|
Microbial Consortium
A microbial consortium or microbial community, is two or more bacterial or microbial groups living symbiotically. Consortiums can be endosymbiotic or ectosymbiotic, or occasionally may be both. The protist '' Mixotricha paradoxa'', itself an endosymbiont of the ''Mastotermes darwiniensis'' termite, is always found as a consortium of at least one endosymbiotic coccus, multiple ectosymbiotic species of flagellate or ciliate bacteria, and at least one species of helical '' Treponema'' bacteria that forms the basis of ''Mixotricha'' protists' locomotion. The concept of a consortium was first introduced by Johannes Reinke in 1872, and in 1877 the term symbiosis was introduced and later expanded on. Evidence for symbiosis between microbes strongly suggests it to have been a necessary precursor of the evolution of land plants and for their transition from algal communities in the sea to land. Overview Microbes hold promising application potential to raise the efficiency of bioprocesses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignocellulose
Lignocellulose refers to plant dry matter (biomass), so called lignocellulosic biomass. It is the most abundantly available raw material on the Earth for the production of biofuels. It is composed of two kinds of carbohydrate polymers, cellulose and hemicellulose, and an aromatic-rich polymer called lignin. Any biomass rich in cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin are commonly referred to as lignocellulosic biomass. Each component has a distinct chemical behavior. Being a composite of three very different components makes the processing of lignocellulose challenging. The evolved resistance to degradation or even separation is referred to as recalcitrance. Overcoming this recalcitrance to produce useful, high value products requires a combination of heat, chemicals, enzymes, and microorganisms. These carbohydrate-containing polymers contain different sugar monomers (six and five carbon sugars) and they are covalently bound to lignin. Lignocellulosic biomass can be broadly classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biocontrol
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological pest control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insect pests, also known as biological control agents, include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and competitors. Biological control agents of plant diseases are most often referred to as antagonists. Biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytohormone
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
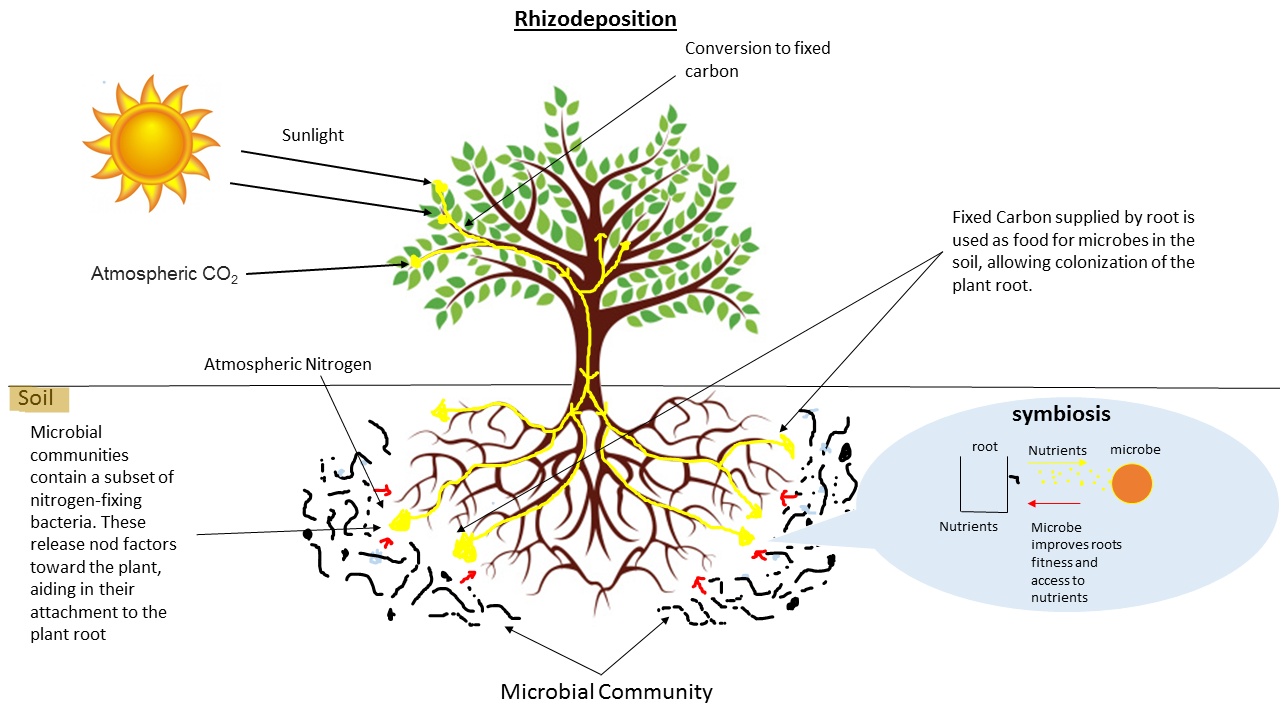
Rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed ''rhizodeposition'', and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants, occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolic products of symbiotic and pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives. The ''rhizoplane'' refers to the root surface including its associated soil particles which closely interact with each other. The plant-soil feedback loop and other phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizosphere Microbial Consortia
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed ''rhizodeposition'', and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants, occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolic products of symbiotic and pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives. The ''rhizoplane'' refers to the root surface including its associated soil particles which closely interact with each other. The plant-soil feedback loop and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Mat
A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, or bacteria alone. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. A few are found as endosymbionts of animals. Although only a few centimetres thick at most, microbial mats create a wide range of internal chemical environments, and hence generally consist of layers of microorganisms that can feed on or at least tolerate the dominant chemicals at their level and which are usually of closely related species. In moist conditions mats are usually held together by slimy substances secreted by the microorganisms. In many cases some of the bacteria form tangled webs of filaments which make the mat tougher. The best known physical forms are flat mats and stubby pillars called stromatolites, but there are also spherical forms. Microbial mats are the earliest form of life on Earth for which there is good foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementation (geology)
Cementation involves ions carried in groundwater chemically precipitating to form new crystalline material between sedimentary grains. The new pore-filling minerals forms "bridges" between original sediment grains, thereby binding them together. In this way, ''sand'' becomes sandstone, and ''gravel'' becomes conglomerate or breccia. Cementation occurs as part of the diagenesis or lithification of sediments. Cementation occurs primarily below the water table regardless of sedimentary grain sizes present. Large volumes of pore water must pass through sediment pores for new mineral cements to crystallize and so millions of years are generally required to complete the cementation process. Common mineral cements include calcite, quartz, and silica phases like cristobalite, iron oxides, and clay minerals; other mineral cements also occur. Cementation is continuous in the groundwater zone, so much so that the term "zone of cementation" is sometimes used interchangeably. Cementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. "Marine photosynthesis is dominated by microalgae, which together with cyanobacteria, are collectively called phytoplankton." Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulphate-reducing Bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as terminal electron acceptor, reducing it to hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Therefore, these sulfidogenic microorganisms "breathe" sulfate rather than molecular oxygen (O2), which is the terminal electron acceptor reduced to water (H2O) in aerobic respiration. Most sulfate-reducing microorganisms can also reduce some other oxidized inorganic sulfur compounds, such as sulfite (), dithionite (), thiosulfate (), trithionate (), tetrathionate (), elemental sulfur (S8), and polysulfides (). Depending on the context, "sulfate-reducing microorganisms" can be used in a broader sense (including all species that can reduce any of these sulfur compounds) or in a narrower sense (including only species that reduce sulfate, and excluding strict thiosulfate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |