|
Mutable
In object-oriented and functional programming, an immutable object (unchangeable object) is an object whose state cannot be modified after it is created.Goetz et al. ''Java Concurrency in Practice''. Addison Wesley Professional, 2006, Section 3.4. Immutability This is in contrast to a mutable object (changeable object), which can be modified after it is created. In some cases, an object is considered immutable even if some internally used attributes change, but the object's state appears unchanging from an external point of view. For example, an object that uses memoization to cache the results of expensive computations could still be considered an immutable object. Strings and other concrete objects are typically expressed as immutable objects to improve readability and runtime efficiency in object-oriented programming. Immutable objects are also useful because they are inherently thread-safe. Other benefits are that they are simpler to understand and reason about and offer h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Const Correctness
In some programming languages, const is a type qualifier (a keyword applied to a data type) that indicates that the data is read-only. While this can be used to declare constants, in the C family of languages differs from similar constructs in other languages in being part of the ''type,'' and thus has complicated behavior when combined with pointers, references, composite data types, and type-checking. In other languages, the data is not in a single memory location, but copied at compile time on each use. Languages which utilize it include C, C++, D, JavaScript, Julia, and Rust. Introduction When applied in an object declaration, it indicates that the object is a constant: its value may not be changed, unlike a variable. This basic use – to declare constants – has parallels in many other languages. However, unlike in other languages, in the C family of languages the const is part of the ''type'', not part of the ''object''. For example, in C, declares an objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant (programming)
In computer programming, a constant is a value that should not be altered by the program during normal execution, i.e., the value is ''constant''. When associated with an identifier, a constant is said to be "named," although the terms "constant" and "named constant" are often used interchangeably. This is contrasted with a '' variable,'' which is an identifier with a value that can be changed during normal execution, i.e., the value is ''variable.'' Constants are useful for both programmers and compilers: For programmers they are a form of self-documenting code and allow reasoning about correctness, while for compilers they allow compile-time and run-time checks that verify that constancy assumptions are not violated, and allow or simplify some compiler optimizations. There are various specific realizations of the general notion of a constant, with subtle distinctions that are often overlooked. The most significant are: compile-time (statically valued) constants, run-time (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by applying and composing functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are trees of expressions that map values to other values, rather than a sequence of imperative statements which update the running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local identifiers), passed as arguments, and returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a declarative and composable style, where small functions are combined in a modular manner. Functional programming is sometimes treated as synonymous with purely functional programming, a subset of functional programming which treats all functions as deterministic mathematical functions, or pure functions. When a pure function is called wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Intern Pool
In computer science, string interning is a method of storing only one copy of each distinct string value, which must be immutable. Interning strings makes some string processing tasks more time- or space-efficient at the cost of requiring more time when the string is created or interned. The distinct values are stored in a string intern pool. The single copy of each string is called its ''intern'' and is typically looked up by a method of the string class, for example String.intern() in Java. All compile-time constant strings in Java are automatically interned using this method. String interning is supported by some modern object-oriented programming languages, including Java, Python, PHP (since 5.4), Lua and .NET languages. Lisp, Scheme, Julia, Ruby and Smalltalk are among the languages with a symbol type that are basically interned strings. The library of the Standard ML of New Jersey contains an atom type that does the same thing. Objective-C's selectors, which are mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intern (computer Science)
In computer science, string interning is a method of storing only one copy of each distinct string value, which must be immutable. Interning strings makes some string processing tasks more time- or space-efficient at the cost of requiring more time when the string is created or interned. The distinct values are stored in a string intern pool. The single copy of each string is called its ''intern'' and is typically looked up by a method of the string class, for example String.intern() in Java. All compile-time constant strings in Java are automatically interned using this method. String interning is supported by some modern object-oriented programming languages, including Java, Python, PHP (since 5.4), Lua and .NET languages. Lisp, Scheme, Julia, Ruby and Smalltalk are among the languages with a symbol type that are basically interned strings. The library of the Standard ML of New Jersey contains an atom type that does the same thing. Objective-C's selectors, which are mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
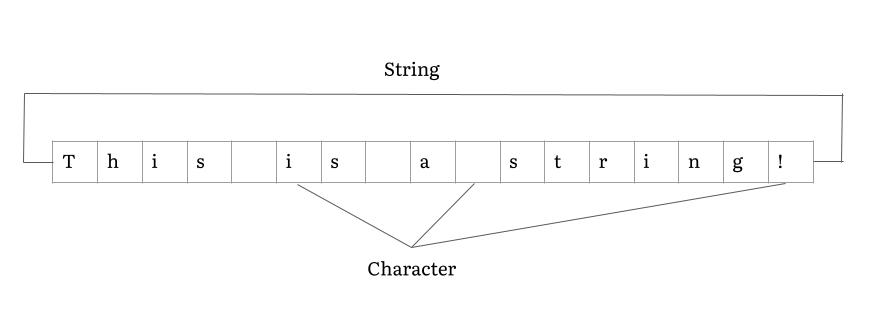
StringBuffer
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference (computer Science)
In computer programming, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular data, such as a variable's value or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the datum, and accessing the datum is called dereferencing the reference. A reference is distinct from the datum itself. A reference is an abstract data type and may be implemented in many ways. Typically, a reference refers to data stored in memory on a given system, and its internal value is the memory address of the data, i.e. a reference is implemented as a pointer. For this reason a reference is often said to "point to" the data. Other implementations include an offset (difference) between the datum's address and some fixed "base" address, an index, unique key, or identifier used in a lookup operation into an array or table, an operating system handle, a physical address on a storage device, or a network address such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Computer Programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as ''methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defensive Copy
In object-oriented programming, object copying is creating a copy of an existing object, a unit of data in object-oriented programming. The resulting object is called an ''object copy'' or simply ''copy'' of the original object. Copying is basic but has subtleties and can have significant overhead. There are several ways to copy an object, most commonly by a copy constructor or cloning. Copying is done mostly so the copy can be modified or moved, or the current value preserved. If either of these is unneeded, a reference to the original data is sufficient and more efficient, as no copying occurs. Objects in general store composite data. While in simple cases copying can be done by allocating a new, uninitialized object and copying all fields (attributes) from the original object, in more complex cases this does not result in desired behavior. Methods of copying The design goal of most objects is to give the resemblance of being made out of one monolithic block even though most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Programming Language
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as ''methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as ''methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |