|
Organogermanium
Organogermanium compounds are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to germanium or hydrogen to germanium chemical bond. Organogermanium chemistry is the corresponding chemical science. Germanium shares group 14 in the periodic table with silicon, tin and lead, and not surprisingly the chemistry of organogermanium is in between that of organosilicon compounds and organotin compounds. One reason that limited synthetic value of organogermanium compound is costs of germanium compounds. On the other hand, germanium is advocated as a non-toxic alternative to many toxic organotin reagents. Compounds like tetramethylgermanium and tetraethylgermanium are used in the microelectronics industry as precursors for germanium dioxide chemical vapor deposition. The first organogermanium compound, tetraethylgermane, was synthesised by Winkler in 1887, by the reaction of germanium tetrachloride with diethylzinc. The organogermanium compound ''bis (2-Carboxyethylgermanium)sesquioxide' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobutylgermane
Isobutylgermane (IBGe, Chemical formula: (CH3)2CHCH2GeH3, is an organogermanium compound. It is a colourless, volatile liquid that is used in MOVPE (Metalorganic Vapor Phase Epitaxy) as an alternative to germane. IBGe is used in the deposition of Ge films and Ge-containing thin semiconductor films such as SiGe in strained silicon application, and GeSbTe in NAND Flash applications. Properties IBGe is a non-pyrophoric liquid source for chemical vapor deposition ( CVD) and atomic layer deposition (ALD) of semiconductors. It possesses very high vapor pressure and is considerably less hazardous than germane gas. IBGe also offers lower decomposition temperature (the onset of decomposition at ca. 325-350 °C).,Safer alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-carboxyethylgermasesquioxane
Propagermanium ( INN), also known by a variety of other names including bis(2-carboxyethylgermanium) sesquioxide and 2-carboxyethylgermasesquioxane, is an organometallic compound of germanium that is sold as an alternative medicine. It is a polymeric compound with the formula ((HOOCCH2CH2Ge)2O3)''n''. The compound was first synthesized in 1967 at the Asai Germanium Research Institute in Japan Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n .... It is a water-soluble organogermanium compound used as raw material in health foods. The compound displays low toxicity in studies with rats. References Organogermanium compounds Germanium(IV) compounds Inorganic polymers Propionic acids Polyelectrolytes {{Alt-med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Compound
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraethylgermanium
Tetraethylgermanium (common name tetraethyl germanium), abbreviated TEG, is an organogermanium compound with the formula ( CH3CH2)4 Ge. Tetraethylgermanium is an important chemical compound used in vapour deposition of germanium which is in a tetrahedral shape. Synthesis Clemens Winkler first reported the compound in 1887 from diethylzinc Diethylzinc (C2H5)2Zn, or DEZ, is a highly pyrophoric and reactive organozinc compound consisting of a zinc center bound to two ethyl groups. This colourless liquid is an important reagent in organic chemistry. It is available commercially as a ... and germanium tetrachloride, shortly after germanium was discovered in 1887. References {{Reflist External links * TetraethylgermaniuDatasheet commercial supplier Organogermanium compounds Germanium(IV) compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosilicon
Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an '' inorganic'' compound. History In 1846 Von Ebelman's had synthesized Tetraethyl orthosilicate (Si(OC2H5)4). In 1863 Friedel and Crafts managed to make the first organosilieon compound with C-Si bonds which gone byound the syntheses of orthosilicic acid esters. The same year they also described a «polysilicic acid ether» in the preparation of ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. The early extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneerd in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic Kipping. He also had coined the term «silicone» (akin to ketones) in relation to these materials in 1904. In recognition of Kipping's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds. Structure and bonding The geometry of a molecule of BF3 is trigonal planar. Its D3h symmetry conforms with the prediction of VSEPR theory. The molecule has no dipole moment by virtue of its high symmetry. The molecule is isoelectronic with the carbonate anion, . BF3 is commonly referred to as " electron deficient," a description that is reinforced by its exothermic reactivity toward Lewis bases. In the boron trihalides, BX3, the length of the B–X bonds (1.30 Å) is shorter than would be expected for single bonds, and this shortness may indicate stronger B–X π-bonding in the fluoride. A facile explanation invokes the symmetry-allowed overlap of a p orbital on the boron atom with the in-phase combination of the three similarly oriented p orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium Tetrachloride
Germanium tetrachloride is a colourless, fuming liquid with a peculiar, acidic odour. It is used as an intermediate in the production of purified germanium metal. In recent years, GeCl4 usage has increased substantially due to its use as a reagent for fiber optic production. Production Most commercial production of germanium is from treating flue-dusts of zinc- and copper-ore smelters, although a significant source is also found in the ash from the combustion of certain types of coal called vitrain. Germanium tetrachloride is an intermediate for the purification of germanium metal or its oxide, GeO2."Germanium" Mineral Commodity Profile, U.S. Geological Survey, 2005. Germanium tetrachloride can be generated directly from GeO2 (germanium dioxide) by dissolution of the oxide in concentrated hydrochloric acid. The resulting mixture is fractionally distilled to purify and separate the germanium tetrachloride from other products and impurities."The Elements" C. R. Hammond, David R. Lide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakurai Reaction
The Sakurai reaction (also known as the Hosomi–Sakurai reaction) is the chemical reaction of carbon electrophiles (such as a ketone shown here) with allyltrimethylsilane catalyzed by strong Lewis acids. Lewis acid activation is essential for complete reaction. Strong Lewis acids such as titanium tetrachloride, boron trifluoride, tin tetrachloride, and AlCl(Et)2 are all effective in promoting the Hosomi reaction. The reaction is a type of electrophilic allyl shift with formation of an intermediate beta-silyl carbocation. Driving force is the stabilization of said carbocation by the beta-silicon effect. The Hosomi-Sakurai reaction can be performed on a number of functional groups. An electrophilic carbon, activated by a Lewis acid, is required. Below is a list of different functional groups that can be used in the Hosomi–Sakurai reaction. The reaction achieves results similar to the addition of an allyl Grignard reagent A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
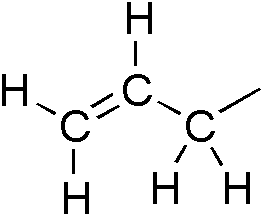
Allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |