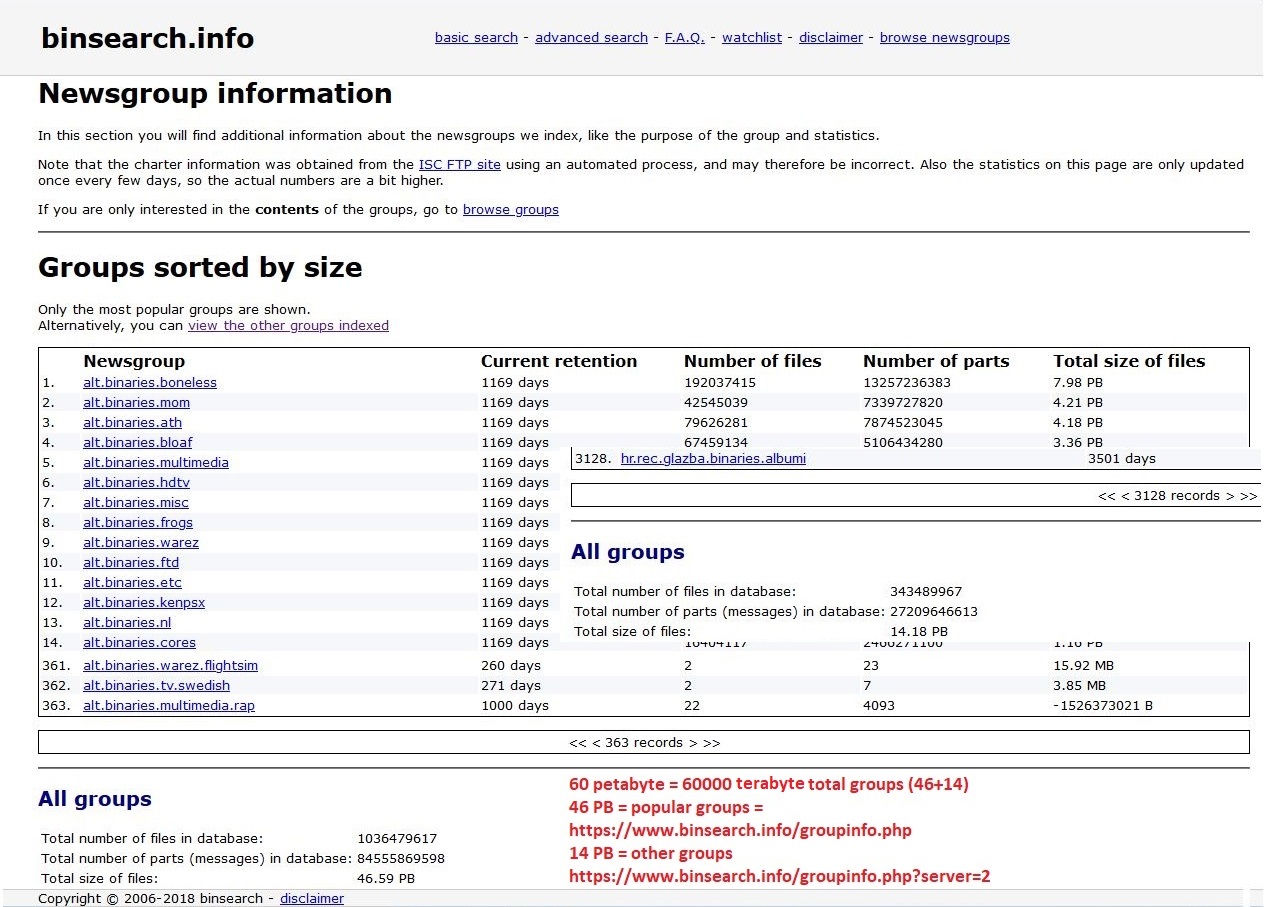
|
News Group
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) protocol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Repository
A software repository, or repo for short, is a storage location for software packages. Often a table of contents is also stored, along with metadata. A software repository is typically managed by source control or repository managers. Package managers allow automatically installing and updating repositories (sometimes called "packages"). Overview Many software publishers and other organizations maintain servers on the Internet for this purpose, either free of charge or for a subscription fee. Repositories may be solely for particular programs, such as CPAN for the Perl programming language, or for an entire operating system. Operators of such repositories typically provide a package management system, tools intended to search for, install and otherwise manipulate software packages from the repositories. For example, many Linux distributions use Advanced Packaging Tool (APT), commonly found in Debian based distributions, or yum found in Red Hat based distributions. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Off-topic
In the context of mailing lists, discussion groups, discussion forums, bulletin boards, newsgroups, and wikis a contribution is off-topic if it is not within the bounds of the current discussion, and on-topic if it is. Even on very specialized forums and lists, off-topic posting is not necessarily frowned upon, but a common netiquette convention is to mark a new off-topic posting or email by beginning it with "OT" The Tolkien Newsgroups FAQ - for example in a forum discussing the op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Completion Rate
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terabytes
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as The Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Client
A newsreader is an application program that reads articles on Usenet distributed throughout newsgroups. Newsreaders act as clients which connect to a news server, via the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), to download articles and post new articles. In addition to text-based articles, Usenet is also used to distribute binary files, generally in dedicated "binaries" newsgroups. The term ''newsreader'' is sometimes (erroneously) used interchangeably with ''news aggregator''. Newsreaders that help users to adhere to the established conventions of Usenet, known as netiquette, are evaluated by the Good Netkeeping Seal of Approval (GNKSA). Types of newsreaders There are several different types of newsreaders, depending on the type of service the user needs—whether intended primarily for discussion or for downloading files posted to the alt.binaries hierarchy: ; Desktop newsreaders : Designed to integrate well with common GUI environments, and often integrated with a web brows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YEnc
yEnc is a binary-to-text encoding scheme for transferring binary files in messages on Usenet or via e-mail. It reduces the overhead over previous US-ASCII-based encoding methods by using an 8-bit encoding method. yEnc's overhead is often (if each byte value appears approximately with the same frequency on average) as little as 1–2%, compared to 33–40% overhead for 6-bit encoding methods like uuencode and Base64. yEnc was initially developed by Jürgen Helbing, and its first release was early 2001. By 2003 yEnc became the de facto standard encoding system for binary files on Usenet. The name yEncode is a wordplay on ''"Why encode?"'', since the idea is to only encode characters if it is absolutely required to adhere to the message format standard. How yEnc works Usenet and email message bodies were intended to contain only ASCII characters ( or ). Most competing encodings represent binary files by converting them into printable ASCII characters, because the range of printabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base64
In computer programming, Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes that represent binary data (more specifically, a sequence of 8-bit bytes) in sequences of 24 bits that can be represented by four 6-bit Base64 digits. Common to all binary-to-text encoding schemes, Base64 is designed to carry data stored in binary formats across channels that only reliably support text content. Base64 is particularly prevalent on the World Wide Web where one of its uses is the ability to embed image files or other binary assets inside textual assets such as HTML and CSS files. Base64 is also widely used for sending e-mail attachments. This is required because SMTP – in its original form – was designed to transport 7-bit ASCII characters only. This encoding causes an overhead of 33–37% (33% by the encoding itself; up to 4% more by the inserted line breaks). Design Each Base64 digit can take on 64 different values, encoding 6 bits of data. Which characters are chosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codec
A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder. In electronic communications, an endec is a device that acts as both an encoder and a decoder on a signal or data stream, and hence is a type of codec. ''Endec'' is a portmanteau of encoder/decoder. A coder or encoder encodes a data stream or a signal for transmission or storage, possibly in encrypted form, and the decoder function reverses the encoding for playback or editing. Codecs are used in videoconferencing, streaming media, and video editing applications. History In the mid-20th century, a codec was a device that coded analog signals into digital form using pulse-code modulation (PCM). Later, the name was also applied to software for converting between digital signal formats, including companding functions. Examples An audio codec converts analog audio signals into digital signals for transmission or encodes them for storage. A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character Set
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as "code points" and collectively comprise a "code space", a "code page", or a "character map". Early character codes associated with the optical or electrical telegraph could only represent a subset of the characters used in written languages, sometimes restricted to upper case letters, numerals and some punctuation only. The low cost of digital representation of data in modern computer systems allows more elaborate character codes (such as Unicode) which represent most of the characters used in many written languages. Character encoding using internationally accepted standards permits worldwide interchange of text in electronic form. History The history of character codes illustrates the evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leech (computing)
In computing and specifically in Internet slang, a leech is one who benefits, usually deliberately, from others' information or effort but does not offer anything in return, or makes only token offerings in an attempt to avoid being called a leech. In economics, this type of behavior is called "free riding" and is associated with the free rider problem. The term originated in the bulletin board system era, when it referred to users that would download files and upload nothing in return. Depending on context, leeching does not necessarily refer to ''illegal'' use of computer resources, but often instead to ''greedy'' use according to etiquette: to wit, using too much of what is freely given without contributing a reasonable amount back to the community that provides it. The word is also used without any pejorative connotations, simply meaning to download large sets of information: for example the offline readerbr>Leech the Usenet newsreader NewsLeecher, the audio recording sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. The concept has inspired new structures and philosophies in many areas of human interaction. In such social contexts, peer-to-peer as a meme refers to the egalitarian so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |