|
Neutronium
Neutronium (or neutrium, neutrite, or element zero) is a hypothetical substance made purely of neutrons. The word was coined by scientist Andreas von Antropoff in 1926 (before the 1932 discovery of the neutron) for the hypothetical "element of atomic number zero" (with no protons in its nucleus) that he placed at the head of the periodic table (denoted by -). However, the meaning of the term has changed over time, and from the last half of the 20th century onward it has been also used to refer to extremely dense substances resembling the neutron-degenerate matter theorized to exist in the cores of neutron stars. In neutron stars Neutronium is used in popular physics literature to refer to the material present in the cores of neutron stars (stars which are too massive to be supported by electron degeneracy pressure and which collapse into a denser phase of matter). In scientific literature the term "neutron-degenerate matter" or simply neutron matter is used for this mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
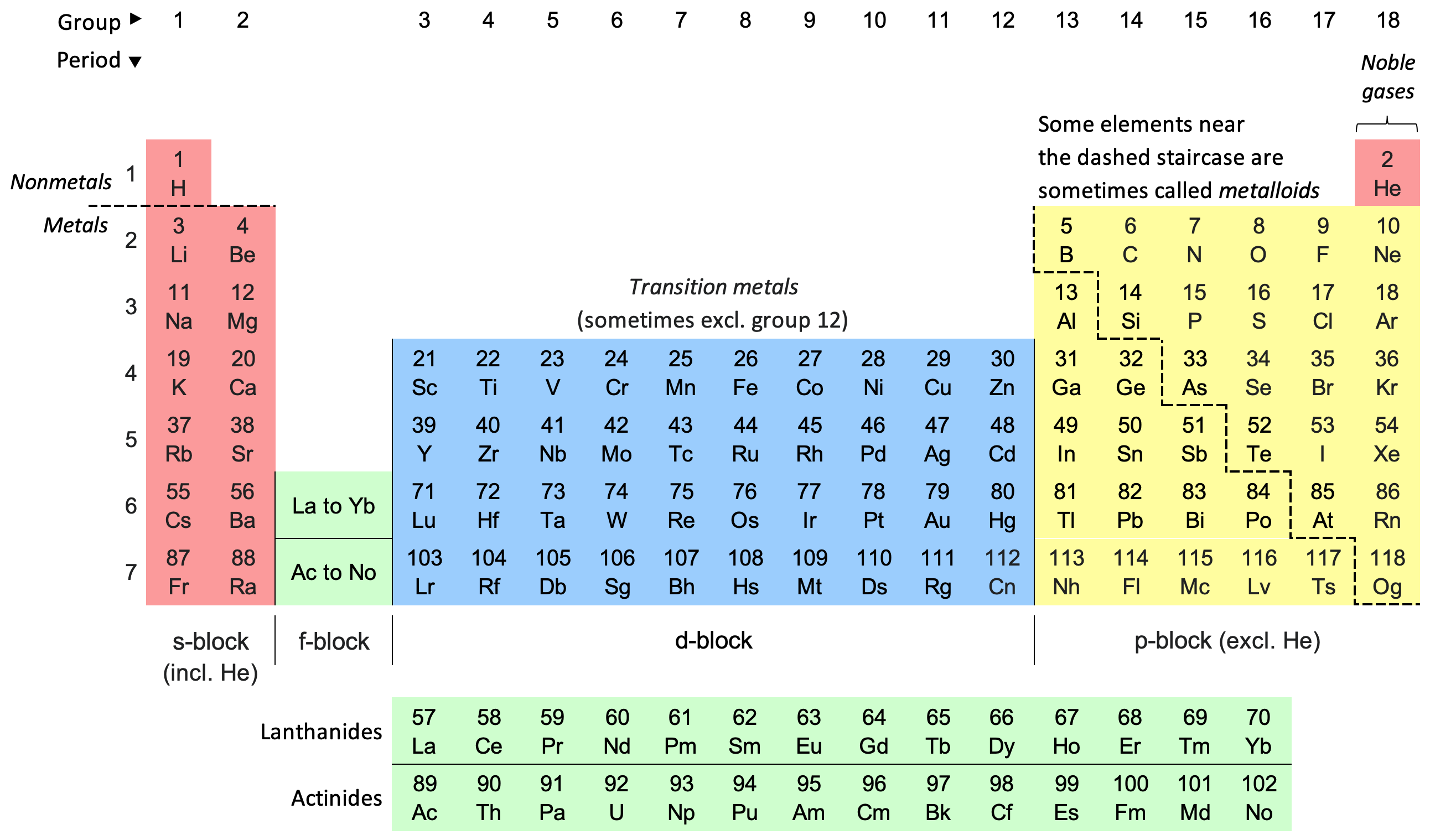
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Andreas Von Antropoff
} Andreas von Antropoff (; 16 August 1878, Reval, Russian Empire — 2 June 1956, Bonn) — Russian (Estonian-born) and German scientist-chemist, professor at the Bonn University and is known to have coined the term "neutronium" and developed a temporarily and widely used alternative periodic table of elements in 1926. Biography His father was Roman von Antropoff, a lawyer and owner of a manor house and his mother was Sophie Emilie von Antropoff. Antropoff had four brothers and one sister: * Roman Andreas von Antropoff * Elisabeth Molly von Antropoff * Sergei von Antropoff * Nikolai Alexander von Antropoff * Karl Alexander von Antropoff From 1889 to 1892 Andreas von Antropoff attended the Domschule of the St Mary's Cathedral, Tallinn, in 1893 the Lajusschule and later the secondary school in Reval. He studied mechanical engineering at the Polytechnic School in Riga from 1897 to 1899 and chemistry from 1899 to 1904. From 1904 to 1907 he studied chemistry in Heidelberg, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tetraneutron
The tetraneutron is considered an unbound isotope with a lifetime around 10−22 seconds. The stability of this cluster of four neutrons is not supported by current models of nuclear forces. Recent empirical evidence is "consistent with a quasi-bound tetraneutron state existing for a very short time". Marqués' experiment Francisco-Miguel Marqués and co-workers at the GANIL accelerator in Caen used a particle accelerator to fire atomic nuclei at carbon targets and observed the "spray" of particles from the resulting collisions. In this case the experiment involved firing beryllium-14, boron-15 and lithium-11 nuclei at a small carbon target, the most successful being beryllium-14. This isotope of beryllium has a nuclear halo that consists of four clustered neutrons; this allows it to be easily separated intact in the high-speed collision with the carbon target. Current nuclear models suggest that four separate neutrons should result when beryllium-10 is produced, but the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom which contains protons, neutrons and electrons, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in daltons (making a quantity called the " relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Physics (American Physical Society Magazine)
''Physics'' is an open access online publication containing commentaries on the best of the peer-reviewed research published in the journals of the American Physical Society. The editor-in-chief of ''Physics'' is Matteo Rini. It highlights papers in ''Physical Review Letters ''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. The journal is considered one of the most prestigious in the field of physics ...'' and the '' Physical Review'' family of journals. The magazine was established in 2008. Features ''Physics'' contains three types of commentaries on research papers: journalistic articles ("Focus"), in depth pieces written by active researchers ("Viewpoints"), and short summaries of a research paper ("Synopsis") written by editorial staff. Readers get free access to the underlying research papers on which the commentaries are based. References External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Janet
Charles Janet (; 15 June 1849 – 7 February 1932) was a French engineer, company director, inventor and biologist. He is also known for his left-step periodic table of chemical elements. Life and work Janet graduated from the École Centrale Paris in 1872, and worked for some years as a chemist and engineer in a few factories in Puteaux (1872), Rouen (1873–74), and Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine, Saint-Ouen (1875–76). He was then employed by Philippe Alphonse Dupont, at Société A. Dupont & Cie, a factory that produced bone buttons and fine brushes. He married Berthe Marie Antonia Dupont, the daughter of the owner, in November 1877, and worked there for the rest of his life, finding time for research in various branches of science. Janet's collection of 50,000 fossils and other specimens was dispersed after his death. His studies of the morphology of the heads of ants, wasps and bees, and his micrographs were of remarkable quality. He also worked on plant biology and wrote a series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edgar Emerson
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and '' gar'' "spear"). Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Middle Ages; it was, however, revived in the 18th century, and was popularised by its use for a character in Sir Walter Scott's ''The Bride of Lammermoor'' (1819). The name was more common in the United States than elsewhere in the Anglosphere during the 19th century. It has been a particularly fashionable name in Latin American countries since the 20th century. People with the given name * Edgar the Peaceful (942–975), king of England * Edgar the Ætheling (c. 1051 – c. 1126), last member of the Anglo-Saxon royal house of England * Edgar of Scotland (1074–1107), king of Scotland * Edgar Alaffita (born 1996), Mexican footballer * Edgar Allan (other), multiple people * Edgar Allen (other), multiple people * Edgar Angara (1934–2018), Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Drury Clark
John Drury Clark, Ph.D. (August 15, 1907 – July 6, 1988) was an American rocket fuel developer, chemist, and science fiction writer. He was instrumental in the revival of interest in Robert E. Howard's '' Conan'' stories and influenced the writing careers of L. Sprague de Camp, Fletcher Pratt, and other authors.De Camp, L. Sprague. "John D. ("Doc") Clark" (obituary) in ''Locus'', August 1988, pages 64-65. Life and career Clark was born in Fairbanks, Alaska."John D. Clark, 80, Rocket Fuel Developer" (obituary) in the ''New York Times'', July 9, 1988, page 33. He attended the University of Alaska, and then the |
Journal Of Physics G
''Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics'' is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes theoretical and experimental research into nuclear physics, particle physics and particle astrophysics, including all interface areas between these fields. The editor-in-chief is Jacek Dobaczewski, University of York, England. Scope The journal publishes research articles on: * theoretical and experimental topics in the physics of elementary particles and fields; * intermediate-energy physics and nuclear physics; * experimental and theoretical research in particle, neutrino, and nuclear astrophysics; * research arising from all interface areas among these fields. Research is published in the following formats: * Research Papers: Reports of original and high-quality research work; * Research Notes: Contributions from individuals (or small groups) within large collaborations, containing early results of analyses, detector development, simulations, etc. which might not otherwise be publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. The journal is considered one of the most prestigious in the field of physics. Over a quarter of Physics Nobel Prize-winning papers between 1995 and 2017 were published in it. ''PRL'' is published both online and as a print journal. Its focus is on short articles ("letters") intended for quick publication. The Lead Editor is Hugues Chaté. The Managing Editor is Robert Garisto. History The journal was created in 1958. Samuel Goudsmit, who was then the editor of '' Physical Review'', the American Physical Society's flagship journal, organized and published ''Letters to the Editor of Physical Review'' into a new standalone journal'','' which became ''Physical Review Letters''. It was the first journal intended for the rapid publication of short articles, a format that eventually became popular in many other fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exotic Nuclei
A hypernucleus is similar to a conventional atomic nucleus, but contains at least one hyperon in addition to the normal protons and neutrons. Hyperons are a category of baryon particles that carry non-zero strangeness quantum number, which is conserved by the strong and electromagnetic interactions. A variety of reactions give access to depositing one or more units of strangeness in a nucleus. Hypernuclei containing the lightest hyperon, the lambda (Λ), tend to be more tightly bound than normal nuclei, though they can decay via the weak force with a mean lifetime of around . Sigma (Σ) hypernuclei have been sought, as have doubly-strange nuclei containing xi baryons (Ξ) or two Λ's. Nomenclature Hypernuclei are named in terms of their atomic number and baryon number, as in normal nuclei, plus the hyperon(s) which are listed in a left subscript of the symbol, with the caveat that atomic number is interpreted as the total charge of the hypernucleus, including charged hyperons suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |