|
Noisy Market Hypothesis
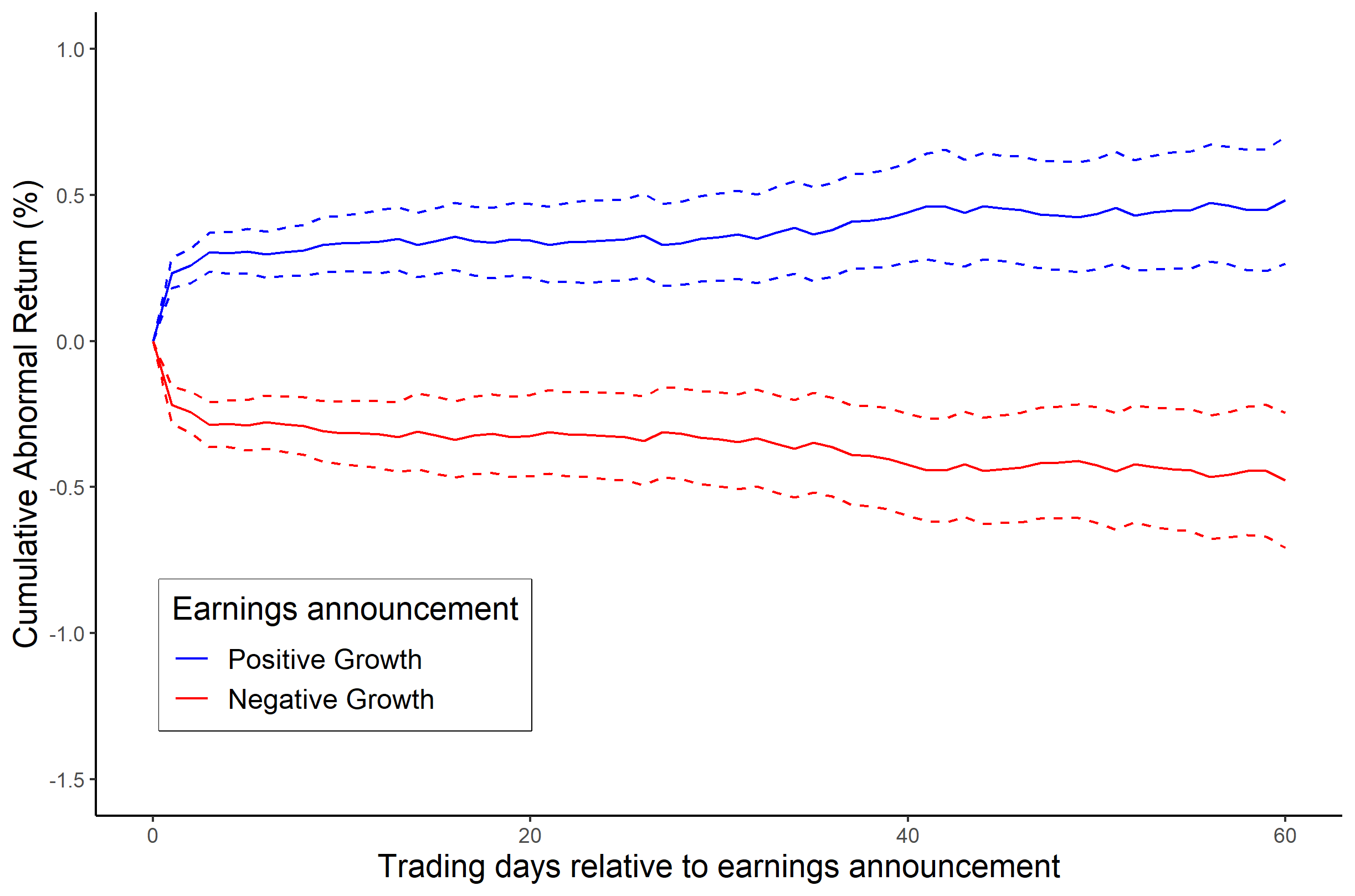
In finance, the noisy market hypothesis contrasts the efficient-market hypothesis in that it claims that the prices of securities are not always the best estimate of the true underlying value of the firm. It argues that prices can be influenced by speculators and momentum traders, as well as by insiders and institutions that often buy and sell stocks for reasons unrelated to fundamental value, such as for diversification, liquidity and taxes. These temporary shocks referred to as "noise" can obscure the true value of securities and may result in mispricing of these securities, potentially for many years. , |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient-market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum Trader
Momentum investing is a system of buying stocks or other security (finance), securities that have had high returns over the past three-to-twelve months, and selling those that have had poor returns over the same period. While momentum investing is well-established as a phenomenon no consensus exists about the explanation for this strategy, and economists have trouble reconciling momentum with the efficient market hypothesis and random walk hypothesis. Two main hypotheses have been submitted to explain the momentum effect in terms of an efficient market. In the first, it is assumed that momentum investors bear significant Financial risk, risk for assuming this strategy, and, therefore, the high returns are a compensation for the risk. Momentum strategies often involve disproportionately trading in stocks with high bid–ask spreads; thus, it is important to take transactions costs into account when evaluating momentum profitability. The second theory assumes that momentum investors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise (economic)
Economic noise, or simply noise, describes a theory of pricing developed by Fischer Black. Black describes noise as the opposite of information: hype, inaccurate ideas, and inaccurate data. His theory states that noise is everywhere in the economy and we can rarely tell the difference between it and information. Noise has two broad implications. *It allows speculative trading to occur (see below). *It is indicative of market inefficiency. Loudon and Della Bitta (1988) refer to noise as “a type of disruption in the communication process” and go further stating that "each state of the communication process is susceptible to (this) message distortion." (As cited in Wu & Newell, 2003). Therefore, we can say that noise is a disruption within the communication process and can be found in all forms within the communication process. and in a procces have a something special, because they have a same synonym. Some examples of noise could be distortion of a television advertisement or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvi Bodie
Zvi Bodie (born April 27, 1943) is an American economist, author and professor. He was the Norman and Adele Barron Professor of Management at Boston University, teaching finance at Questrom for 43 years before retiring in 2015. His textbook, ''Investments'', (with Kane and Marcus) is the market leader and is used in the certification programs of the CFA Institute and the Society of Actuaries. Bodie's work has centered on pension finance and investment strategy. He continues to do consulting work and media interviews. Education and background Bodie holds a Ph.D. in economics (1975) from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, a M.A. in economics (1970) from the Hebrew University, and a B.A. with Honors in philosophy (1965) from Brooklyn College. He has served on the finance faculty at the Harvard Business School and MIT Sloan School of Management. Bodie was on the editorial board of the ''Journal of Pension Economics and Finance'', and served as an advisory member to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGraw Hill Education
McGraw Hill is an American education science company that provides educational content, software, and services for students and educators across various levels—from K-12 to higher education and professional settings. They produce textbooks, digital learning tools, and adaptive technology to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. It is one of the "big three" educational publishers along with Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson Education. McGraw Hill also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888, when James H. McGraw, co-founder of McGraw Hill, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' (''WSJ''), also referred to simply as the ''Journal,'' is an American newspaper based in New York City. The newspaper provides extensive coverage of news, especially business and finance. It operates on a subscription model, requiring readers to pay for access to most of its articles and content. The ''Journal'' is published six days a week by Dow Jones & Company, a division of News Corp. As of 2023, ''The'' ''Wall Street Journal'' is the largest newspaper in the United States by print circulation, with 609,650 print subscribers. It has 3.17 million digital subscribers, the second-most in the nation after ''The New York Times''. The newspaper is one of the United States' newspapers of record. The first issue of the newspaper was published on July 8, 1889. The editorial page of the ''Journal'' is typically center-right in its positions. The newspaper has won 39 Pulitzer Prizes. History Founding and 19th century A predecessor to ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremy Siegel
Jeremy James Siegel (born November 14, 1945) is an American economist who is the Russell E. Palmer Professor Emeritus of Finance at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. He appears regularly on networks including CNN, CNBC and NPR, and writes regular columns for Kiplinger's Personal Finance and Yahoo! Finance. Siegel's paradox is named after him. Early life and education Siegel was born into a Jewish family in Chicago, Illinois, and graduated from Highland Park High School. He majored in mathematics and economics as an undergraduate at Columbia University, graduating in 1967 with a Bachelor of Arts (B.A.), ''summa cum laude'', with membership in Phi Beta Kappa. He obtained a Ph.D. in economics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1971. As a graduate student he studied under Nobel Prize winners Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow. Career Academics He taught at the University of Chicago for four years before moving to the Wharton School of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Market Hypothesis
The adaptive market hypothesis, as proposed by Andrew Lo,Lo, 2004. is an attempt to reconcile economic theories based on the efficient market hypothesis (which implies that markets are efficient) with behavioral economics, by applying the principles of evolution to financial interactions: competition, adaptation, and natural selection. This view is part of a larger school of thought known as Evolutionary Economics. Under this approach, the traditional models of modern financial economics can coexist with behavioral models. This suggests that investors are capable of an optimal dynamic allocation. Lo argues that much of what behaviorists cite as counterexamples to economic rationality—loss aversion, overconfidence, overreaction, and other behavioral biases—are consistent with an evolutionary model of individuals adapting to a changing environment using simple heuristics. Even fear and greed, which are viewed as the usual culprits in the failure of rational thinking by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent-based Computational Economics
Agent-based computational economics (ACE) is the area of computational economics that studies economic processes, including whole economies, as dynamic systems of interacting agents. As such, it falls in the paradigm of complex adaptive systems. In corresponding agent-based models, the " agents" are "computational objects modeled as interacting according to rules" over space and time, not real people. The rules are formulated to model behavior and social interactions based on incentives and information. Such rules could also be the result of optimization, realized through use of AI methods (such as Q-learning and other reinforcement learning techniques). As part of non-equilibrium economics, the theoretical assumption of mathematical optimization by agents in equilibrium is replaced by the less restrictive postulate of agents with bounded rationality ''adapting'' to market forces. ACE models apply numerical methods of analysis to computer-based simulations of complex dynamic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Cascade
An information cascade or informational cascade is a phenomenon described in behavioral economics and network theory in which a number of people make the same decision in a sequential fashion. It is similar to, but distinct from herd behavior. An information cascade is generally accepted as a two-step process. For a cascade to begin an individual must encounter a scenario with a decision, typically a binary one. Second, outside factors can influence this decision, such as the individual observing others' choices and the apparent outcomes. The two-step process of an informational cascade can be broken down into five basic components: # There is a decision to be made – for example; whether to adopt a new technology, wear a new style of clothing, eat in a new restaurant, or support a particular political position # A limited action space exists (e.g. an adopt/reject decision) # People make the decision sequentially, and each person can observe the choices made by those who acte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Trader
A noise trader is a stock trader whose decisions to buy or sell are based on "factors they believe to be helpful but in reality will give them no better returns than random choices". These factors may include hype or rumor, which noise traders believe to be reliable signals of future returns, but which are actually forms of economic noise that cannot be used to accurately predict the future value of a stock. Noise traders do not trade randomly; their decisions are systematic. However, their trading decisions are not based on professional advice or a business's fundamentals, and the purported signals used by noise traders are more unreliable than those used by technical analysts. Therefore, returns on their trading decisions are expected to be no better than random choices. Noise traders often act irrationally: they tend to be emotion-driven, impulsive, reactive, and herd-like. The presence of noise traders in financial markets can cause prices and risk levels to diverge from ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |