|
Metal Peroxide
Metal peroxides are metal-containing compounds with ionically- or covalently-bonded peroxide () groups. This large family of compounds can be divided into ionic and covalent peroxide. The first class mostly contains the peroxides of the alkali and alkaline earth metals whereas the covalent peroxides are represented by such compounds as hydrogen peroxide and peroxymonosulfuric acid (H2SO5). In contrast to the purely ionic character of alkali metal peroxides, peroxides of transition metals have a more covalent character. Bonding in O22− The peroxide ion is composed of two oxygen atoms that are linked by a single bond. The molecular orbital diagram of the peroxide dianion predicts a doubly occupied antibonding π* orbital and a bond order of 1. The bond length is 149 pm, which is larger than in the ground state ( triplet oxygen) of the oxygen molecule (3O2, 121 pm). This translates into the smaller force constant of the bond (2.8 N/cm vs. 11.4 N/cm for 3O2) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
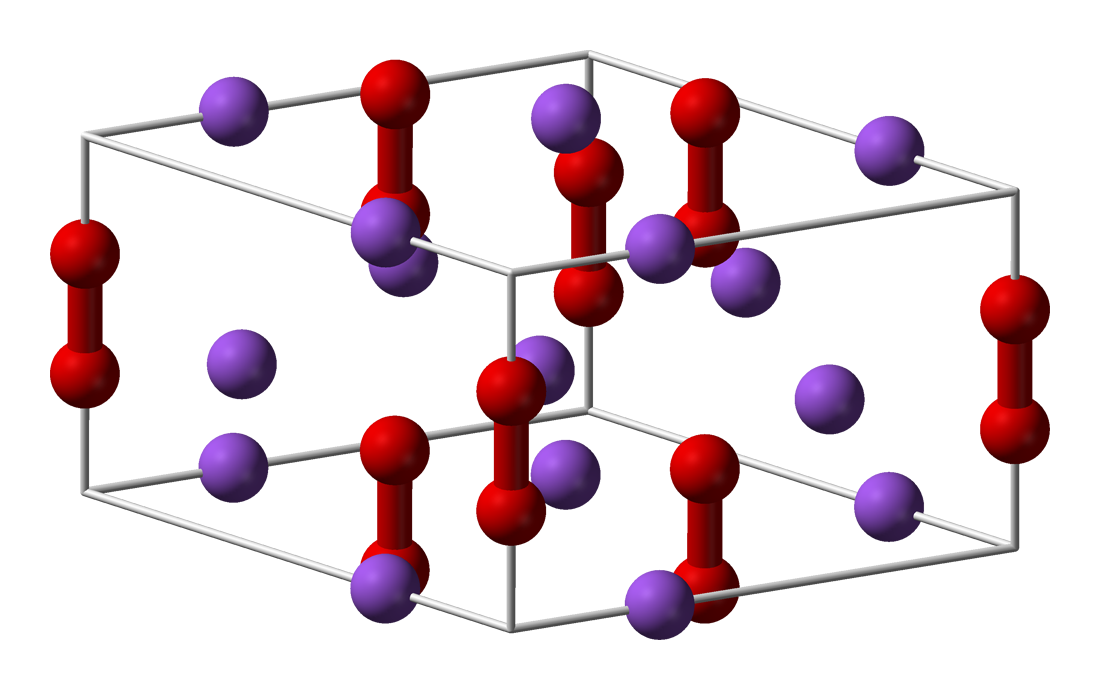
Calcium Peroxide
Calcium peroxide or calcium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaO2. It is the peroxide (O22−) salt of Ca2+. Commercial samples can be yellowish, but the pure compound is white. It is almost insoluble in water. Structure and stability As a solid, it is relatively stable against decomposition. In contact with water however it hydrolyzes with release of oxygen. Upon treatment with an acid, it forms hydrogen peroxide. Preparation Calcium peroxide is produced by combining calcium salts and hydrogen peroxide: :Ca(OH)2 + H2O2 → CaO2 + 2 H2O The octahydrate precipitates upon the reaction of calcium hydroxide with dilute hydrogen peroxide. Upon heating it dehydrates. Applications It is mainly used as an oxidant to enhance the extraction of precious metals from their ores. In its second main application, it is used as a food additive under the E number E930 it is used as flour bleaching agent and improving agent. In agriculture it is used in the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdate
In chemistry a molybdate is a compound containing an oxoanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxoanions which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxoanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxoanions range in size from the simplest , found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, , , and ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten. Examples of molybdate anions Examples of molybdate oxoani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(VI) Oxide Peroxide
Chromium(VI) peroxide or chromium oxide peroxide is an unstable compound with the formula CrO5. This compound contains one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands, making a total of five oxygen atoms per chromium atom. Preparation and properties Chromium(VI) peroxide is formed by the addition of acidified hydrogen peroxide solutions to solutions of metal chromates or dichromates, such as sodium chromate or potassium dichromate. The generally yellow chromates or orange dichromates turn to dark blue as chromium(VI) peroxide is formed. Chromate or dichromate reacts with hydrogen peroxide and an acid to give chromium peroxide and water. :CrO42− + 2 H2O2 + 2 H+ → CrO5 + 3 H2O With this method, the chromium(VI) peroxide will decompose after a few seconds, turning green as chromium(III) compounds are formed. :2 CrO5 + 7 H2O2 + 6 H+ → 2 Cr3+ + 10 H2O + 7 O2 To avoid this decomposition, it is possible to stabilize chromium(VI) oxide peroxide in water-immiscible organic solvents such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidentate Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dioxygen Complex
Transition or transitional may refer to: Mathematics, science, and technology Biology * Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ T) * Transitional fossil, any fossilized remains of a lifeform that exhibits the characteristics of two distinct taxonomic groups * A phase during childbirth contractions during which the cervix completes its dilation Gender and sex * Gender transitioning, the process of changing one's gender presentation to accord with one's internal sense of one's gender – the idea of what it means to be a man or woman * Sex reassignment therapy, the physical aspect of a gender transition Physics * Phase transition, a transformation of the state of matter; for example, the change between a solid and a liquid, between liquid and gas or between gas and plasma * Quantum phase transition, a phase transformation between different quantum phases * Quantu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Peroxide
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Peroxide
Zinc peroxide (ZnO2) appears as a bright yellow powder at room temperature. It was historically used as a surgical antiseptic. More recently zinc peroxide has also been used as an oxidant in explosives and pyrotechnic mixtures. Its properties have been described as a transition between ionic and covalent peroxides. Zinc peroxide can be synthesized through the reaction of zinc chloride and hydrogen peroxide. Preparation Zinc hydroxide is reacted with a mixture of hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide and precipitated with sodium hydroxide also containing hydrogen peroxide to ensure a higher yield of zinc peroxide. Unlike in the preparation of copper peroxide, the zinc ion does not cause the peroxide to decompose. Applications Since the 1930s zinc peroxide has been applied in a variety of settings, from medicine to aesthetics and even fireworks. Medical Use The treatment of burrowing ulcers in the abdominal wall with zinc peroxide was first recorded in 1933 and throughout the 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 12 Element
Group 12, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. It includes zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and copernicium (Cn). Formerly this group was named ''IIB'' (pronounced as "group two B", as the "II" is a Roman numeral) by CAS and old IUPAC system. The three group 12 elements that occur naturally are zinc, cadmium and mercury. They are all widely used in electric and electronic applications, as well as in various alloys. The first two members of the group share similar properties as they are solid metals under standard conditions. Mercury is the only metal that is a liquid at room temperature. While zinc is very important in the biochemistry of living organisms, cadmium and mercury are both highly toxic. As copernicium does not occur in nature, it has to be synthesized in the laboratory. Physical and atomic properties Like other groups of the periodic table, the members of group 12 show patterns in its electron configuration, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner. Occurrence Rutile is a common accessory mineral in high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic rocks and in igneous rocks. Thermodynamical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


4-3D-balls.png)