|
Opensource
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of open-source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open-source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open-source appropriate technology, and open-source drug discovery. Open source promotes universal access via an open-source or free license to a product's design or blueprint, and universal redistribution of that design or blueprint. Before the phrase ''open source'' became widely adopted, developers and producers have used a variety of other terms. ''Open source'' gaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software. Open-source software development can bring in diverse perspectives beyond those of a single company. A 2008 report by the Standish Group stated that adoption of open-source software models has resulted in savings of about $60 billion per year for consumers. Open source code can be used for studying and allows capable end users to adapt software to their personal needs in a similar way user scripts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software Movement
The open-source-software movement is a movement that supports the use of open-source licenses for some or all software, as part of the broader notion of open collaboration. The open-source movement was started to spread the concept/idea of open-source software. Programmers who support the open-source-movement philosophy contribute to the open-source community by voluntarily writing and exchanging programming code for software development.Wyllys, R.E. (2000)Overview of the Open-Source Movement Retrieved November 22, 2009, from The University of Texas at Austin Graduate School of Library & Information Science The term "open source" requires that no one can discriminate against a group in not sharing the edited code or hinder others from editing their already-edited work. This approach to software development allows anyone to obtain and modify open-source code. These modifications are distributed back to the developers within the open-source community of people who are working with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software License
A software license is a legal instrument (usually by way of contract law, with or without printed material) governing the use or redistribution of software. Under United States copyright law, all software is copyright protected, in both source code and object code forms, unless that software was developed by the United States Government, in which case it cannot be copyrighted. Authors of copyrighted software can donate their software to the public domain, in which case it is also not covered by copyright and, as a result, cannot be licensed. A typical software license grants the licensee, typically an end-user, permission to use one or more copies of software in ways where such a use would otherwise potentially constitute copyright infringement of the software owner's exclusive rights under copyright. Software licenses and copyright law Most distributed software can be categorized according to its license type (see table). Two common categories for software under cop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
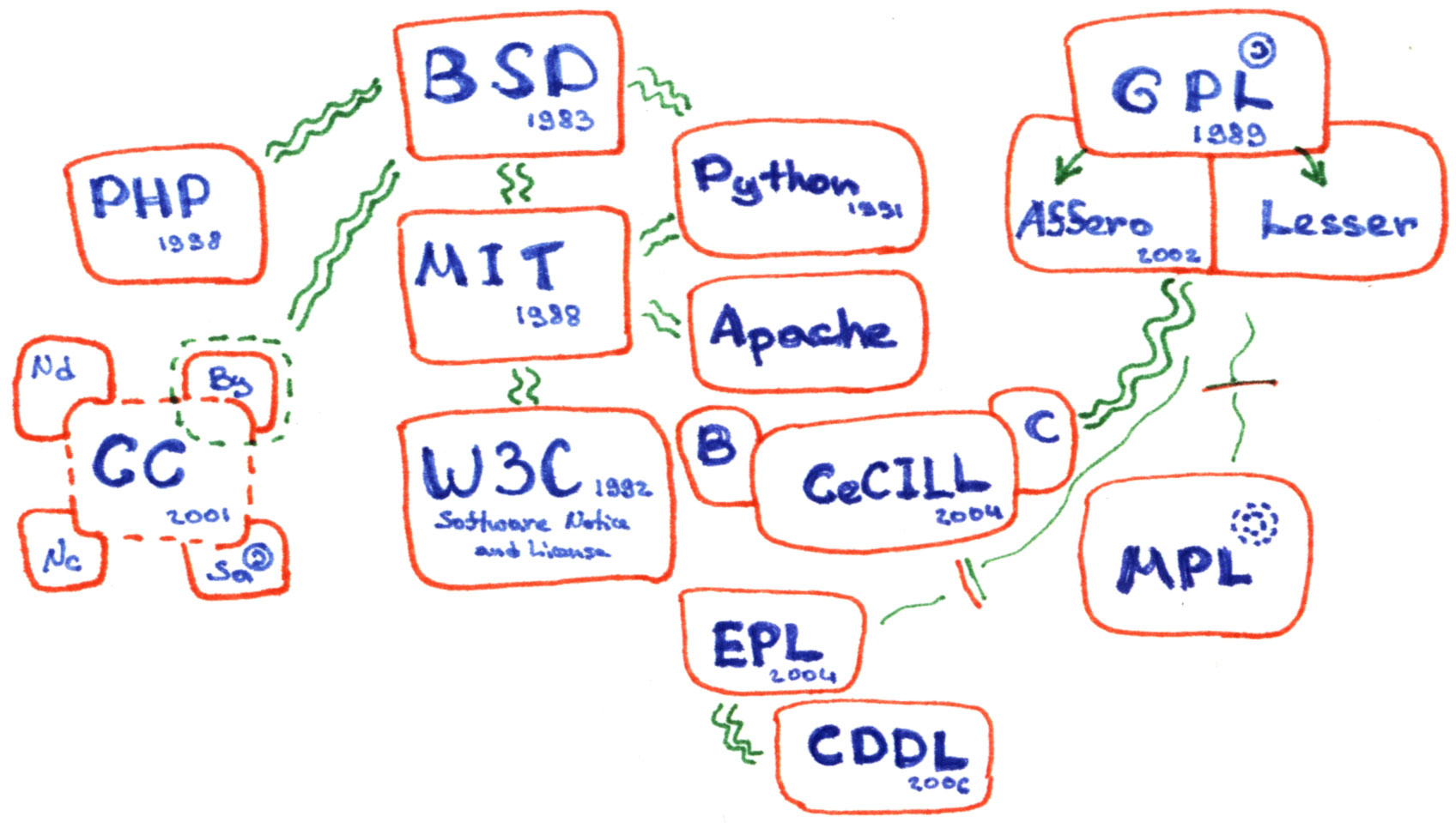
Open-source License
An open-source license is a type of license for computer software and other products that allows the source code, blueprint or design to be used, modified and/or shared under defined terms and conditions. This allows end users and commercial companies to review and modify the source code, blueprint or design for their own customization, curiosity or troubleshooting needs. Open-source licensed software is mostly available free of charge, though this does not necessarily have to be the case. Licenses which only permit non-commercial redistribution or modification of the source code for personal use only are generally not considered as open-source licenses. However, open-source licenses may have some restrictions, particularly regarding the expression of respect to the origin of software, such as a requirement to preserve the name of the authors and a copyright statement within the code, or a requirement to redistribute the licensed software only under the same license (as in a copyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting his or her freedoms. It is often contrasted with Open-source software, open-source or free software. For this reason, it is also known as non-free software or closed-source software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s computers—large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than Sales, sold. Service and all software available were usually supplied by manufacturers without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free License
A free license or open license is a license which allows others to reuse another creator’s work as they wish. Without a special license, these uses are normally prohibited by copyright, patent or commercial license. Most free licenses are worldwide, royalty-free, non-exclusive, and perpetual (see copyright durations). Free licenses are often the basis of crowdsourcing and crowdfunding projects. The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the hacker culture of the 1970s public domain software ecosystem, the social and political free software movement (since 1980) and the open source movement (since the 1990s). These rights were codified by different groups and organizations for different domains in Free Software Definition, Open Source Definition, Debian Free Software Guidelines, Definition of Free Cultural Works and The Open Definition. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Vehicle Manufacturers Association
The Automobile Manufacturers Association was a trade group of automobile manufacturers which operated under various names in the United States from 1911 to 1999. A different group called the Automobile Manufacturers' Association was active in the very early 1900s, but then dissolved. Another early group was the Association of Licensed Automobile Manufacturers, formed in 1903 and which was involved in licensing and collecting royalties from the George Baldwin Selden engine patent. Henry Ford effectively defeated the patent in court in 1911 and the Association of Licensed Automobile Manufacturers dissolved. However, the same manufacturers regrouped later in 1911 and formed the Automobile Board of Trade. In 1913, this became the National Automobile Chamber of Commerce. In 1934, this group renamed itself to the Automobile Manufacturers Association. This was the name the group had the longest and became the best known by. It focused upon establishing a code for fair competition. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of mass production. By creating the first automobile that middle-class Americans could afford, he converted the automobile from an expensive luxury into an accessible conveyance that profoundly impacted the landscape of the 20th century. His introduction of the Ford Ford Model T, Model T automobile revolutionized transportation and American Industry (manufacturing), industry. As the Ford Motor Company owner, he became one of the richest and best-known people in the world. He is credited with "Fordism", the mass production of inexpensive goods coupled with high wages for workers. Ford had a global vision, with consumerism as the key to peace. His intense commitment to systematically lowering costs resulted in many technical and business innov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George B
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Cycle
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular thing. This contrasts with a monopsony which relates to a single entity's control of a market to purchase a good or service, and with oligopoly and duopoly which consists of a few sellers dominating a market. Monopolies are thus characterized by a lack of economic competition to produce the good or service, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |