|
Neoclassical Finance
Neoclassical finance is an approach within finance, developing since the mid-1960s, which holds that markets are efficient, and that prices will thus tend to equilibrium and be "rational"; and asset pricing models must then reflect these. It may be contrasted with, for example, behavioral finance which is based on differing, less idealized, assumptions regarding markets and investors. It built on earlier developments such as the Austrian School of economics, and cross-fertilized with atomic physics (see state price) and other heavily quantitative disciplines. See also * Financial economics and particularly, #Arbitrage-free pricing and equilibrium * Neoclassical economics * Fundamental theorem of asset pricing * Modern portfolio theory * Post-modern portfolio theory Simply stated, post-modern portfolio theory (PMPT) is an extension of the traditional modern portfolio theory (MPT) of Markowitz and Sharpe. Both theories provide analytical methods for rational investors to use diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
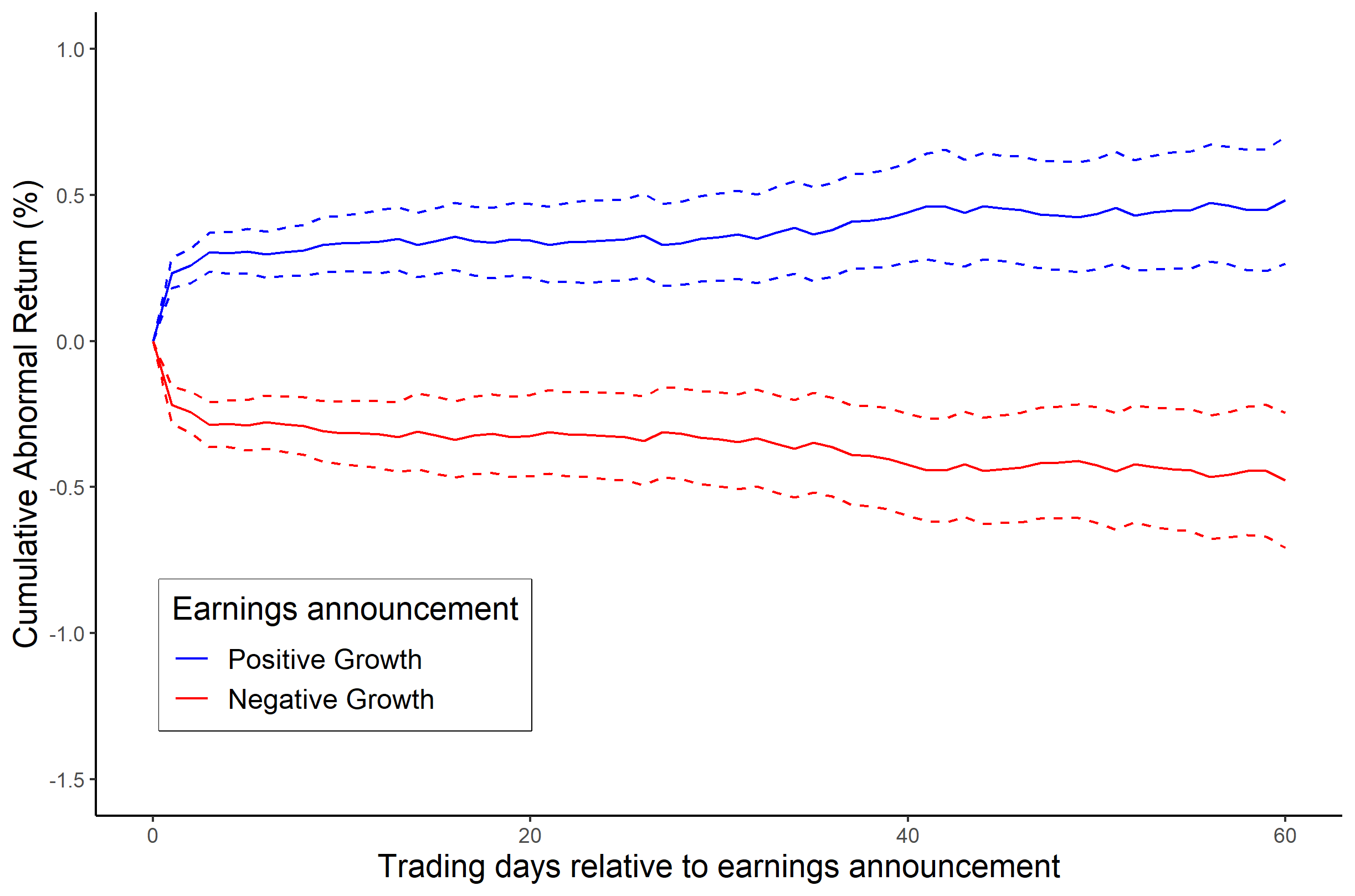
Efficient Market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
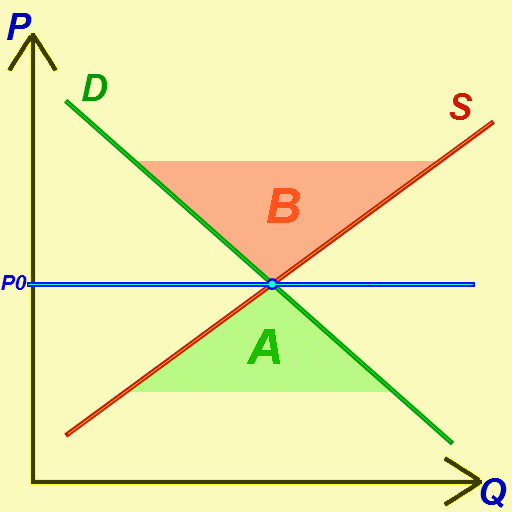
Equilibrium (economics)
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rational Pricing
Rational pricing is the assumption in financial economics that asset prices – and hence asset pricing models – will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away". This assumption is useful in pricing fixed income securities, particularly bonds, and is fundamental to the pricing of derivative instruments. Arbitrage mechanics Arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of a state of imbalance between two (or possibly more) markets. Where this mismatch can be exploited (i.e. after transaction costs, storage costs, transport costs, dividends etc.) the arbitrageur can "lock in" a risk-free profit by purchasing and selling simultaneously in both markets. In general, arbitrage ensures that "the law of one price" will hold; arbitrage also equalises the prices of assets with identical cash flows, and sets the price of assets with known future cash flows. The law of one price The same asset must trade at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asset Pricing
In financial economics, asset pricing refers to a formal treatment and development of two interrelated Price, pricing principles, outlined below, together with the resultant models. There have been many models developed for different situations, but correspondingly, these stem from either General equilibrium theory, general equilibrium asset pricing or Rational pricing, rational asset pricing, the latter corresponding to risk neutral pricing. Investment theory, which is near synonymous, encompasses the body of knowledge used to support the decision-making process of choosing investments, and the asset pricing models are then applied in determining the Required rate of return, asset-specific required rate of return on the investment in question, and for hedging. General equilibrium asset pricing Under general equilibrium theory prices are determined through Market price, market pricing by supply and demand. See, e.g., Tim Bollerslev (2019)"Risk and Return in Equilibrium: The C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Behavioral Finance
Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory. Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. Behavioral economics began as a distinct field of study in the 1970s and 1980s, but can be traced back to 18th-century economists, such as Adam Smith, who deliberated how the economic behavior of individuals could be influenced by their desires. The status of behavioral economics as a subfield of economics is a fairly recent development; the breakthroughs that laid the foundation for it were published through the last three decades of the 20th century. Behavioral economics is still growing as a field, being used increasingly in res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Austrian School
