|
Moondust
Lunar soil is the fine fraction of the regolith found on the surface of the Moon. Its properties can differ significantly from those of terrestrial soil. The physical properties of lunar soil are primarily the result of mechanical disintegration of basaltic and anorthositic rock, caused by continual meteoric impacts and bombardment by solar and interstellar charged atomic particles over billions of years. The process is largely one of mechanical weathering in which the particles are ground to progressively finer size over time. This situation contrasts fundamentally to terrestrial dirt formation, mediated by the presence of molecular oxygen (O2), humidity, atmospheric wind, and a robust array of contributing biological processes. ''Lunar soil'' typically refers to only the finer fraction of lunar regolith, which is composed of grains 1 cm in diameter or less, but is often used interchangeably. Lunar dust generally connotes even finer materials than ''lunar soil''. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestrial planets and moons. Etymology The term '' regolith'' combines two Greek words: (), 'blanket', and (), 'rock'. The American geologist George P. Merrill first defined the term in 1897, writing: Earth Earth's regolith includes the following subdivisions and components: * soil or pedolith * alluvium and other transported cover, including that transported by aeolian, glacial, marine, and gravity flow processes. * "saprolith'", generally divided into the ** ''upper saprolite'': completely oxidised bedrock ** ''lower saprolite'': chemically reduced partially weathered rocks ** ''saprock'': fractured bedrock with weathering restricted to fracture margins * volcanic ash and lava flows that are interbedded with unconsolidated materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11 Bootprint
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the '' kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. The IAU officially defines meteorites as 30 micrometers to 1 meter; micrometeorites are the small end of the range (~submillimeter). They are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter Earth's atmosphere at high velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through atmospheric friction and compression. Micrometeorites individually weigh between 10−9 and 10−4 g and collectively comprise most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present-day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to describe dust-sized objects that fall to the Earth. Sometimes meteoroids and micrometeoroids entering the Earth's atmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Hydration
In chemistry, mineral hydration is an inorganic chemical reaction which adds water to the crystal structure of a mineral, usually creating a new mineral, usually called a '' hydrate''. In geological terms, the process of mineral hydration is known as ''retrograde alteration'' and is a process occurring in retrograde metamorphism. It commonly accompanies metasomatism and is often a feature of wall rock alteration around ore bodies. Hydration of minerals occurs generally in concert with hydrothermal circulation which may be driven by tectonic or igneous activity. Processes There are two main ways in which minerals hydrate. One is conversion of an oxide to a double hydroxide, as with the hydration of calcium oxide—CaO—to calcium hydroxide—Ca(OH)2, the other is with the incorporation of water molecules directly into the crystalline structure of a new mineral. The later process is exhibited in the hydration of feldspars to clay minerals, garnet to chlorite, or kyanite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 15
Apollo 15 (July 26August 7, 1971) was the ninth crewed mission in the United States' Apollo program and the fourth to land on the Moon. It was the first J mission, with a longer stay on the Moon and a greater focus on science than earlier landings. Apollo 15 saw the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle. The mission began on July 26 and ended on August 7, with the lunar surface exploration taking place between July 30 and August 2. Commander David Scott and Lunar Module Pilot James Irwin landed near Hadley Rille and explored the local area using the rover, allowing them to travel further from the lunar module than had been possible on previous missions. They spent 18 hours on the Moon's surface on four extravehicular activities (EVA), and collected of surface material. At the same time, Command Module Pilot Alfred Worden orbited the Moon, operating the sensors in the scientific instrument module (SIM) bay of the service module. This suite of instruments col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadley–Apennine (Moon)
Hadley–Apennine is a region on the near side of Earth's Moon that served as the landing site for the American Apollo 15 mission, the fourth manned landing on the Moon and the first of the " J-missions", in July 1971. The site is located on the eastern edge of Mare Imbrium on a lava plain known as Palus Putredinis. Hadley–Apennine is bordered by the Montes Apenninus (often referred to as "Apennine Front"), a mountain range, and Hadley Rille, a meandering channel, on the east and west, respectively. Data obtained from the composition of soil samples collected on Apollo 15 show that most (about 90%) of the samples from the Apennine Front are brown-glass breccias, and approximately 60–70% obtained from the mare surface are basalt. Although the basalts seem to vary in their texture, their ages appear to be approximately the same. Most of the samples obtained on the Apennine Front are KREEP (potassium, rare-earth elements, phosphorus) materials, anorthosites, recrystallized norit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon or traveled beyond low Earth orbit. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walked on the Moon, while Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans orbited above. Schmitt was the only professional geologist to land on the Moon; he was selected in place of Joe Engle, as NASA had been under pressure to send a scientist to the Moon. The mission's heavy emphasis on science meant the inclusion of a number of new experiments, including a biological experiment containing five mice that was carried in the command module. Mission planners had two primary goals in deciding on the landing site: to sample lunar highland material older than that at Mare Imbrium and to investigate the possibility of relatively recent volcanic activity. They therefore selected Taurus–Littrow, where formations that had been viewed and pictured from orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shorty Crater
Shorty is a feature on Earth's Moon, an impact crater in the Taurus–Littrow valley. Astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt visited it in 1972, on the Apollo 17 mission. It is the location of the famous "orange soil", which geologists believe to be small bits of rapidly-cooled molten rock ejected in a fire fountain. It is about in diameter and up to deep. To the east of Shorty are Victory, Camelot, and the Apollo 17 landing site. To the southeast is Brontë. To the southwest are Lara and Nansen. The crater was named after the character "Shorty" in Richard Brautigan's 1967 novel ''Trout Fishing in America'', as well as to honor the genre of the short story with particular reference to J. D. Salinger. Apollo 17 Lunar Surface Journal, Corrected Transcript and Commentary Copyright 1995 by Eric M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
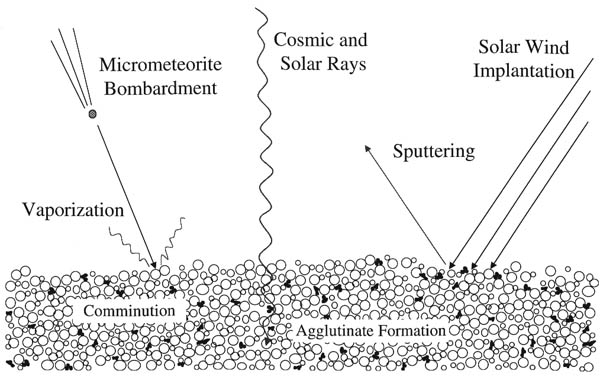
Space Weathering
Space weathering is the type of weathering that occurs to any object exposed to the harsh environment of outer space. Bodies without atmospheres (including the Moon, Mercury, the asteroids, comets, and most of the moons of other planets) take on many weathering processes: * collisions of galactic cosmic rays and solar cosmic rays, * irradiation, implantation, and sputtering from solar wind particles, and * bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. Space weathering is important because these processes affect the physical and optical properties of the surface of many planetary bodies. Therefore, it is critical to understand the effects of space weathering in order to properly interpret remotely sensed data. History Much of our knowledge of the space weathering process comes from studies of the lunar samples returned by the Apollo program, particularly the lunar soils (or regolith). The constant flux of high energy particles and micrometeorites, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)