|
Oviraptorosaur
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like skulls, with or without bony crests atop the head. They ranged in size from ''Caudipteryx'', which was the size of a turkey, to the 8-meter-long, 1.4-ton ''Gigantoraptor''. The group (along with all maniraptoran dinosaurs) is close to the ancestry of birds. Some researchers such as Maryanska ''et al'' (2002) and Osmólska ''et al.'' (2004) have proposed that they may represent primitive flightless birds.Osmólska, Halszka, Currie, Philip J., Brasbold, Rinchen (2004) "The Dinosauria" Weishampel, Dodson, Osmólska. "Chapter 8 Oviraptorosauria" University of California Press. The most complete oviraptorosaur specimens have been found in Asia. The North American oviraptorosaur record is sparse.Varricchio, D. J. 2001. Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Theropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigantoraptor
''Gigantoraptor'' () is a genus of large oviraptorosaur dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. It is known from the Iren Dabasu Formation of Inner Mongolia, where the first remains were found in 2005. ''Gigantoraptor'' was the largest-known oviraptorosaur, reaching in length and in body mass. It had an extensively pneumatized vertebral column and elongated arms and legs. Both femur and tibia measured over in length, an unusual trait among giant theropods. The lower jaws were Toothlessness, toothless and ended in a keratinous beak, as seen in other oviraptorosaurs. Though several oviraptorosaur species are known to have developed a full coat of feathers, ''Gigantoraptor'', due to its size, could have lost some of this integument. The genus is classified as an oviraptorosaurian dinosaur, a group of generally small feathered animals. Though it was originally found to represent a basal oviraptorid, subsequent analyses have shown it to be a caenagnathid. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisivosaurus
''Incisivosaurus'' ("incisor lizard") is a genus of small, probably herbivorous theropod dinosaurs from the early Cretaceous Period of what is now the People's Republic of China. The first specimen to be described (by Xu ''et al.'' in 2002), IVPP V13326, is a skull that was collected from the lowermost levels (the fluvial Lujiatun beds) of the Yixian Formation (dating to the Barremian stage about 126 million years ago) in the Sihetun area, near Beipiao City, in western Liaoning Province. The most significant, and highly unusual, characteristic of this dinosaur is its apparent adaptation to an herbivorous or omnivorous lifestyle. It was named for its prominent, rodent-like front teeth, which show wear patterns commonly found in plant-eating dinosaurs. The specific name ''gauthieri'' honors Dr. Jacques Gauthier, a pioneer of the phylogenetic method of classification. Description The initial description of ''Incisivosaurus'' by Xu ''et al.'' showed that the skull, which measures a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningyuansaurus Wangi
''Ningyuansaurus'' is a pennaraptoran dinosaur genus. It contains the single species ''Ningyuansaurus wangi'', known from a fossil specimen from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation (Aptian stage, 124.6 Ma ago) of Jianchang, western Liaoning Province, People's Republic of China. It was originally thought to be the basalmost species of oviraptorosaur, based on its long skull and a greater number of teeth in comparison to any other known oviraptorosaur. However, later research showed that it is a member of Halszkaraptorinae. The generic name ''Ningyuansaurus'' is derived from Ningyuan, an ancient name for Xingcheng City. The specific name honors Wang Qiuwu, the private owner of the specimen who donated it for scientific study. The specimen is now in the Confuciusornis Museum in Xingcheng. Description The only known fossil specimen of ''N. wangi'' is notable for having a large number of teeth compared to more advanced oviraptorosaurs, but the teeth in the back of the upper jaw (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenagnathidae
Caenagnathidae is a family of derived caenagnathoid dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and Asia. They are a member of the Oviraptorosauria, and relatives of the Oviraptoridae. Like other oviraptorosaurs, caenagnathids had specialized beaks, long necks, and short tails, and would have been covered in feathers. The relationships of caenagnathids were long a puzzle. The family was originally named by Raymond Martin Sternberg in 1940 as a family of flightless birds. The discovery of skeletons of the related oviraptorids revealed that they were in fact non-avian theropods, and the discovery of more complete caenagnathid remains revealed that ''Chirostenotes pergracilis'', originally named on the basis of a pair of hands, and ''Citipes elegans'', originally thought to be an ornithomimid, named from a foot, were caenagnathids as well. Discovery The name ''Caenagnathus'' (and hence Caenagnathidae) means "recent jaws"—when first discovered, it was thought that caenagnath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citipati
''Citipati'' (; meaning "funeral pyre lord") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. It is mainly known from the Ukhaa Tolgod locality at the Djadochta Formation, where the first remains were collected during the 1990s. The genus and type species ''Citipati osmolskae'' were named and described in 2001. A second species from the adjacent Zamyn Khondt locality may also exist. ''Citipati'' is one of the best-known oviraptorids thanks to a number of well-preserved specimens, including individuals found in Avian incubation, brooding positions atop nests of eggs, though most of them were initially referred to the related ''Oviraptor''. These nesting specimens have helped to solidify the link between non-avian dinosaurs and birds. ''Citipati'' was among the largest oviraptorids; it is estimated to have been around in length and to have weighed . Its skull was highly Skeletal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Of Birds
The scientific question of which larger group of animals birds evolved within has traditionally been called the "origin of birds". The present scientific consensus is that birds are a group of maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs that originated during the Mesozoic era. A close relationship between birds and dinosaurs was first proposed in the nineteenth century after the discovery of the primitive bird '' Archaeopteryx'' in Germany. Birds and extinct non-avian dinosaurs share many unique skeletal traits. Moreover, fossils of more than thirty species of non-avian dinosaur with preserved feathers have been collected. There are even very small dinosaurs, such as ''Microraptor'' and ''Anchiornis'', which have long, vaned arm and leg feathers forming wings. The Jurassic basal avialan '' Pedopenna'' also shows these long foot feathers. Paleontologist Lawrence Witmer concluded in 2009 that this evidence is sufficient to demonstrate that avian evolution went through a four-winged stage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuanyanglong
''Yuanyanglong'' (meaning " lovebird dragon") is an extinct genus of oviraptorosaurian theropod dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous Miaogou Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, ''Yuanyanglong bainian'', known from two partial skeletons. Discovery and naming The ''Yuanyanglong'' fossil material, was discovered in 2021 in sediments of the Miaogou Formation (Maortu locality) in the Gobi Desert of Chilantai, Inner Mongolia, China. Two incomplete skeletons were found in association on the same block, which are assumed to represent the same species based on comparable anatomy and body size. The holotype specimen, PV02476-1, consists of the pelvic girdle, the right hindlimb missing the foot, the pectoral girdle, the right forelimb missing the hand, several ribs, and dorsal and caudal vertebrae. The associated referred specimen, PV02476-2, includes an incomplete poorly-preserved skull, partial hindlimb without the foot, incomplete pelvis, several dorsal vertebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
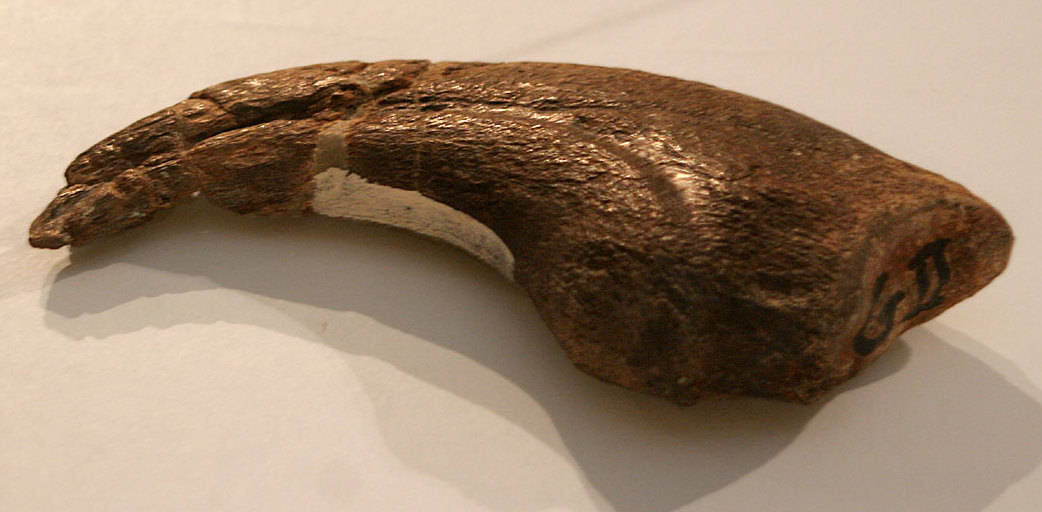
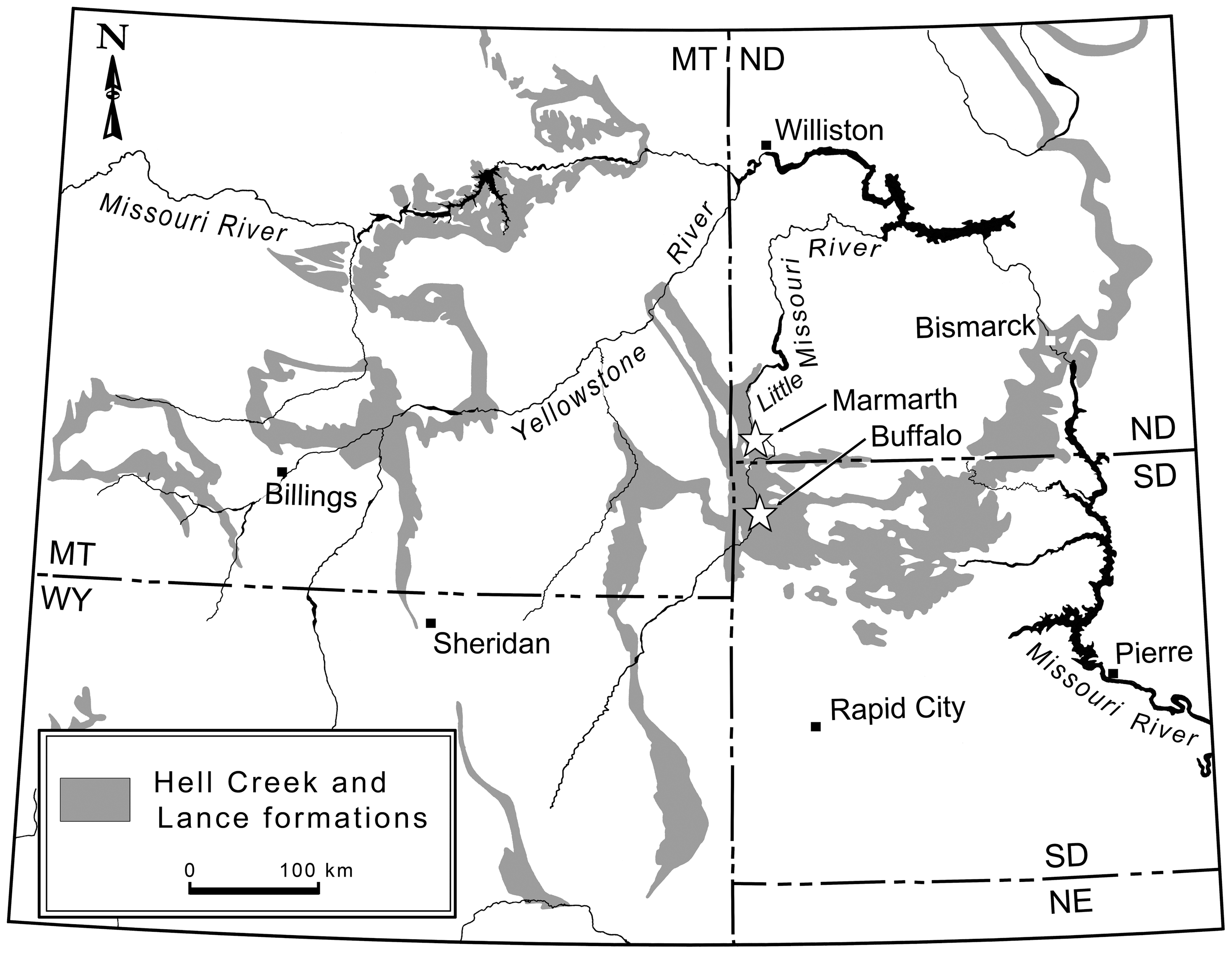
Anzu Wyliei
''Anzu'' (named for Anzû (mythology), Anzû, a bird-like Daemon (classical mythology), daemon in Ancient Mesopotamian religion) is a monospecific genus of caenagnathidae, caenagnathid dinosaur from North Dakota, South Dakota and Montana that lived during the Late Cretaceous (upper Maastrichtian stage, 67.2-66.0 Ma) in what is now the Hell Creek Formation. The type species and only species, ''Anzu wyliei'' is known from numerous skeletons that preserve skull, cranial and postcranial elements. It was named in 2014 in paleontology, 2014 by Matthew C. Lamanna, Hans-Dieter Sues, Emma R. Schachner, and Tyler R. Lyson. ''Anzu'' was listed as one of 2014’s "Top 10 New Species" discovered, with the findings being of significant scientific value. It was acknowledged again, in 2015, as an unprecedented discovery of scientific worth by the International Institute for Species Exploration. History of discovery In 1998, Fred Nuss of Nuss Fossils discovered the first two partial skeletons o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudipteryx
''Caudipteryx'' (meaning "tail feather") is a genus of small oviraptorosaur dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Early Cretaceous, around 124.6 million years ago. They were feathered and extremely birdlike in their overall appearance, to the point that some paleontologists suggested it was a bird. Two species have been described: ''C. zoui'' (the type species), in 1998, and ''C. dongi'', in 2000. It had a stout trunk, long legs and was probably a swift runner. The discovery of ''Caudipteryx'' has led to many intensive studies and debate over the relationship of birds and dinosaurs. History In 1997, several well-preserved dinosaur skeletons were recovered from the Jiulongsong Member of the Chaomidianzi Formation (now Jianshangou Bed of the Yixian Formation), at the Sihetun locality of Liaoning province, China. The fossils were later described in 1998 and used as the type specimens for the new dinosaur taxa ''Caudipteryx'' and '' Protarchaeopteryx''. ''Caudipteryx'' was ere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviraptoridae
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between one and two metres long in most cases, though some possible oviraptorids were enormous. Oviraptorids are currently known only from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, with the most well-known species and complete specimens found only in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia and northwestern China. Description The most characteristic feature of this group is the skull structure. Oviraptorids had short snouts and very deep mandibles. Some taxa (such as ''Citipati'', '' Corythoraptor'', ''Rinchenia'') had a midline crest on top of the skull, resembling that of a cassowary. Other distinguishing characteristics include a bony spike intruding on the mandibular fenestra, nostrils placed very high and far back on the snout, an extremely thin bony bar beneath the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avimimus
''Avimimus'' ( ), meaning "bird mimic" (Latin ''avis'' = bird + ''mimus'' = mimic), is a genus of oviraptorosaurian theropod dinosaur, named for its bird-like characteristics, that lived in the late Cretaceous in what is now Mongolia, around 85 to 70 million years ago. Discovery and species The remains of ''Avimimus'' were recovered by Russian paleontologists"Avimimus." In: Dodson, Peter & Britt, Brooks & Carpenter, Kenneth & Forster, Catherine A. & Gillette, David D. & Norell, Mark A. & Olshevsky, George & Parrish, J. Michael & Weishampel, David B. ''The Age of Dinosaurs''. Publications International, LTD. p. 130. . and officially described by Dr. Sergei Kurzanov in 1981. The ''Avimimus'' fossils were initially described as having come from the Djadokta Formation by Kurzanov; however, in a 2006 description of a new specimen, Watabe and colleagues noted that Kurzanov was probably mistaken about the provenance, and it is more likely that ''Avimimus'' hailed from the more re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |