|
Molecular Wires
Molecular wires (or sometimes called molecular nanowires) are molecular chains that conduct electric current. They are the proposed building blocks for molecular electronic devices. Their typical diameters are less than three nanometers, while their lengths may be macroscopic, extending to centimeters or more. Examples Most types of molecular wires are derived from organic molecules. One naturally occurring molecular wire is DNA. Prominent inorganic examples include polymeric materials such as Li2Mo6Se6 and Mo6S9−xIx, d4(CO)4(OAc)4Pd(acac)2 and single-molecule extended metal atom chains (EMACs) which comprise strings of transition metal atoms directly bonded to each other. Molecular wires containing paramagnetic inorganic moieties can exhibit Kondo peaks. Conduction of electrons Molecular wires conduct electricity. They typically have non-linear current-voltage characteristics, and do not behave as simple ohmic conductors. The conductance follows typical power law behavio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Metal Atom Chains
In organometallic chemistry, extended metal atom chains (EMACs) are molecules that consist of a linear chain of directly bonded metal atoms, surrounded by organic ligands. These compounds represent the smallest molecular wires. Such species are researched for the bottom-up approach to nanoelectronics, although no applications are near term. Structure An EMAC molecule contains a linear string of transition metals (typically Cr, Co, Ni, or Cu) that are bonded to each other and surrounded helically by organic ligands. The metal chains are usually end-capped by anions, usually halides. The organic ligands often pyridylamide, pyridone, naphthyridine, or their derivatives. Each metal atom is six-coordinate, bonded to two other metals along the axis of the molecule (except terminal metals, which are bonded to one metal and one capping anion) and to four nitrogen atoms perpendicular to the axis. The organic ligands template the formation of the chains by bringing the metal ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Synthesis
DNA synthesis is the natural or artificial creation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotide units, which are linked by covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, in a repeating structure. DNA synthesis occurs when these nucleotide units are joined to form DNA; this can occur artificially (''in vitro'') or naturally (''in vivo''). Nucleotide units are made up of a nitrogenous base (cytosine, guanine, adenine or thymine), pentose sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate group. Each unit is joined when a covalent bond forms between its phosphate group and the pentose sugar of the next nucleotide, forming a sugar-phosphate backbone. DNA is a complementary, double stranded structure as specific base pairing (adenine and thymine, guanine and cytosine) occurs naturally when hydrogen bonds form between the nucleotide bases. There are several different definitions for DNA synthesis: it can refer to DNA replication - DNA biosynthesis (''in vivo'' DNA amplifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
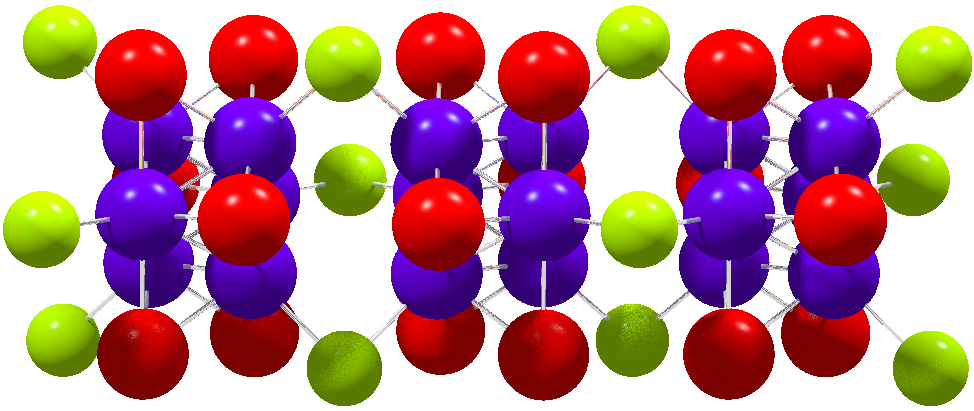
Molybdenum Compounds
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low solubility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanobalance
A microbalance is an instrument capable of making precise measurements of weight of objects of relatively small mass: of the order of a million parts of a gram. In comparison, a standard analytical balance is 100 times less sensitive; i.e. it is limited in precision to 0.1 milligrams. Microbalances are generally used in a laboratory as standalone instruments but are also incorporated into other instruments, such as thermogravimetry, sorption/desorption systems, and surface property instruments. It is the precision of the microbalance that distinguishes it from other weighing devices. Types A quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) is a very sensitive mass deposition sensor based on the piezoelectric properties of the quartz crystal. This technique uses the changes in resonance frequency of the crystal to measure the mass on the surface because the resonance frequency is highly dependent on any changes of the crystal mass. A quartz crystal microbalance is capable of measuring mass d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion Nanobalance
A microbalance is an instrument capable of making precise measurements of weight of objects of relatively small mass: of the order of a million parts of a gram. In comparison, a standard analytical balance is 100 times less sensitive; i.e. it is limited in precision to 0.1 milligrams. Microbalances are generally used in a laboratory as standalone instruments but are also incorporated into other instruments, such as thermogravimetry, sorption/desorption systems, and surface property instruments. It is the precision of the microbalance that distinguishes it from other weighing devices. Types A quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) is a very sensitive mass deposition sensor based on the piezoelectric properties of the quartz crystal. This technique uses the changes in resonance frequency of the crystal to measure the mass on the surface because the resonance frequency is highly dependent on any changes of the crystal mass. A quartz crystal microbalance is capable of measuring mass d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronics
Molecular electronics is the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components. It is an interdisciplinary area that spans physics, chemistry, and materials science. The unifying feature is use of molecular building blocks to fabricate electronic components. Due to the prospect of size reduction in electronics offered by molecular-level control of properties, molecular electronics has generated much excitement. It provides a potential means to extend Moore's Law beyond the foreseen limits of small-scale conventional silicon integrated circuits. Molecular scale electronics Molecular scale electronics, also called single-molecule electronics, is a branch of nanotechnology that uses single molecules, or nanoscale collections of single molecules, as electronic components. Because single molecules constitute the smallest stable structures possible, this miniaturization is the ultimate goal for shrinking electrical circuits. Conventiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampoule
An ampoule (also ampul and ampule) is a small sealed vial which is used to contain and preserve a sample, usually a solid or liquid. Ampoules are usually made of glass. Modern ampoules are most commonly used to contain pharmaceuticals and chemicals that must be protected from air and contaminants. They are hermetically sealed by melting the thin top with an open flame, and usually opened by snapping off the neck. The space above the chemical may be filled with an inert gas before sealing. The walls of glass ampoules are usually sufficiently strong to be brought into a glovebox without any difficulty. Glass ampoules are more expensive than bottles and other simple containers, but there are many situations where their superior imperviousness to gases and liquids and all-glass interior surface are worth the extra cost. Examples of chemicals sold in ampoules are injectable pharmaceuticals, air-sensitive reagents like tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0), hygroscopic material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |