|
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa. Flagella and other characteristics A common characteristic of opisthokonts is that flagellate cells, such as the sperm of most animals and the spores of the chytrid fungi, propel themselves with a single ''posterior'' flagellum. It is this feature that gives the group its name. In contrast, flagellate cells in other eukaryote groups propel themselves with one or more ''anterior'' flagella. Flagellate cells however have been secondarily lost in some opisthokont groups, including most of the fungi. Opisthokont characteristics include synthesis of extracellular chitin in exoskeleton, cyst/spore wall, or cell wall of filamentous growth and hyphae; the extracellular digestion of substrates with os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
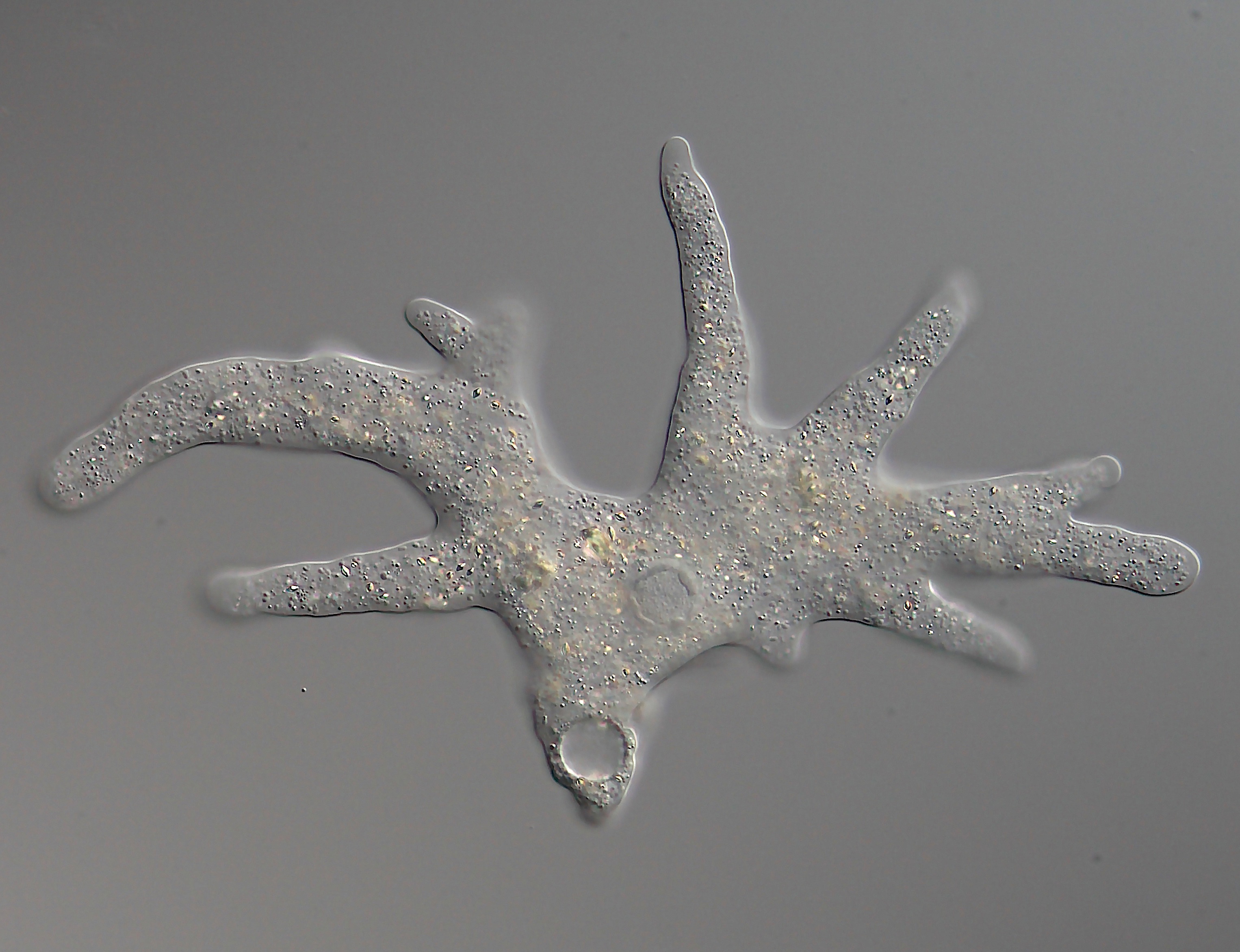
Nucleariida
The nucleariids, or nucleariid amoebae, are a group of amoebae that compose the sister clade of the fungi. Together, they form the clade Holomycota. They are aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine habitats, as well as in faeces. They are free-living phagotrophic predators that mostly consume algae and bacteria. Nucleariids are characterized by simple, spherical or flattened single-celled bodies with filopodia (fine, thread-like pseudopods), covered by a mucous coat. They lack flagella and microtubules. Inside the cytoplasm of some species are endosymbiotic proteobacteria. Some species are naked, with only the mucous coat as cover, while others (known as 'scaled' nucleariids) have silica-based or exogenous particles of various shapes. An exceptional nucleariid, ''Fonticula alba'', develops multicellular fruting bodies (sorocarps) for spore dispersal. It is one of several cases of independently evolved multicellularity within Opisthokonta, the clade that houses both Holo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holomycota
Holomycota or Nucletmycea are a basal Opisthokont clade as sister of the Holozoa. It consists of the Cristidiscoidea and the kingdom Fungi. The position of nucleariids, unicellular free-living phagotrophic amoebae, as the earliest lineage of Holomycota suggests that animals and fungi independently acquired complex multicellularity from a common unicellular ancestor and that the osmotrophic lifestyle (one of the fungal hallmarks) was originated later in the divergence of this eukaryotic lineage. Opisthosporidians is a recently proposed taxonomic group that includes aphelids, Microsporidia and Cryptomycota, three groups of endoparasites. '' Rozella'' ( Cryptomycota) is the earliest diverging fungal genus in which chitin has been observed at least in some stages of their life cycle, although the chitinous cell wall (another fungal hallmark) and osmotrophy originated in a common ancestor of Blastocladiomycota and Chytridiomycota, which still contain some ancestral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holozoa
Holozoa () is a clade of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. Together they amount to more than 1.5 million species of purely heterotrophic organisms, including around 300 unicellular species. It consists of various subgroups, namely Metazoa (or animals) and the protists Choanoflagellata, Filasterea, Pluriformea and Ichthyosporea. Along with fungi and some other groups, Holozoa is part of the Opisthokonta, a supergroup of eukaryotes. Choanofila was previously used as the name for a group similar in composition to Holozoa, but its usage is discouraged now because it excludes animals and is therefore paraphyletic. The holozoan protists play a crucial role in understanding the evolutionary steps leading to the emergence of multicellular animals from single-celled ancestors. Recent genomic studies have shed light on the evolutionary relationships between the various holozoan lineages, revealin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filasterea
Filasterea is a proposed basal Filozoan clade of single-celled ameboid eukaryotes that includes '' Ministeria'' and '' Capsaspora''. It is a sister clade to the Choanozoa in which the Choanoflagellatea and Animals appeared, originally proposed by Shalchian-Tabrizi et al. in 2008, based on a phylogenomic analysis with 78 genes. Filasterea was found to be the sister-group to the clade composed of Metazoa and Choanoflagellata within the Opisthokonta, a finding that has been further corroborated with additional, more taxon-rich, phylogenetic analyses. Etymology From Latin ''filum'' meaning "thread" and Greek ''aster'' meaning "star", it indicates the main morphological features shared by all their integrants: small, rounded amoeboids with a mononucleated cellular body, covered in long and radiating cell protrusions known as filopodia. These filopodia may be involved in substrate adhesion and capture of prey. Applications There are currently cultures from two filasterean species: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
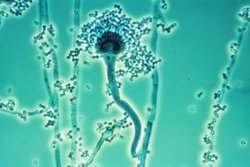
Mesomycetozoea
The Ichthyosporea (or DRIP clade, or Mesomycetozoea) are a small group of Opisthokonta in Eukaryota (formerly protists), mostly parasites of fish and other animals. Significance They are not particularly distinctive morphologically, appearing in host tissues as enlarged spheres or ovals containing spores, and most were originally classified in various groups as fungi, protozoa, or colorless algae. However, they form a coherent group on molecular trees, closely related to both animals and fungi and so of interest to biologists studying their origins. In a 2008 study they emerge robustly as the sibling-group of the clade Filozoa, which includes the animals. Huldtgren et al., following x-ray tomography of microfossils of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation, has interpreted them as mesomycetozoan spore capsules. Terminology The name DRIP is an acronym for the first protozoa identified as members of the group, Cavalier-Smith Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, Royal Society, FRS, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusomonadida
The apusomonads (family Apusomonadidae) are a group of protozoan zooflagellates that glide on surfaces, and mostly consume prokaryotes. They are of particular evolutionary interest because they appear to be the sister group to the Opisthokonts, the clade that includes both animals and fungi. Together with the Breviatea, these form the Obazoa clade. Characteristics Apusomonads are small gliding heterotrophic biflagellates (i.e. with two flagella) that possess a proboscis, formed partly or entirely by the anterior flagellum surrounded by a membranous sleeve. There is a pellicle under the dorsal cell membrane that extends into the proboscis sleeve and into a skirt that covers the sides of the cell. Apusomonads present two different cell plans: *Derived cell plan, represented by '' Apusomonas'', with a round cell body and a mastigophore, a projection of the cell containing both basal bodies at its end. *"''Amastigomonas''-like" cell plan, with an oval or oblong cell that gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclearia Thermophila
''Nuclearia'' is a genus of nucleariid The nucleariids, or nucleariid amoebae, are a group of amoebae that compose the sister clade of the fungi. Together, they form the clade Holomycota. They are aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine habitats, as well as in faeces. They ... amoebae with filose pseudopodia and discoid mitochondrial cristae. Nominal species treated as members of the genus include: * ''Astrodisculus affinis'' Schouteden 1905 * ''Astrodisculus araneiformis'' Schewiakoff 1893 * ''Astrodisculus laciniatus'' Penard 1904 'Chlamydaster lacinatus'' (Penard 1904) Rainer 1968* ''Astrodisculus marinus'' Kufferath 1952 * ''Astrodisculus minutus'' Greeff 1869 * ''Heliophrys variabilis'' * ''Nuclearina similis'' * ''N. amphizonellae'' Penard 1917 * ''N. conspicua'' West 1903 * ''Nuclearia delicatula'' Cienkowsky 1865 * ''N. lohmanni'' Kufferath 1952 * ''N. pseudotenelloides'' * ''N. flavescens'' (Greef 1869) Patterson 1984 'Astrodisculus flavescens'' Greeff 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obazoa
Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa (which together form Amorphea). The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadidae, the group's three constituent clades. Determining the placement of Breviatea and Apusomonadida and their properties is of interest for the development of the opisthokonts in which the main lineages of animals and fungi A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ... emerged. The relationships among opisthokonts, breviates and apusomonads are not conclusively resolved (as of 2018), though Breviatea is usually inferred to be the most basal of the three lineages. The phylogeny of the Obazoa is shown in the cladogram. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22087764 Amorphea taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, several derivations of the term "flagellate" (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellate") are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic animals, a flagellate is an organism with one or more flagella. Some cells in other animals may be flage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breviata
''Breviata anathema'' is a single-celled flagellate amoeboid eukaryote, previously studied under the name '' Mastigamoeba invertens''. The cell lacks mitochondria, much like the pelobionts to which the species was previously assigned, but has remnant mitochondrial genes, and possesses an organelle believed to be a modified anaerobic mitochondrion, similar to the mitosomes and hydrogenosomes found in other eukaryotes that live in low-oxygen environments. Early molecular data placed ''Breviata'' in the Amoebozoa, but without obvious affinity to known amoebozoan groups. More recently, phylogenomic analysis has shown that the class Breviatea is a sister group to the Opisthokonta and Apusomonadida. Together, these three groups form the clade Obazoa Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa (which together form Amorphea). The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadidae, the group's three constituent clades. Determining the place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below Domain (biology), domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called Phylum, phyla (singular phylum). Traditionally, textbooks from Canada and the United States have used a system of #Six kingdoms, six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungus, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria or Eubacteria), while textbooks in other parts of the world, such as Bangladesh, Brazil, Greece, India, Pakistan, Spain, and the United Kingdom have used #Five kingdoms, five kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not Monophyly, monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the Lineal descendant, descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, ''funga'' (for fungi) are also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |