|
Naphthoylindole
Naphthoylindoles are a class of synthetic cannabinoids. Pharmacology Behaving similarly in vivo to endocannabinoids such as anandamide or 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), Naphthoylindoles can bind to endocannabinoid receptors in animals, presenting as CB1 and/or CB2 partial/ full agonists. History They have gained notoriety over the years for illicit usage and distribution in Europe and North America, typically marketed as "herbal incense blends." See also * Structural scheduling of synthetic cannabinoids * List of JWH cannabinoids, includes many naphthoylindoles * Naphthoyl, an acyl group, derived, in this case, from 1-naphthoic acid * Indole Indole is an organic compound with the formula . Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole ... References {{Cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of JWH Cannabinoids
The John W. Huffman research group at Clemson University synthesized over 450 cannabinoids. Some of those are: [Baidu] |
Synthetic Cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids, or neocannabinoids, are a class of designer drug molecules that bind to the same receptors to which cannabinoids ( THC, CBD and many others) in cannabis plants attach. These novel psychoactive substances should not be confused with synthetic phytocannabinoids (obtained by chemical synthesis) or synthetic endocannabinoids from which they are distinct in many aspects. Typically, synthetic cannabinoids are sprayed onto plant matter and are usually smoked, although they have also been ingested as a concentrated liquid form in the United States and United Kingdom since 2016. They have been marketed as herbal incense, or "herbal smoking blends", and sold under common names such as K2, spice, and synthetic marijuana. They are often labeled "not for human consumption" for liability defense. A large and complex variety of synthetic cannabinoids are designed in an attempt to avoid legal restrictions on cannabis, making synthetic cannabinoids designer drugs. Most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Scheduling Of Synthetic Cannabinoids
To combat the illicit synthetic cannabinoid industry many jurisdictions have created a system to control these cannabinoids through their general (or Markush structure, Markush) structure as opposed to their specific identity. In this way new analogs are already controlled before they are even created. A large number of cannabinoids have been grouped into classes based on similarities in their Structural formula, chemical structure, and these classes have been widely adopted across a variety of jurisdictions. Typical groups of compounds included for control may include naphthoylindoles, phenylacetylindoles, benzoylindoles, cyclohexylphenols, naphthylmethylindoles, naphthoylpyrroles, naphthylmethylindenes, indole-3-carboxamides, indole-3-carboxylates, indazole-3-carboxamides and sometimes others, each with specific substitutions on specific atoms of the molecule. The scope of definitions and the range of compounds included may vary substantially between jurisdictions, so compounds whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JWH018
{{disambig ...
JWH may refer to: * John Wesley Hardin, an American gun-fighter from the 18th century * John W. Henry, futures trader and owner of the Boston Red Sox * John Winston Howard, former Prime Minister of Australia * JWH-133, a medication used to prevent Alzheimer's disease * John W. Huffman, creator of the JWH cannabinoids * Jared Waerea-Hargreaves, New Zealand rugby league player for Hull Kingston Rovers Hull Kingston Rovers (often abbreviated to Hull KR) are a professional rugby league club based in Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, England. The club play home games at Craven Park, Hull, Craven Park and compete in Super League, the top tier of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Group
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an organyl group () or hydrogen in the case of formyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC name alkanoyl if the organyl group is alkyl) is usually derived from a carboxylic acid, in which case it has the formula , where R represents an organyl group or hydrogen. Although the term is almost always applied to organic compounds, acyl groups can in principle be derived from other types of acids such as sulfonic acids and phosphonic acids. In the most common arrangement, acyl groups are attached to a larger molecular fragment, in which case the carbon and oxygen atoms are linked by a double bond. Reactivity trends There are five main types of acyl derivatives. Acid halides are the most reactive towards nucleophiles, followed by anhydrides, esters, and amides. Carboxylate ions are esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthoyl
Naphthoyl (naphthalenecarbonyl) is an acyl group derived from naphthoic acid. It may refer to: * 1-naphthoyl (naphthalene-1-carbonyl), derived from 1-naphthoic acid * 2-naphthoyl (naphthalene-2-carbonyl), derived from 2-naphthoic acid See also * Naphthalene * Carbonyl In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ... References {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
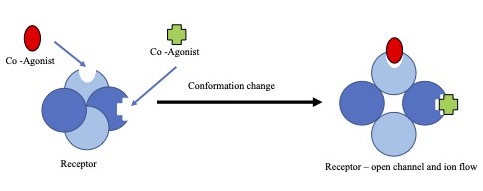
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given Receptor (biochemistry), receptor, but have only partial Intrinsic activity, efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered Ligand (biochemistry), ligands which display both agonistic and Receptor antagonist, antagonistic effects—when both a full agonist and partial agonist are present, the partial agonist actually acts as a competitive antagonist, competing with the full agonist for receptor occupancy and producing a net decrease in the receptor activation observed with the full agonist alone. Clinically, partial agonists can be used to activate receptors to give a desired submaximal response when inadequate amounts of the endogenous ligand are present, or they can reduce the overstimulation of receptors when excess amounts of the endogenous ligand are present. Some currently common drugs that have been classed as partial agonists at particular receptors include buspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptors can be activated by either agonists (such as |