|
Nanometers
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling), is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth ( short scale) or one thousand million (long scale) of a meter (0.000000001 m) and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as 1 × 10−9 m and as m. History The nanometre was formerly known as the "''millimicrometre''" – or, more commonly, the "''millimicron''" for short – since it is of a micrometer. It was often denoted by the symbol ''mμ'' or, more rarely, as ''μμ'' (however, ''μμ'' should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron). Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
22 Nanometer
The "22 nm" node is the process step following 32 nm in CMOS MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. It was first demonstrated by semiconductor companies for use in RAM in 2008. In 2010, Toshiba began shipping 24 nm flash memory chips, and Samsung Electronics began mass-producing 20 nm flash memory chips. The first consumer-level CPU deliveries using a 22 nm process started in April 2012 with the Intel Ivy Bridge processors. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch on a "22nm" device is twenty-two nanometers. The ITRS 2006 Front End Process Update indicates that equivalent physical oxide thickness will not scale below 0.5 nm (about twice the diameter of a silicon atom), which is the expected value at the 22 nm node. This is an indication that CMOS scaling in this area has reached a wall at this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
32 Nanometer
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technology level. Toshiba produced commercial 32 GiB NAND flash memory chips with the "32nm" process in 2009. Intel and AMD produced commercial microchips using the "32 nm" process in the early 2010s. IBM and the Common Platform also developed a "32 nm" high-κ metal gate process. Intel began selling its first "32 nm" processors using the Westmere architecture on 7 January 2010. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, nor metal pitch, nor gate pitch on a "32nm" device is thirty-two nanometers. The "28 nm" node is an intermediate half-node die shrink based on the "32 nm" process. The "32 nm" process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
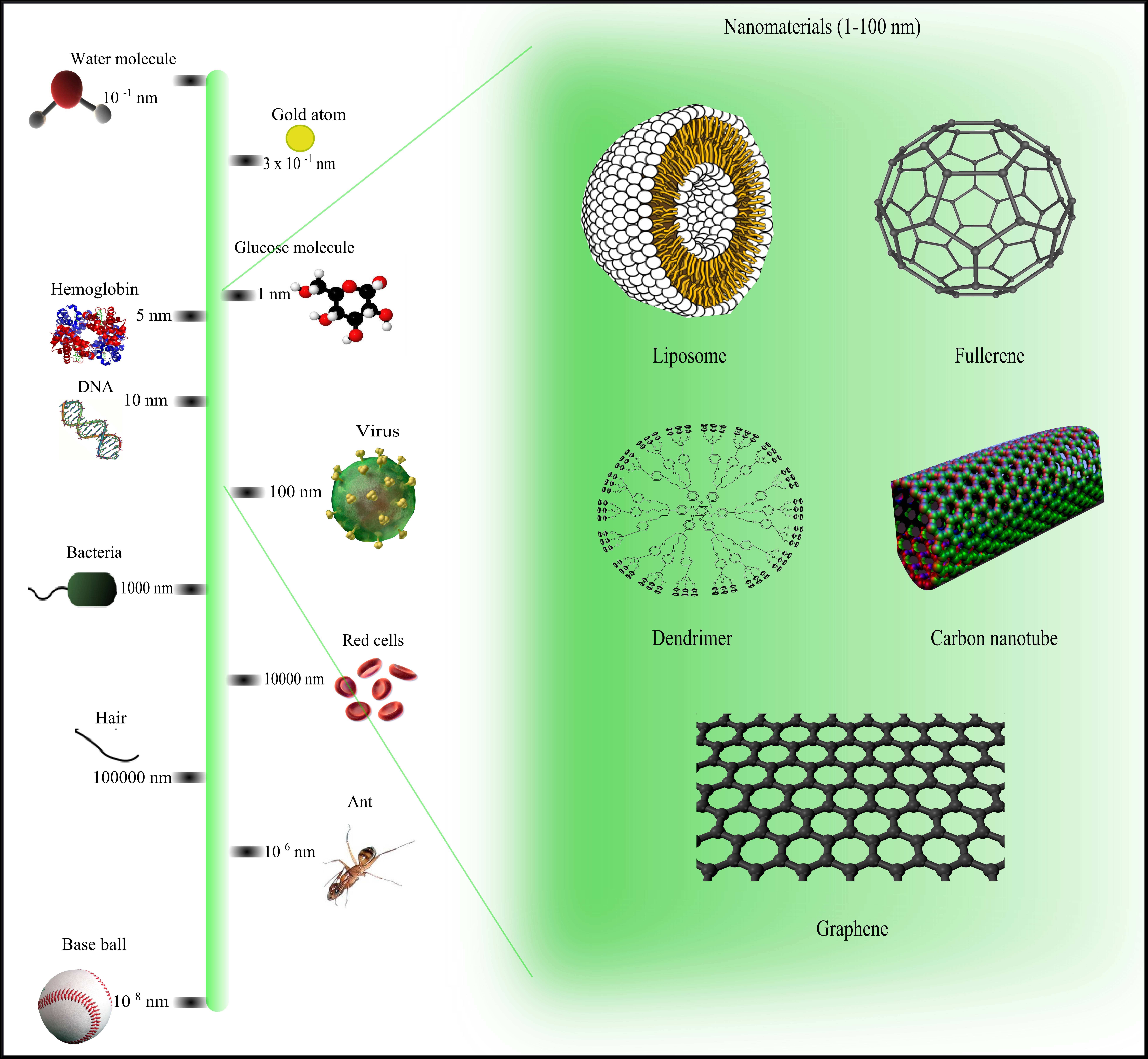
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electromagnetic Radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ranging from radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All forms of EMR travel at the speed of light in a vacuum and exhibit wave–particle duality, behaving both as waves and as discrete particles called photons. Electromagnetic radiation is produced by accelerating charged particles such as from the Sun and other celestial bodies or artificially generated for various applications. Its interaction with matter depends on wavelength, influencing its uses in communication, medicine, industry, and scientific research. Radio waves enable broadcasting and wireless communication, infrared is used in thermal imaging, visible light is essential for vision, and higher-energy radiation, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among all the Chemical element, elements, and it does not have a melting point at standard pressures. It is the second-lightest and second-most Abundance of the chemical elements, abundant element in the observable universe, after hydrogen. It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and Jupiter, because of the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4 with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nanoscopic Scale
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
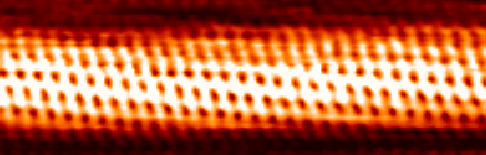
Carbon Nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized: * ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') have diameters around 0.5–2.0 nanometres, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They can be idealised as cutouts from a two-dimensional graphene sheet rolled up to form a hollow cylinder. * ''Multi-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consist of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes in a nested, tube-in-tube structure. Double- and triple-walled carbon nanotubes are special cases of MWCNT. Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and strength of the bonds between carbon atoms. Some SWCNT structures exhibit high electrical conductivity while others are semiconductors. In addition, carbon nanotubes can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imperial Units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, related but differing system of United States customary units, customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester measure, Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had metrication, officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nano-
Nano (symbol n) is a unit prefix meaning one billionth. Used primarily with the metric system, this prefix denotes a factor of 10−9 or . It is frequently encountered in science and electronics for prefixing units of time and length. The prefix derives from the Greek (Latin ), meaning "dwarf". The General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) officially endorsed the usage of ''nano'' as a standard prefix in 1960. When used as a prefix for something other than a unit of measure (as for example in words like "nanoscience"), nano refers to nanotechnology, or means "on a scale of nanometres" ( nanoscale). Nanometre X-rays have a wavelength ranging from the size of 0.01 nm to 10 nm. Three gold atoms lined up are about one nanometer (nm) long. Human fingernails grow at approximately one nanometer per second. Nanosecond One nanosecond (ns) is about the time required for light to travel 30 cm in air, or 20 cm in an optical fiber. See also * RKM code The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the International System of Units (SI) system, the base unit for length is the metre. Length is commonly understood to mean the most extended size, dimension of a fixed object. However, this is not always the case and may depend on the position the object is in. Various terms for the length of a fixed object are used, and these include height, which is vertical length or vertical extent, width, breadth, and depth. ''Height'' is used when there is a base from which vertical measurements can be taken. ''Width'' and ''breadth'' usually refer to a shorter dimension than ''length''. ''Depth'' is used for the measure of a third dimension. Length is the measure of one spatial dimension, whereas area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ångström
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten- billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). It was originally spelled with Swedish letters, as Ångström and later as ångström (). The latter spelling is still listed in some dictionaries, but is now rare in English texts. Some popular US dictionaries list only the spelling ''angstrom''. The unit's symbol is Å, which is a letter of the Swedish alphabet, regardless of how the unit is spelled. However, "A" or "A.U." may be used in less formal contexts or typographically limited media. The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals, wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, and dimensions of integrated circuit p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be emitted and received by antenna (radio), antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most building materials. Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon energies and the shortest wavelengths—much smaller than an atomic nucleus. Gamma rays, X-rays, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |