|
Mesoscale Convective Vortex
A mesovortex is a small-scale rotational feature found in a convective storm, such as a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS, i.e. squall line), a supercell, or the eyewall of a tropical cyclone. Mesovortices range in diameter from tens of miles to a mile or less and can be immensely intense. Eyewall mesovortex An ''eyewall mesovortex'' is a small-scale rotational feature found in an eyewall of an intense tropical cyclone. Eyewall mesovortices are similar, in principle, to small "suction vortices" often observed in multiple-vortex tornadoes. In these vortices, wind speed can be up to 10% higher than in the rest of the eyewall. Eyewall mesovortices are most common during periods of intensification in tropical cyclones. Eyewall mesovortices often exhibit unusual behavior in tropical cyclones. They usually revolve around the low pressure center, but sometimes they remain stationary. Eyewall mesovortices have even been documented to cross the eye of a storm. These phenomena have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or '' spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a '' pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the '' orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere of an astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), heavy precipitation ( snowstorm, rainstorm), heavy freezing rain (ice storm), strong winds (tropical cyclone, windstorm), wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere such as in a dust storm, among other forms of severe weather. Storms have the potential to harm lives and property via storm surge, heavy rain or snow causing flooding or road impassibility, lightning, wildfires, and vertical and horizontal wind shear. Systems with significant rainfall and duration help alleviate drought in places they move through. Heavy snowfall can allow special recreational activities to take place which would not be possible otherwise, such as skiing and snowmobiling. The English word comes from Proto-Germanic ''*sturmaz'' meaning "noise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
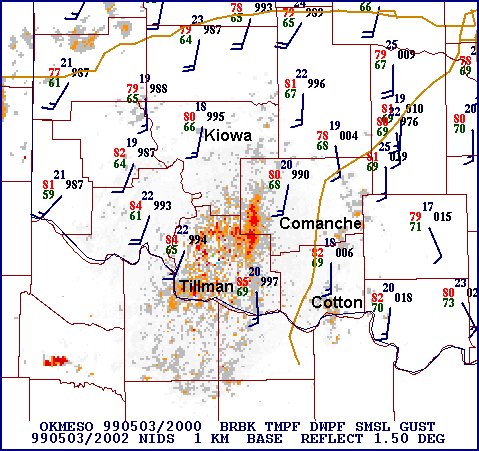
Mesonet
In meteorology and climatology, a mesonet, portmanteau of mesoscale network, is a network of automated weather and, often, environmental monitoring stations designed to observe mesoscale meteorological phenomena and/or microclimates. Dry lines, squall lines, and sea breezes are examples of phenomena observed by mesonets. Due to the space and time scales associated with mesoscale phenomena and microclimates, weather stations comprising a mesonet are spaced closer together and report more frequently than synoptic scale observing networks, such as the WMO Global Observing System (GOS) and US ASOS. The term mesonet refers to the collective group of these weather stations, which are usually owned and operated by a common entity. Mesonets generally record in situ surface weather observations but some involve other observation platforms, particularly vertical profiles of the planetary boundary layer (PBL). Other environmental parameters may include insolation and various variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEXRAD
NEXRAD or Nexrad (Next-Generation Radar) is a network of 160 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United States Department of Commerce, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) within the Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Air Force within the Department of Defense. Its technical name is WSR-88D (''Weather Surveillance Radar, 1988, Doppler''). NEXRAD detects precipitation and atmospheric movement or wind. It returns data which when processed can be displayed in a mosaic map which shows patterns of precipitation and its movement. The radar system operates in two basic modes, selectable by the operator – a slow-scanning ''clear-air mode'' for analyzing air movements when there is little or no activity in the area, and a ''precipitation mode'', with a faster scan for tracking active weather. NEXRAD has an increased emphasis on automa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are moni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the intensity of the precipitation. Both types of data can be analyzed to determine the structure of storms and their potential to cause severe weather. During World War II, radar operators discovered that weather was causing echoes on their screen, masking potential enemy targets. Techniques were developed to filter them, but scientists began to study the phenomenon. Soon after the war, surplus radars were used to detect precipitation. Since then, weather radar has evolved on its own and is now used by national weather services, research departments in universities, and in television stations' weather departments. Raw images are routinely used and specialize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Weather Observation
Surface weather observations are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station. The ICAO defines the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), which is the model of the standard variation of pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity with altitude in the Earth's atmosphere, and is used to reduce a station pressure to sea level pressure. Airport observations can be transmitted worldwide through the use of the METAR observing code. Personal weather stations taking automated observations can transmit their data to the United States mesonet through the Citizen Weather Observer Program (CWOP), the UK Met Office through their Weather Observations Website (WOW), or internationally through the Weat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoscale Convective System
A mesoscale convective system (MCS) is a complex of thunderstorms that becomes organized on a scale larger than the individual thunderstorms but smaller than extratropical cyclones, and normally persists for several hours or more. A mesoscale convective system's overall cloud and precipitation pattern may be round or linear in shape, and include weather systems such as tropical cyclones, squall lines, lake-effect snow events, polar lows, and mesoscale convective complexes (MCCs), and generally forms near weather fronts. The type that forms during the warm season over land has been noted across North and South America, Europe, and Asia, with a maximum in activity noted during the late afternoon and evening hours. Forms of MCS that develop within the tropics use either the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) or monsoon troughs as a focus for their development, generally within the warm season between spring and fall. One exception is that of lake-effect snow bands, which form d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolow
A squall is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds. They are usually associated with active weather, such as rain showers, thunderstorms, or heavy snow. Squalls refer to the increase of the sustained winds over that time interval, as there may be higher gusts during a squall event. They usually occur in a region of strong sinking air or cooling in the mid-atmosphere. These force strong localized upward motions at the leading edge of the region of cooling, which then enhances local downward motions just in its wake. Etymology There are different versions of the word's origins: * By one version, the word appears to be Nordic in origin, but its etymology is considered obscure. It probably has its roots in the word ''skvala'' an Old Norse word meaning literally ''to squeal''. * By another version, it is an alteration of ''squeal'' influenced by ''bawl''. Character of the wind The term "squall" is used to refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). * A second is an area where wind divergence aloft occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsushima MCV
Tsushima may refer to: Places * Tsushima Island, part of Nagasaki Prefecture ** Tsushima, Nagasaki, a city in Nagasaki Prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Province, a historical province, coterminous with modern Tsushima Subprefecture ** Tsushima Subprefecture, an administrative subdivision of Nagasaki prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Fuchū Domain, a feudal domain of the early modern period, largely if not entirely contiguous with the Province * Tsushima Basin, also known as Ulleung Basin, located at the juncture of the Sea of Japan and the Korea Strait * Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait * Tsushima, Aichi, a city in Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima, Ehime, a town dissolved in August 2005, formerly located in Ehime Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, located in the city of Mitoyo, Kagawa Prefecture and only accessible one day a year in early August Events * Battle of Tsushima (1905), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoptic Scale Meteorology
The synoptic scale in meteorology (also known as large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometers (about 620 miles) or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions (e.g., extratropical cyclones). Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps (such as surface weather analyses) are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word ''synoptic'' is derived from the Greek word ('), meaning ''seen together''. The Navier–Stokes equations applied to atmospheric motion can be simplified by scale analysis in the synoptic scale. It can be shown that the main terms in horizontal equations are Coriolis force and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_eye_close-up.jpg)