The Austrian school is a Heterodox economics, heterodox Schools of economic thought, school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result primarily from the motivations and actions of individuals along with their self interest. Austrian-school theorists hold that economic theory should be exclusively derived from basic principles of human action.Ludwig von Mises. Human Action, p. 11, "Purposeful Action and Animal Reaction". Referenced 2011-11-23. The Austrian school originated in 1871 in Vienna with the work of Carl Menger, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk, Friedrich von Wieser, and others. It was methodologically opposed to the Historical school of economics, Historical school, in a dispute known as ''Methodenstreit'', or methodology quarrel. Current-day economists working in this tradition are located in many countries, but their work is still referred to as Austrian economics. Among the theoretical contribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term ''atom'' includes ions. The term ''atomic physics'' can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of ''atomic'' and ''nuclear'' in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei. As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
State Price
In financial economics, a state-price security, also called an Arrow–Debreu security (from its origins in the Arrow–Debreu model), a pure security, or a primitive security is a contract that agrees to pay one unit of a numeraire (a currency or a commodity) if a particular state occurs at a particular time in the future and pays zero numeraire in all the other states. The price of this security is the state price of this particular state of the world. The state price vector space, vector is the vector of state prices for all states. See . An Arrow security is an instrument with a fixed payout of one unit in a specified state and no payout in other states. It is a type of hypothetical asset used in the Arrow market structure model. In contrast to the Arrow-Debreu model, Arrow-Debreu market structure model, an Arrow market is a market in which the individual agents engage in trading assets at every time period t. In an Arrow-Debreu model, trading occurs only once at the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade".William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus:Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of Financial capital, capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama and Miller (1972), ''The Theory of Finance'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory. Neoclassical economics is the dominant approach to microeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s onward. Classification The term was originally introduced by Thorstein Veblen in his 1900 article "Preconceptions of Economic Science", in which he related marginalists in the tradition of Alfred Marshall ''et al.'' to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fundamental Theorem Of Asset Pricing
The fundamental theorems of asset pricing (also: of arbitrage, of finance), in both financial economics and mathematical finance, provide necessary and sufficient conditions for a market to be arbitrage-free, and for a market to be complete. An arbitrage opportunity is a way of making money with no initial investment without any possibility of loss. Though arbitrage opportunities do exist briefly in real life, it has been said that any sensible market model must avoid this type of profit.Pascucci, Andrea (2011) ''PDE and Martingale Methods in Option Pricing''. Berlin: Springer-Verlag The first theorem is important in that it ensures a fundamental property of market models. Completeness is a common property of market models (for instance the Black–Scholes model). A complete market is one in which every contingent claim can be replicated. Though this property is common in models, it is not always considered desirable or realistic. Discrete markets In a discrete (i.e. finite sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |