|
Opcode
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code, also known as instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel or opstring) is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operation to be performed. Beside the opcode itself, most instructions also specify the data they will process, in the form of operands. In addition to opcodes used in the instruction set architectures of various CPUs, which are hardware devices, they can also be used in abstract computing machines as part of their byte code specifications. Overview Specifications and format of the opcodes are laid out in the instruction set architecture ( ISA) of the processor in question, which may be a general CPU or a more specialized processing unit. Opcodes for a given instruction set can be described through the use of an opcode table detailing all possible opcodes. Apart from the opcode itself, an instruction normally also has one or more specifiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opcode Prefix
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code, also known as instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel or opstring) is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operation to be performed. Beside the opcode itself, most instructions also specify the data they will process, in the form of operands. In addition to opcodes used in the instruction set architectures of various CPUs, which are hardware devices, they can also be used in abstract computing machines as part of their byte code specifications. Overview Specifications and format of the opcodes are laid out in the instruction set architecture ( ISA) of the processor in question, which may be a general CPU or a more specialized processing unit. Opcodes for a given instruction set can be described through the use of an opcode table detailing all possible opcodes. Apart from the opcode itself, an instruction normally also has one or more specifiers f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an ''assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book ''The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllable (computing)
In computing, a syllable is a name for a platform-dependent unit of information storage. Depending on the target hardware, various bit widths (and sometimes internal groupings) are associated with it. Commonly used in the 1960s and 1970s, the term has mostly fallen into disuse in favour of terms like byte or word. Examples: * 3-bit syllables: some experimental CISC designs * 8-bit syllables: English Electric KDF9 (represented as syllabic octals and also called slob-octals or slobs in this context) and Burroughs large systems (see also: Burroughs B6x00-7x00 instruction set) * 12-bit syllables: NCR computers such as the NCR 315 (also called slabs in this context) and Burroughs large systems * 13-bit syllables: Saturn Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (LVDC) and Gemini Spacecraft On-Board Computer (OBC) See also * Byte * Catena (computing) * Instruction syllable * Nibble * Opcode * Opstring * Parcel (computing) * Syllable (in linguistics) * Word (computer architecture) In co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Code
In computer programming, machine code is any low-level programming language, consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). Each instruction causes the CPU to perform a very specific task, such as a load, a store, a jump, or an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more units of data in the CPU's registers or memory. Early CPUs had specific machine code that might break backwards compatibility with each new CPU released. The notion of an instruction set architecture (ISA)Â defines and specifies the behavior and encoding in memory of the instruction set of the system, without specifying its exact implementation. This acts as an abstraction layer, enabling compatibility within the same family of CPUs, so that machine code written or generated according to the ISA for the family will run on all CPUs in the family, including future CPUs. In general, each architecture family (e.g. x86, ARM) has its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
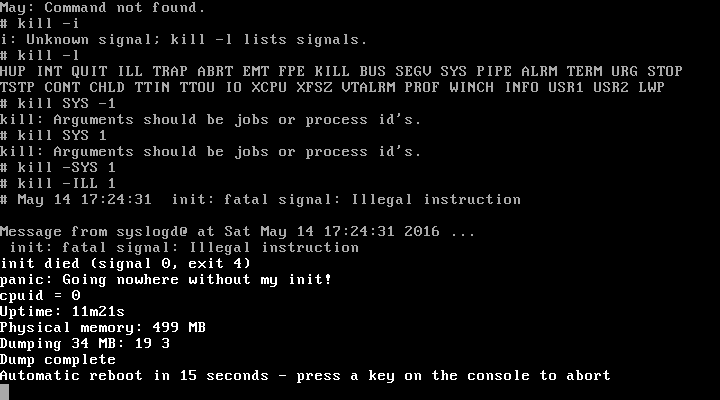
Illegal Opcode
An illegal opcode, also called an unimplemented operation, unintended opcode or undocumented instruction, is an instruction to a CPU that is not mentioned in any official documentation released by the CPU's designer or manufacturer, which nevertheless has an effect. Illegal opcodes were common on older CPUs designed during the 1970s, such as the MOS Technology 6502, Intel 8086, and the Zilog Z80. On these older processors, many exist as a side effect of the wiring of transistors in the CPU, and usually combine functions of the CPU that were not intended to be combined. On old and modern processors, there are also instructions intentionally included in the processor by the manufacturer, but that are not documented in any official specification. The effect of many illegal opcodes, on many processors, is just a trap to an error handler. However, some processors that trap for most illegal opcodes do not do so for some illegal opcodes, and some other processors do not check for il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operand
In mathematics, an operand is the object of a mathematical operation, i.e., it is the object or quantity that is operated on. Example The following arithmetic expression shows an example of operators and operands: :3 + 6 = 9 In the above example, '+' is the symbol for the operation called addition. The operand '3' is one of the inputs (quantities) followed by the addition operator, and the operand '6' is the other input necessary for the operation. The result of the operation is 9. (The number '9' is also called the sum of the augend 3 and the addend 6.) An operand, then, is also referred to as "one of the inputs (quantities) for an operation". Notation Expressions as operands Operands may be complex, and may consist of expressions also made up of operators with operands. :(3 + 5) \times 2 In the above expression '(3 + 5)' is the first operand for the multiplication operator and '2' the second. The operand '(3 + 5)' is an expression in itself, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opcode Database
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about Vulnerability (computer science), security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and Intrusion-detection system, IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company Rapid7. Its best-known sub-project is the open-source software, open-source Metasploit Framework, a tool for developing and executing Exploit (computer security), exploit code against a remote target machine. Other important sub-projects include the Opcode Database, shellcode archive and related research. The Metasploit Project includes Anti-computer forensics, anti-forensic and evasion tools, some of which are built into the Metasploit Framework. Metasploit is pre-installed in the Kali Linux operating system. History Metasploit was created by H. D. Moore in 2003 as a portable network tool using Perl. By 2007, the Metasploit Framework had been completely rewritten in Ruby (programming l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadget (machine Instruction Sequence)
Return-oriented programming (ROP) is a computer security exploit technique that allows an attacker to execute code in the presence of security defenses such as executable space protection and code signing. In this technique, an attacker gains control of the call stack to hijack program control flow and then executes carefully chosen machine instruction sequences that are already present in the machine's memory, called "gadgets". Each gadget typically ends in a return instruction and is located in a subroutine within the existing program and/or shared library code. Chained together, these gadgets allow an attacker to perform arbitrary operations on a machine employing defenses that thwart simpler attacks. Background Return-oriented programming is an advanced version of a stack smashing attack. Generally, these types of attacks arise when an adversary manipulates the call stack by taking advantage of a bug in the program, often a buffer overrun. In a buffer overrun, a function t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Intermediate Language
Common Intermediate Language (CIL), formerly called Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) or Intermediate Language (IL), is the intermediate language binary instruction set defined within the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) specification. CIL instructions are executed by a CLI-compatible runtime environment such as the Common Language Runtime. Languages which target the CLI compile to CIL. CIL is object-oriented, stack-based bytecode. Runtimes typically just-in-time compile CIL instructions into native code. CIL was originally known as Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) during the beta releases of the .NET languages. Due to standardization of C# and the CLI, the bytecode is now officially known as CIL. Windows Defender virus definitions continue to refer to binaries compiled with it as MSIL. General information During compilation of CLI programming languages, the source code is translated into CIL code rather than into platform- or processor-specific object code. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp (programming Language)
Lisp (historically LISP) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the read†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Virtual Machine
A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required in a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform. The JVM reference implementation is developed by the OpenJDK project as open source code and includes a JIT compiler called HotSpot. The commercially supported Java releases available from Oracle are based on the OpenJDK runtime. Eclipse OpenJ9 is another open source JVM for OpenJDK. JVM specification The Java virtual machine is an abstract (virtual) computer defined by a specification. It is a part of java runtime environment. The garbage-collection algorithm u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Class File
A Java class file is a file (with the filename extension A filename extension, file name extension or file extension is a suffix to the name of a computer file (e.g., .txt, .docx, .md). The extension indicates a characteristic of the file contents or its intended use. A filename extension is typically d ...) containing Java bytecode that can be executed on the Java virtual machine, Java Virtual Machine (JVM). A Java class file is usually produced by a Java compiler from Java (programming language), Java programming language source files ( files) containing Java Class (programming), classes (alternatively, other JVM languages can also be used to create class files). If a source file has more than one class, each class is compiled into a separate class file. JVMs are available for many platform (computing), platforms, and a class file compiled on one platform will execute on a JVM of another platform. This makes Java applications cross-platform, platform-independent. History On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |