|
Mesazon
The ( gr, μεσάζων, mesazōn, intermediary) was a high dignitary and official during the last centuries of the Byzantine Empire, who acted as the chief minister and principal aide of the Byzantine emperor. History and functions The term's origins lie in the 10th century, when senior ministers were sometimes referred to as the (), i.e. 'mediators' between the emperor and his subjects (cf. ). The title first became official in the mid-11th century, when it was conferred to Constantine Leichoudes, the future Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople.. In the Komnenian period, it was awarded to senior government officials who functioned as ''de facto'' prime ministers, such as the and the , but had not yet acquired a permanent and specific function, nor the power that would characterize it in later years. Rather, it was a title bestowed on the principal imperial secretary of the moment, who acted precisely as an "intermediary" between the emperor and other officials. This reflec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Styppeiotes
Theodore Styppeiotes or Stypeiotes ( gr, Θεόδωρος Στυπ ��ιώτης, Theodōros Styp iōtēs) was a high-ranking bureaucrat of the Byzantine Empire and a member of the court of Emperor Manuel I Komnenos (). A well-educated and capable man, he advanced rapidly in the imperial hierarchy from imperial secretary (''grammatikos'') to the influential post of '' kanikleios'', keeper of the imperial inkstand. In he engineered the downfall of John Hagiotheodorites, and succeeded him as ''mesazon'', the ''de facto'' chief minister of the Empire. He long enjoyed the favour and trust of Manuel, who even wed him with his niece Eudokia. However, in 1158/59, Styppeiotes abruptly fell from power and was imprisoned and blinded. The sources provide different reasons, from Styppeiotes conspiring to deprive the Emperor of power to the machinations of his rival, John Kamateros, and scholars still dispute the true background of this event. Life The origin and early life of Theodore Styppei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kamateros (logothetes Tou Dromou)
John Kamateros ( gr, Ἰωάννης Καματηρός, Iōannēs Kamatēros) was a Byzantine aristocrat and official. Family John was the son of Gregory Kamateros, a man of humble origin but well educated, who held several senior government posts under emperors Alexios I Komnenos and John II Komnenos and advanced to the high rank of '' sebastos'', and of Irene Doukaina, probably a daughter of the '' protostrator'' Michael Doukas, whose sister Irene was wed to Alexios I. The union led to the emergence of the Doukas– Kamateros bureaucratic dynasty, which would reach the peak of its fortunes with John and his brother, Andronikos Doukas Kamateros, who occupied the highest offices in the state. It is possible that John is the unnamed '' logothetes'' whose daughter was the wife of Alexios Kontostephanos. Career John Kamateros enjoyed imperial favour as Manuel I Komnenos' drinking companion; according to the near-contemporary historian Niketas Choniates, Kamateros drank wine by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Aristocracy And Bureaucracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies and theocratic Christian-Eastern concepts had gained power in the eastern Greek-speaking Mediterranean due to the intervention of Important religious figures there such as Eusebius of Caesarea and Origen of Alexandria who had been key to the constant Christianized world of late antiquity. By the 6th century they had already influenced the definitive power of the monarch as the representative of God on earth and his kingdom as an imitation of God's holy realm. The Byzantine empire was a monarchic theocracy, adopting, following and applying the Hellenistic political systems and philosophies. The monarch was the incarnation of the law ''nomos empsychos'', and his power was immeasurable and divine in origin. He was the ultimate benefactor, carer and saviour of his people, '' Evergétis'', '' Philanthrōpía'' and '' Sōtēr''. They in turn were his ''paroikoi'' (subjects). He was the sole administrator and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Choumnos
Nikephoros Choumnos ( el, , 1250/55 – 1327) was a Byzantine scholar and official of the early Palaiologan period, one of the most important figures in the flowering of arts and letters of the so-called "Palaiologan Renaissance". He is notable for his eleven-year tenure as chief minister of emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos, his intense intellectual rivalry with fellow scholar and official Theodore Metochites, and for building the monastery of the Theotokos Gorgoepēkoos (Θεοτόκος Γοργοεπήκοος) in Constantinople. Life Choumnos was born between 1250 and 1255. He came from an already distinguished family, which since the 11th century had provided several high-ranking officials.Kazhdan (1991), p. 433 Nikephoros studied rhetoric and philosophy under the future Patriarch of Constantinople Gregory of Cyprus, and upon conclusion of his studies entered the imperial bureaucracy. He makes his first appearance in history in ca. 1275, with the lowly rank of '' quae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epi Tou Kanikleiou
The ( el, κανίκλειος), more formally or ( el, �αρτουλάριοςἐπὶ τοῦ κανικλείου) was one of the most senior offices in the Byzantine imperial chancery.. Its holder was the keeper of the imperial inkstand, the ''kanikleion'', which was shaped as a little dog ( la, canicula) and contained the scarlet ink with which the Byzantine emperor signed state documents. The office first appears in the 9th century, and was usually held in tandem with other government offices. In the '' Kletorologion'' of 899 it is ranked among the "special dignities" (, ), following the ''synkellos'' and preceding the '' protostrator''. In the overall order of precedence, he ranked behind the '' chartoularios tou vestiariou'' and before the ''protostrator'', and is recorded as usually holding the rank of '' protospatharios''. His proximity to the imperial person and the nature of his task made the very influential, especially in formulating imperial chrysobulls. The of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Metochites
Theodore Metochites ( el, Θεόδωρος Μετοχίτης; 1270–1332) was a Byzantine Greek statesman, author, gentleman philosopher, and patron of the arts. From c. 1305 to 1328 he held the position of personal adviser ('' mesazōn'') to emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos. Life Metochites was born in Constantinople as the son of the archdeacon George Metochites, a fervent supporter of the union of the Orthodox and Catholic Churches. After the Council of Blachernae in 1285, his father was condemned and exiled, and Metochites seems to have spent his adolescence in the monastic milieux of Bithynia in Asia Minor. He devoted himself to studies of both secular and religious authors. When Andronicus II visited Nicaea in 1290/91, Metochites made such an impression on him that he was immediately called to the court and made Logothete of the Herds. Little more than a year later, he was appointed a Senator. Besides carrying out his political duties (embassies to Cilicia in 1295 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradynasteuon
The ''paradynasteuōn'' ( el, παραδυναστεύων, "the one who rules beside") was a term used, especially in the Byzantine Empire, to designate a ruler's favorite, often raised to the position of chief minister. Probably deriving from Thucydides, it was used in the later Roman Empire for people with great authority. It was not an official title or position, but the term was extensively used by chroniclers such as Theophanes the Confessor Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking ... or Theophanes Continuatus to designate an emperor's closest aide and chief minister. It gained greater currency during the Komnenian period and continued to be used by historians of the Palaiologan period, although the more technical term of '' mesazōn'' ("mediator"), which eventually cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios Apokaukos
Alexios Apokaukos ( el, ; died 11 June 1345), also Latinized as Alexius Apocaucus, was a leading Byzantine statesman and high-ranking military officer ('' megas doux'') during the reigns of emperors Andronikos III Palaiologos (r. 1328–1341) and John V Palaiologos (r. 1341–1357). Although he owed his rise to high state offices to the patronage of John VI Kantakouzenos (r. 1347–1354), he became, together with Patriarch John XIV Kalekas, one of the leaders of the faction supporting Emperor John V in the civil war of 1341–1347 against his one-time benefactor. Apokaukos died when he was lynched by political prisoners during an inspection of a new prison. Biography Early life Alexios was of humble origin, and was born in the late 13th century somewhere in Bithynia.. He nevertheless studied under the scholar Theodore Hyrtakenos, and became a tax official. By 1320 he was director of the salt pans, from which he later advanced to the position of '' domestikos'' of the the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg , caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia'' , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328 , coronation = 8 November 1272 , cor-type1 = Coronation , regent = Michael IX Palaiologos , reg-type = Co-emperor , predecessor = Michael VIII Palaiologos (alone) , successor = Andronikos III Palaiologos , spouse = Anna of Hungary Yolande of Montferrat , issue = Michael IX PalaiologosConstantine Palaiologos John Palaiologos Theodore I, Marquis of Montferrat Demetrios Palaiologos Simonis (Simonida Nemanjić), Queen of SerbiaIrene Palaiologina (wife of John II Doukas), Sebastokratorissa of Thessaly , issue-link = #Family , issue-pipe = more... , dynasty = Palaiologos , father = Michael VIII Palaiologos , mother = Theodora Palaiologina , birth_date = 25 March 1259 , birth_place = Nicaea, Empire of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Mouzalon
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory * Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), includes the etymology of the given name and a list of people * Theodore (surname), a list of people Fictional characters * Theodore "T-Bag" Bagwell, on the television series ''Prison Break'' * Theodore Huxtable, on the television series ''The Cosby Show'' Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One racing team See also * Principality of Theodoro The Principality of Theodoro ( el, Αὐθεντία πόλεως Θεοδωροῦς καὶ παραθαλασσίας), also known as Gothia ( el, Γοτθία) or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern p ..., a principality in the south-west Crimea from the 13t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
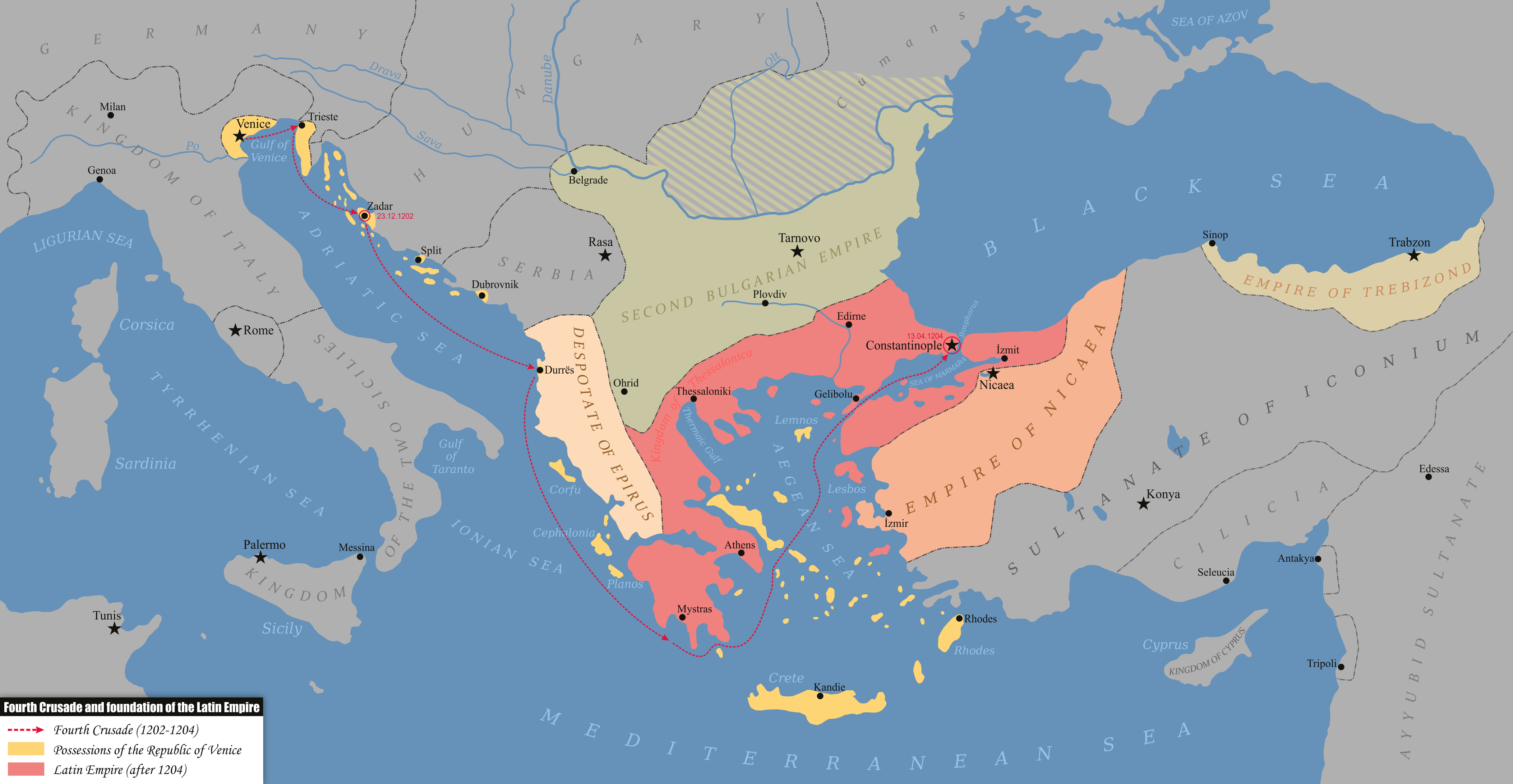
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes ( el, Ιωάννης Δούκας Βατάτζης, ''Iōannēs Doukas Vatatzēs'', c. 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known as Theodore II Laskaris. Life John Doukas Vatatzes, born in about 1192 in Didymoteicho, was probably the son of the general Basil Vatatzes, who was killed in battle in 1194, and his wife, a cousin of the Emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos. John Doukas Vatatzes had two older brothers. The eldest was Isaac Doukas Vatatzes (1188-1261), while his younger brother died young. Through his marriage to Eudokia Angelina he fathered Theodora Doukaina Vatatzaina, who later married Michael VIII Palaiologos. The middle brother's name is unknown, but his daughter married the '' protovestiarios'' Alexios Raoul. A successful soldier from a military family, John was chosen in about 1216 by Emperor Theodore I Laskaris as the second hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |