medical supervision. Etymology The word ''analgesic'' derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carprofen
Carprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the carbazole and propionic acid class that was previously for use in humans and animals but is now only available to veterinarians for prescribing as a supportive treatment for various conditions in animals. Carprofen reduces inflammation by inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2; its specificity for COX-2 varies from species to species. Marketed under many brand names worldwide, carprofen is used as a treatment for inflammation and pain, including joint pain and postoperative pain. Human use Carprofen was used in humans for almost ten years, starting in 1988, for the same conditions as in dogs; namely, joint pain and inflammation. Side effects tended to be mild, usually consisting of nausea or gastrointestinal pain and diarrhoea. It was available by prescription in 150 mg to 600 mg doses. Dosages over 250 mg were reserved for pain caused by severe trauma, such as postoperative inflammation; 150 mg d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symmetry, bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of cephalopod arm, arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt Cephalopod ink, ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, Extant taxon, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus (genus), Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurological Substrate
A neural substrate is a term used in neuroscience to indicate the part of the central nervous system (i.e., brain and spinal cord) that underlies a specific behavior, cognitive process, or psychological state. ''Neural'' is an adjective relating to "a nerve or the nervous system", while a ''substrate'' is an "underlying substance or layer". Some examples are the neural substrates of language acquisition, memory, prediction and reward, pleasure, facial recognition, envisioning the future, intentional empathy, religious experience, spontaneous musical performance, and anxiety. See also * Neural correlate The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) are the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for the occurrence of the mental states to which they are related. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correla ... * Neural substrates of visual imagery References Neuroscience {{neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intention
An intention is a mental state in which a person commits themselves to a course of action. Having the plan to visit the zoo tomorrow is an example of an intention. The action plan is the ''content'' of the intention while the commitment is the ''attitude'' towards this content. Other mental states can have action plans as their content, as when one admires a plan, but differ from intentions since they do not involve a practical commitment to realizing this plan. Successful intentions bring about the intended course of action while unsuccessful intentions fail to do so. Intentions, like many other mental states, have intentionality: they represent possible states of affairs. Theories of intention try to capture the characteristic features of intentions. The ''belief-desire theory'' is the traditionally dominant approach. According to a simple version of it, having an intention is nothing but having a desire to perform a certain action and a belief that one will perform this act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
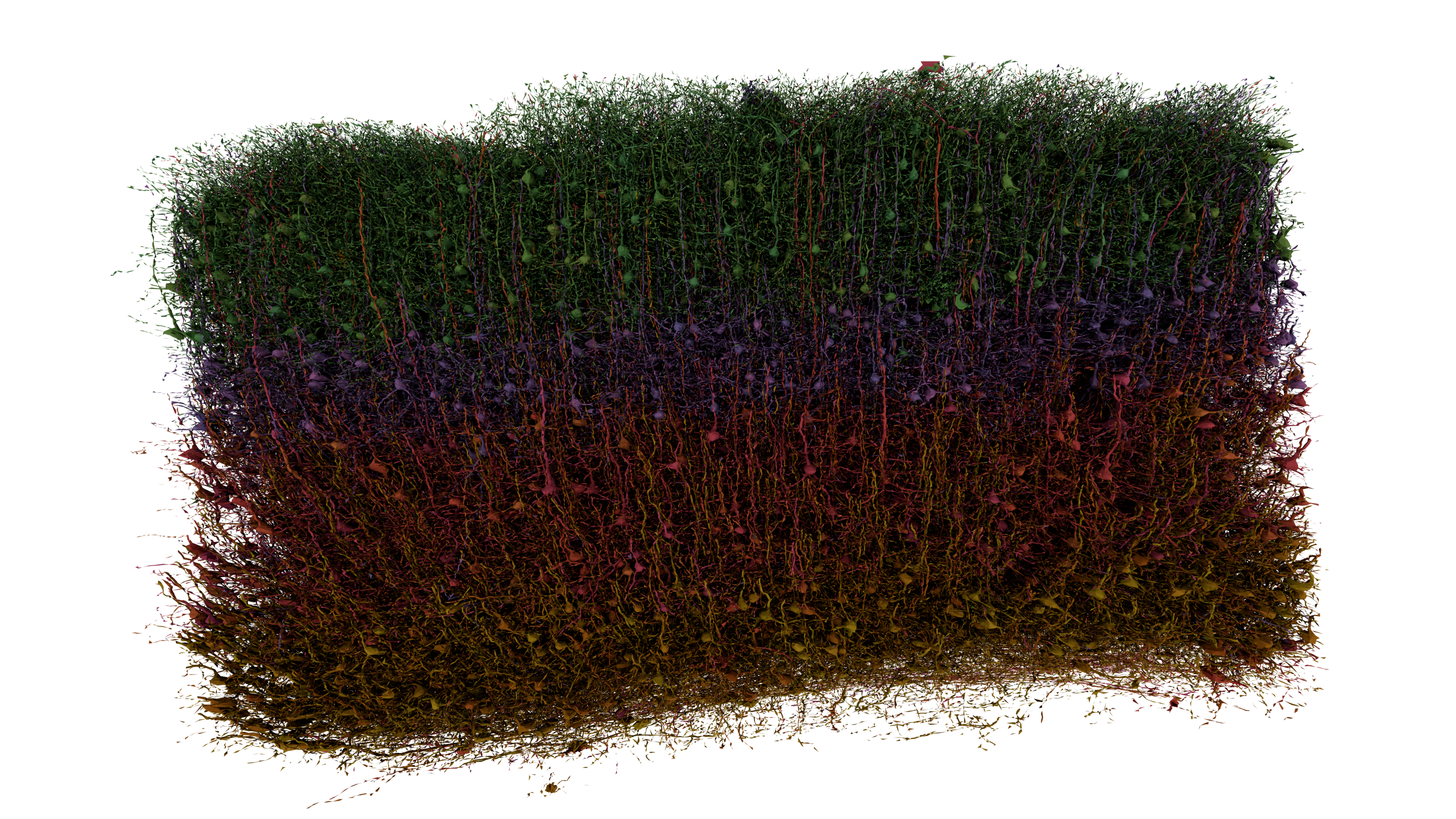
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues. The neocortex cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotes
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/ toads, salamanders/ newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three extraembryonic membranes ( amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenocortical and chromaffin tissues as a discrete pair of glands near their kidneys; more complex kidneys; the presence of an astragalus for better ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Cognition
Animal cognition encompasses the mental capacities of non-human animals, including insect cognition. The study of animal conditioning and learning used in this field was developed from comparative psychology. It has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology; the alternative name cognitive ethology is sometimes used. Many behaviors associated with the term ''animal intelligence'' are also subsumed within animal cognition. Researchers have examined animal cognition in mammals (especially primates, cetaceans, elephants, bears, dogs, cats, pigs, horses, cattle, raccoons and rodents), birds (including parrots, fowl, corvids and pigeons), reptiles ( lizards, snakes, and turtles), fish and invertebrates (including cephalopods, spiders and insects). Historical background Earliest inferences The mind and behavior of non-human animals has captivated the human imagination for centuries. Many writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |