|
Orbital Part Of Frontal Bone
The orbital or horizontal part of the frontal bone (''pars orbitalis'') consists of two thin triangular plates, the orbital plates, which form the vaults of the orbits, and are separated from one another by a median gap, the ethmoidal notch. Surfaces * The inferior surface of each orbital plate is smooth and concave, and presents, laterally, under cover of the zygomatic process, a shallow depression, the lacrimal fossa, for the lacrimal gland; near the nasal part is a depression, the fovea trochlearis, or occasionally a small trochlear spine, for the attachment of the cartilaginous pulley of the obliquus oculi superior. * The superior surface is convex, and marked by depressions for the convolutions of the frontal lobes of the brain, and faint grooves for the meningeal branches of the ethmoidal vessels. ** The ethmoidal notch separates the two orbital plates; it is quadrilateral, and filled, in the articulated skull, by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid. *** The margins o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid
The ethmoid bone (; from ) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbit (anatomy), orbits. The cubical (cube-shaped) bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital lamina of ethmoid bone, orbital plate and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
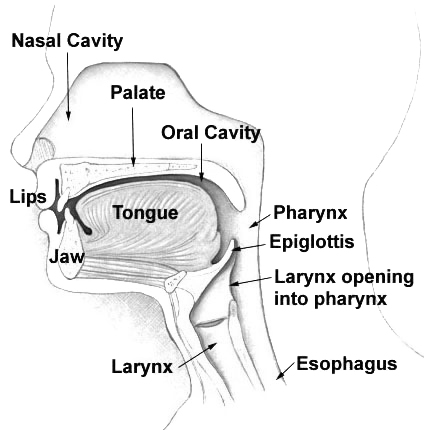
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia. Most of these ostia communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
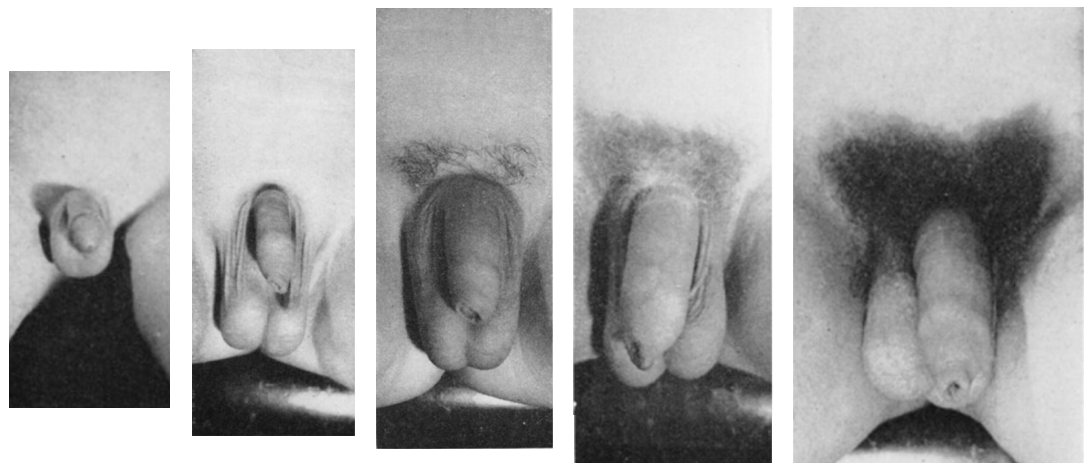
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
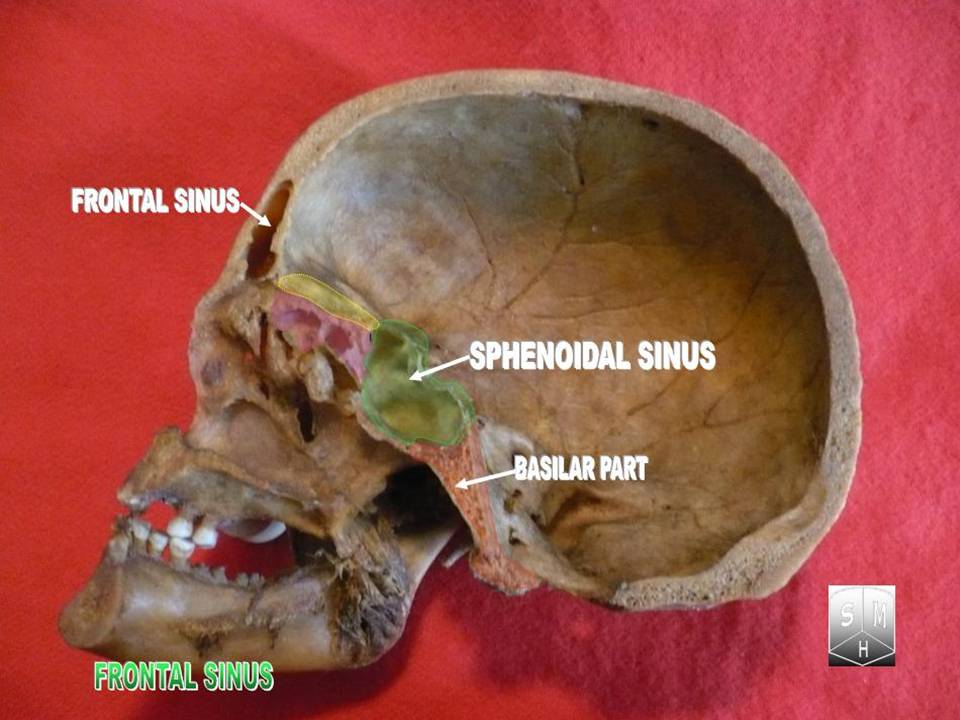
Frontal Air Sinuses
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Each frontal sinus extends into the squamous part of the frontal bone superiorly, and into the orbital part of frontal bone posteriorly to come to occupy the medial part of the roof of the orbit. Each sinus drains through an opening in its inferomedial part into the frontonasal duct. Vasculature The mucous membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Nerve
The ethmoidal nerves, which arise from the nasociliary nerve, supply the ethmoidal cells; the posterior branch leaves the orbital cavity through the posterior ethmoidal foramen and gives some filaments to the sphenoidal sinus. There are two ethmoidal nerves on each side of the face: * posterior ethmoidal nerve * anterior ethmoidal nerve The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1)). It arises in the orbit, and enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensor ... References External links ufl.edu Trigeminal nerve {{neuroanatomy-stub Otorhinolaryngology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasociliary Nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve. Structure Course The nasociliary nerve enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, through the common tendinous ring, and between the two heads of the lateral rectus muscle and between the superior and inferior rami of the oculomotor nerve. It passes across the optic nerve (CN II) along with the ophthalmic artery. It then runs obliquely beneath (inferior to) the superior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to the medial wall of the orbital cavity whereupon it emits the posterior ethmoidal nerve, and the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Branches Branches of the nasociliary nerve include: * posterior ethmoidal nerve * anterior ethmoidal nerve * long ciliary nerves * infratrochlear nerve * communicating branch to cil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Ethmoidal Foramen
The anterior ethmoidal foramen is a small opening in the ethmoid bone in the skull. Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The anterior ethmoidal foramen, situated about the middle of the lateral margin of the olfactory groove, transmits the anterior ethmoidal artery, vein and nerve. The anterior ethmoidal nerve, a branch of the nasociliary nerve, runs in a groove along the lateral edge of the cribriform plate In mammalian anatomy, the cribriform plate (Latin for lit. '' sieve-shaped''), horizontal lamina or lamina cribrosa is part of the ethmoid bone. It is received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. It s ... to the above-mentioned slit-like opening . References External links * () (#5) Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Air Cells
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities ("air cells"). The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. Structure The ethmoid air cells consist of numerous thin-walled cavities in the ethmoidal labyrinthOtorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Anniko, Springer, 2010, page 188 that represent invaginations of the mucous membrane of the nasal wall into the ethmoid bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Notch
The ethmoidal notch separates the two orbital plates; it is quadrilateral, and filled, in the articulated skull, by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid. The margins of the notch present several half-cells which, when united with corresponding half-cells on the upper surface of the ethmoid, complete the ethmoidal sinus The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small ...es. References Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |