|
Oogonia
An oogonium (: oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes. In the mammalian fetus Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells. In humans they start to develop between weeks 4 and 8 and are present in the fetus between weeks 5 and 30. Structure Normal oogonia in human ovaries are spherical or ovoid in shape and are found amongst neighboring somatic cells and oocytes at different phases of development. Oogonia can be distinguished from neighboring somatic cells, under an electron microscope, by observing their nuclei. Oogonial nuclei contain randomly dispersed fibrillar and granular material whereas the somatic cells have a more condensed nucleus that creates a darker outline under the microscope. Oogonial nuclei also contain dense prominent nucleoli. The chromosomal material in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo meiosis, followed by cellular differentiation into mature gametes, either eggs or sperm. Unlike animals, plants do not have germ cells designated in early development. Instead, germ cells can arise from somatic cells in the adult, such as the floral meristem of flowering plants. Introduction Multicellular eukaryotes are made of two fundamental cell types: germ and somatic cells. Germ cells produce gametes and are the only cells that can undergo meiosis as well as mitosis. Somatic cells are all the other cells that form the building blocks of the body and they only divide by mitosis. The lineage of germ cells is called the germline. Germ cell specification begins during cleavage in many animals or in the epiblast during gastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
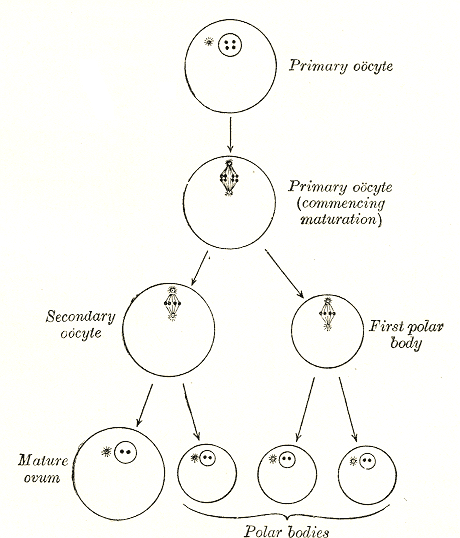
Oogenesis
Oogenesis () or ovogenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated before birth during embryonic development. Oogenesis in non-human mammals In mammals, the first part of oogenesis starts in the germinal epithelium, which gives rise to the development of ovarian follicles, the functional unit of the ovary. Oogenesis consists of several sub-processes: oocytogenesis, ootidogenesis, and finally maturation to form an ovum (oogenesis proper). Folliculogenesis is a separate sub-process that accompanies and supports all three oogenetic sub-processes. Oogonium —(Oocytogenesis)—> Primary Oocyte —(Meiosis I)—> First Polar body (Discarded afterward) + Secondary oocyte —(Meiosis II)—> Second Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Ovum Oocyte meiosis, important to all animal life cycles yet unlike all other instances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genital Ridge
In embryology, the genital ridge (genital fold or gonadal ridge) is the developmental precursor to the gonads. The genital ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic cells. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of cells (pre- granulosa cells). The genital ridge appears at approximately five weeks, and gives rise to the sex cords. Associated genes Genes associated with the developing gonad can be categorized into those that form the sexually indifferent gonad, those that determine whether the indifferent gonad will differentiate as male or female, and those that promote differentiation into male or female parts. Genes that form the sexually indifferent gonad are '' SF1'' and ''WT1''. Genes that determine sex are '' SRY'', ''SOX9'', and '' DAX1''. Genes driving the differentiation into male or female structures are ''SF1'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the trophectoderm. This layer surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid-filled cavity or lumen known as the blastocoel. In the late blastocyst, the trophectoderm is known as the trophoblast. The trophoblast gives rise to the chorion and amnion, the two fetal membranes that surround the embryo. The placenta derives from the embryonic chorion (the portion of the chorion that develops villi) and the underlying uterine tissue of the mother. The corresponding structure in non-mammalian animals is an undifferentiated ball of cells called the blastula. In humans, blastocyst formation begins about five days after fertilization when a fluid-filled cavity opens up in the morula, the early embryonic stage of a ball of 16 cells. The blastocyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomes
Ribosomes () are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anticodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins into membrane-bound Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and Endocytosis, endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. The Golgi apparatus was identified in 1898 by the Italian biologist and pathologist Camillo Golgi. The organelle was later named after him in the 1910s. Discovery Because of its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |