|
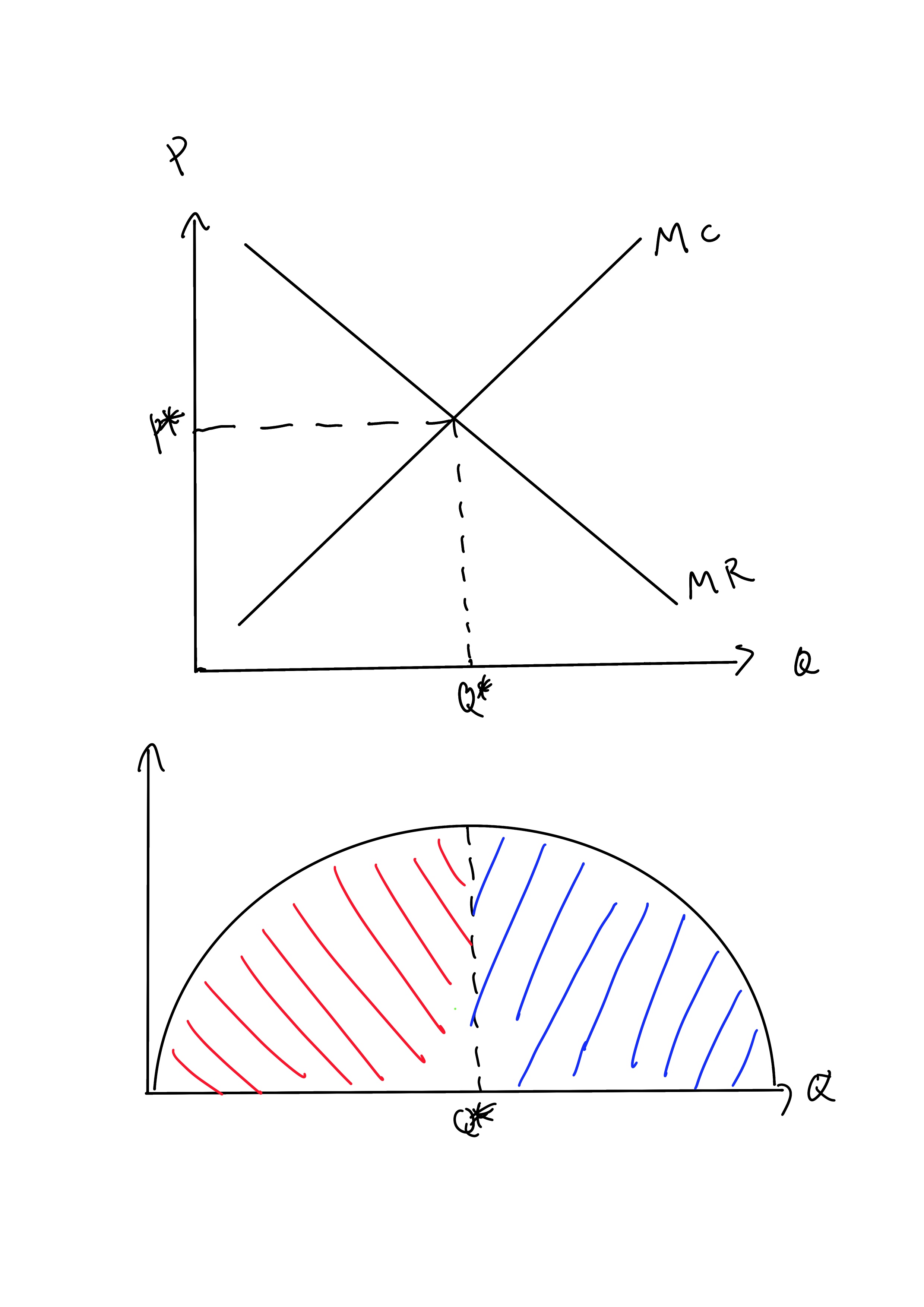
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a type of imperfect competition such that there are many producers competing against each other, but selling products that are differentiated from one another (e.g. by branding or quality) and hence are not perfect substitutes. In monopolistic competition, a company takes the prices charged by its rivals as given and ignores the impact of its own prices on the prices of other companies. If this happens in the presence of a coercive government, monopolistic competition will fall into government-granted monopoly. Unlike perfect competition, the company maintains spare capacity. Models of monopolistic competition are often used to model industries. Textbook examples of industries with market structures similar to monopolistic competition include restaurants, cereals, clothing, shoes, and service industries in large cities. The "founding father" of the theory of monopolistic competition is Edward Hastings Chamberlin, who wrote a pioneering book on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-run Equilibrium Of The Firm Under Monopolistic Competition
In economics, the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. More specifically, in microeconomics there are no fixed factors of production in the long-run, and there is enough time for adjustment so that there are no constraints preventing changing the output level by changing the capital stock or by entering or leaving an industry. This contrasts with the short-run, where some factors are variable (dependent on the quantity produced) and others are fixed (paid once), constraining entry or exit from an industry. In macroeconomics, the long-run is the period when the general price level, contractual wage rates, and expectations adjust fully to the state of the economy, in contrast to the short-run when these variables may not fully adjust. History The diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barriers To Entry
In theories of competition in economics, a barrier to entry, or an economic barrier to entry, is a fixed cost that must be incurred by a new entrant, regardless of production or sales activities, into a market that incumbents do not have or have not had to incur. Because barriers to entry protect incumbent firms and restrict competition in a market, they can contribute to distortionary prices and are therefore most important when discussing antitrust policy. Barriers to entry often cause or aid the existence of monopolies and oligopolies, or give companies market power. Barriers of entry also have an importance in industries. First of all it is important to identify that some exist naturally, such as brand loyalty. Governments can also create barriers to entry to meet consumer protection laws, protecting the public. In other cases it can also be due to inherent scarcity of public resources needed to enter a market. Definitions Various conflicting definitions of "barrier to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a specific person or company, enterprise is the only supplier of a particular thing. This contrasts with a monopsony which relates to a single entity's control of a Market (economics), market to purchase a good or service, and with oligopoly and duopoly which consists of a few sellers dominating a market. Monopolies are thus characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce the good (economics), good or Service (economics), service, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum. Perfect competition provides both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency: * Such markets are ''allocatively efficient'', as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that a factor's price equals the factor's marginal revenue product. It allows for derivation of the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profit Maximization
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit (or just profit in short). In neoclassical economics, which is currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, the firm is assumed to be a "rational agent" (whether operating in a perfectly competitive market or otherwise) which wants to maximize its total profit, which is the difference between its total revenue and its total cost. Measuring the total cost and total revenue is often impractical, as the firms do not have the necessary reliable information to determine costs at all levels of production. Instead, they take a more practical approach by examining how small changes in production influence revenues and costs. When a firm produces an extra unit of product, the additional revenue gained from selling it is called the marginal revenue (\text), and the additional cost to produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept. Economies of scale apply to a variety of the organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Elasticity Of Demand
In economics, the cross elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity of demand measures the percentage change of the quantity demanded for a good to the percentage change in the price of another good, ceteris paribus. In real life, the quantity demanded of good is dependent on not only its own price (Price elasticity of demand) but also the price of other "related" products. \text = \frac The concept is used to identify the relationship between two goods, they can be: * Complements * Substitutes * Unrelated A negative cross elasticity denotes two products that are complements, while a positive cross elasticity denotes two products are substitutes. If products A and B are complements, an increase in the price of B leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded for A, as A is used in conjunction with B. Equivalently, if the price of product B decreases, the demand curve for product A shifts to the right reflecting an increase in A's demand, resulting in a ''negative'' value for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Entry
In economics, free entry is a condition in which firms can freely enter the market for an economic good by establishing production and beginning to sell the product. The assumption of free entry implies that if there are firms earning excessively high profits in a given industry, new firms that also seek a high profit are likely to start to produce or change into a production of the same good to join the market. In such a case there are no barriers preventing a start-up firm from competing. Where an opportunity of a profit arises we assume that there will also be firms entering the market for the certain good and compete for it. In most markets this condition is present only in the long run. The assumption of free entry doesn't mean that a firm is simply able to set up a shop without any costs incurred. It is clear that the new entrant needs to gain the capital that they need for operating in the industry. Therefore, even with a free entry to a market the entrant still has to fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Differentiation
In economics and marketing, product differentiation (or simply differentiation) is the process of distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market. This involves differentiating it from competitors' products as well as from a firm's other products. The concept was proposed by Edward Chamberlin in his 1933 book, '' The Theory of Monopolistic Competition''. Rationale Firms have different resource endowments that enable them to construct specific competitive advantages over competitors. Resource endowments allow firms to be different, which reduces competition and makes it possible to reach new segments of the market. Thus, differentiation is the process of distinguishing the differences of a product or offering from others, to make it more attractive to a particular target market. Although research in a niche market may result in changing a product in order to improve differentiation, the changes themselves are not di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Elasticity Of Demand
A good's price elasticity of demand (E_d, PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good, but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price, holding everything else constant. If the elasticity is −2, that means a one percent price rise leads to a two percent decline in quantity demanded. Other elasticities measure how the quantity demanded changes with other variables (e.g. the income elasticity of demand for consumer income changes). Price elasticities are negative except in special cases. If a good is said to have an elasticity of 2, it almost always means that the good has an elasticity of −2 according to the formal definition. The phrase "more elastic" means that a good's elasticity has greater magnitude, ignoring the sign. Veblen and Giffen goods are two classes of goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Profit
In economics, profit is the difference between the revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and the total cost of its inputs. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs. It is different from accounting profit, which only relates to the explicit costs that appear on a firm's financial statements. An accountant measures the firm's accounting profit as the firm's total revenue minus only the firm's explicit costs. An economist includes all costs, both explicit and implicit costs, when analyzing a firm. Therefore, economic profit is smaller than accounting profit. ''Normal profit'' is often viewed in conjunction with economic profit. Normal profits in business refer to a situation where a company generates revenue that is equal to the total costs incurred in its operation, thus allowing it to remain operational in a competitive industry. It is the minimum profit level that a company can achieve to justify its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Break Even
Break-even (or break even), often abbreviated as B/E in finance, (sometimes called point of equilibrium) is the point of balance making neither a profit nor a loss. Any number below the break-even point constitutes a loss while any number above it shows a profit. The term originates in finance but the concept has been applied in other fields. In economics In economics and business, specifically cost accounting, the break-even point (BEP) is the point at which cost or expenses and revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even". A profit or loss has not been made, although opportunity costs have been "paid" and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In other words, it is the point at which the total revenue of a business exceeds its total costs, and the business begins to create wealth instead of consuming it. It is shown graphically as the point where the total revenue and total cost curves meet. In the linear case the break-even point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |