|
Ocrelizumab
Ocrelizumab, sold under the brand name Ocrevus, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is a humanized anti- CD20 monoclonal antibody. It targets CD20 marker on B lymphocytes and hence is an immunosuppressive drug. Ocrelizumab binds to an epitope that overlaps with the epitope to which rituximab binds. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2017, and the first FDA approved drug for the primary progressive form of MS; it was discovered and developed and is marketed by Hoffmann–La Roche's subsidiary Genentech under the trade name Ocrevus. With the approval, the FDA also required the company to conduct several Phase IV clinical trials to better understand whether the drug is safe and effective in young people, cancer risks, and effects on pregnant women and children they might bear. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses In the US, ocrelizumab is indic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genentech
Genentech, Inc., is an American biotechnology corporation headquartered in South San Francisco, California. It became an independent subsidiary of Roche in 2009. Genentech Research and Early Development operates as an independent center within Roche. Historically, the company is regarded as the world's first biotechnology company. As of July 2021, Genentech employed 13,539 people. History The company was founded in 1976 by venture capitalist Robert A. Swanson and biochemist Herbert Boyer. Boyer is considered to be a pioneer in the field of recombinant DNA technology. In 1973, Boyer and his colleague Stanley Norman Cohen demonstrated that restriction enzymes could be used as "scissors" to cut DNA fragments of interest from one source, to be ligated into a similarly cut plasmid vector. While Cohen returned to the laboratory in academia, Swanson contacted Boyer to found the company. Boyer worked with Arthur Riggs and Keiichi Itakura from the Beckman Research Institute, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD20
B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is expressed on the surface of all B-cells beginning at the pro-B phase ( CD45R+, CD117+) and progressively increasing in concentration until maturity. In humans CD20 is encoded by the ''MS4A1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the membrane-spanning 4A gene family. Members of this nascent protein family are characterized by common structural features and similar intron/exon splice boundaries and display unique expression patterns among hematopoietic cells and nonlymphoid tissues. This gene encodes a B-lymphocyte surface molecule that plays a role in the development and differentiation of B-cells into plasma cells. This family member is localized to 11q12, among a cluster of family members. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants that encode the same protein. Function The protein has no known natural ligand and its function is to enable optimal B-cell immune response, specifically against T-independent antigens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-in-class Medication
A first-in-class medication is a pharmaceutical that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medications and reports on them annually, first-in-class is not considered a regulatory category. Although many first-in-class medications qualify as breakthrough therapies, Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapies and/or orphan drugs, first-in-class status itself has no regulatory effect. Examples Controversy Safety By definition, a first-in-class drug does not have the safety evidence from analogous products that not-first-in-class drugs would have. However, a study investigating recalls and warnings in relation to first-in-class drugs approved between 1997 and 2012 by Health Canada has found that first-in-class drugs actually have a more favourable benefit-to-harm ratio. Economics First-in-class drugs are often seen as commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's response to an infectious or noninfectious insult. Although the definition of SIRS refers to it as an "inflammatory" response, it actually has pro- and anti-inflammatory components. Presentation Complications SIRS is frequently complicated by failure of one or more organs or organ systems. The complications of SIRS include * Acute kidney injury * Shock * Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome Causes The causes of SIRS are broadly classified as infectious or noninfectious. Causes of SIRS include: * bacterial infections * severe malaria * trauma * burns * pancreatitis * ischemia * hemorrhage Other causes include: * Complications of surgery * Adrenal insufficiency * Pulmonary embolism * Complicated aortic aneurysm * Cardiac tamponade * Anaphylaxis * Drug overdose Diagnosis SIRS is a serious condition related to systemic inflammation, organ dysfunction, and organ fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune system (as can occur in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or when being treated with immunosuppressive drugs, as in cancer treatment), an altered microbiome (such as a disruption in gut microbiota), or breached integumentary barriers (as in penetrating trauma). Many of these pathogens do not necessarily cause disease in a healthy host that has a non-compromised immune system, and can, in some cases, act as commensals until the balance of the immune system is disrupted. Opportunistic infections can also be attributed to pathogens which cause mild illness in healthy individuals but lead to more serious illness when given the opportunity to take advantage of an immunocompromised host. Types of opportunistic infections A wide vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
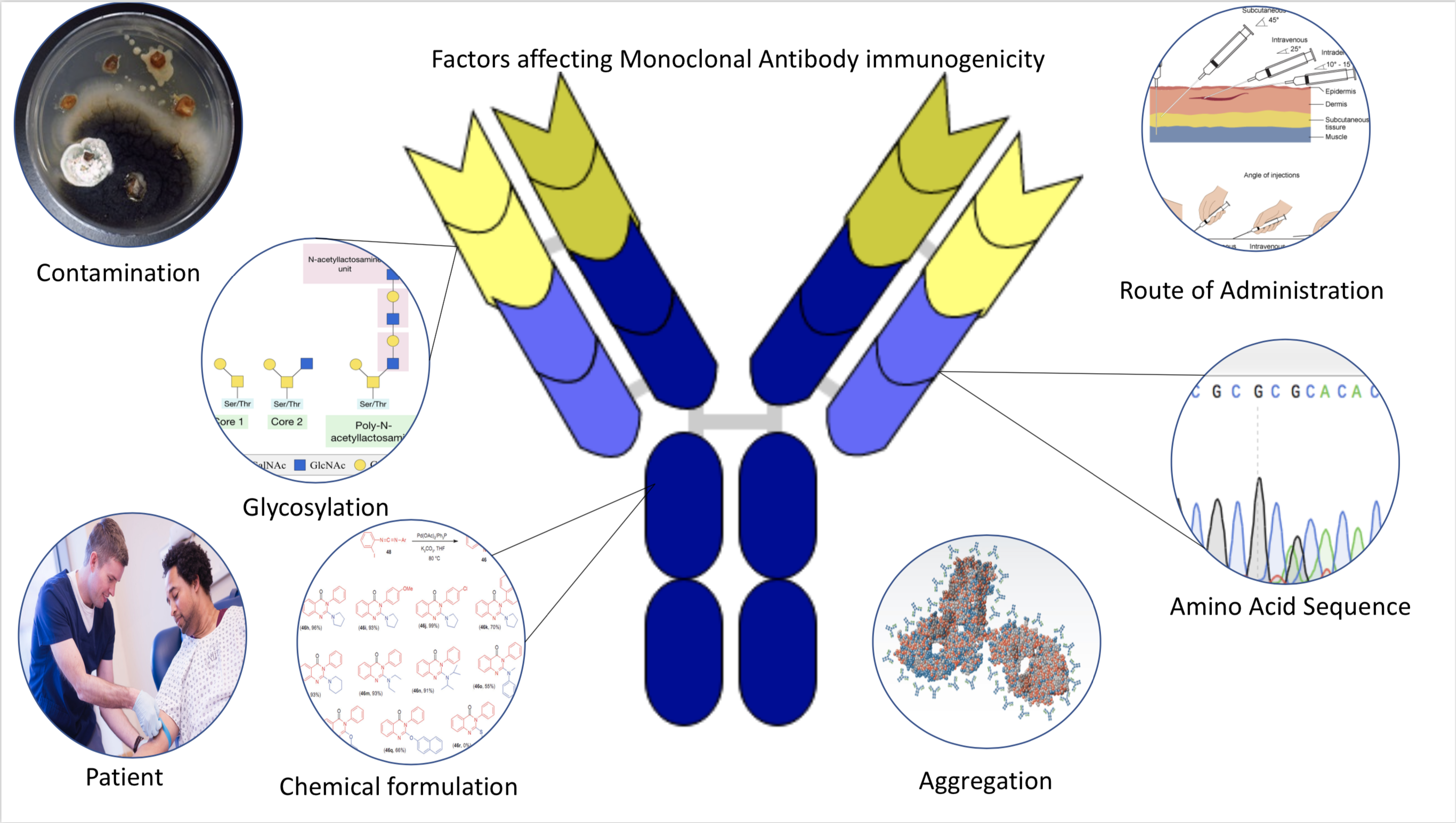
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New England Journal Of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one. History In September 1811, John Collins Warren, a Boston physician, along with James Jackson, submitted a formal prospectus to establish the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and Collateral Branches of Science'' as a medical and philosophical journal. Subsequently, the first issue of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' was published in January 1812. The journal was published quarterly. In 1823, another publication, the ''Boston Medical Intelligencer'', appeared under the editorship of Jerome V. C. Smith. The editors of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' purchased the weekly ''Intelligencer'' for $600 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement-dependent Cytotoxicity
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) is an effector function of IgG and IgM antibodies. When they are bound to surface antigen on target cell (e.g. bacterial or viral infected cell), the classical complement pathway is triggered by bonding protein C1q to these antibodies, resulting in formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC) and target cell lysis. Complement system is efficiently activated by human IgG1, IgG3 and IgM antibodies, weakly by IgG2 antibodies and it is not activated by IgG4 antibodies. It is one mechanism of action by which therapeutic antibodies or antibody fragments can achieve an antitumor effect. Use of CDC assays Therapeutic antibodies Development of antitumor therapeutic antibodies involves ''in vitro'' analysis of their effector functions including ability to trigger CDC to kill target cells. Classical approach is to incubate antibodies with target cells and source of complement ( serum). Then cell death is determined with several approaches: * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), also referred to as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, is a mechanism of cell-mediated immune defense whereby an effector cell of the immune system actively lyses a target cell, whose membrane-surface antigens have been bound by specific antibodies. It is one of the mechanisms through which antibodies, as part of the humoral immune response, can act to limit and contain infection. ADCC is independent of the immune complement system that also lyses targets but does not require any other cell. ADCC requires an effector cell which classically is known to be natural killer (NK) cells that typically interact with immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. However, macrophages, neutrophils and eosinophils can also mediate ADCC, such as eosinophils killing certain parasitic worms known as helminths via IgE antibodies. In general, ADCC has typically been described as the immune response to antibody-coated cells leading ultimately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
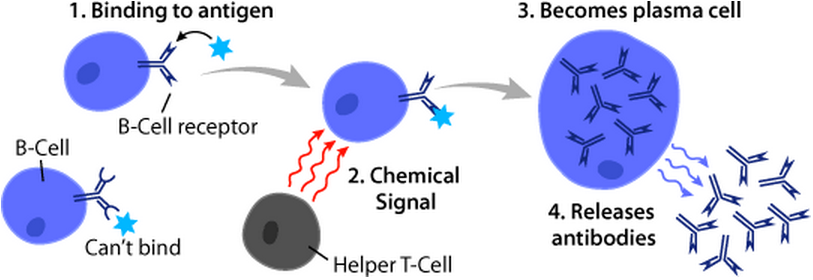
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppresive Drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)